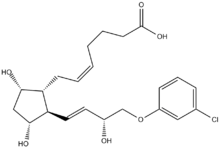
Cloprostenol
Cloprostenol is a synthetic analogue of prostoglandin F2α (PGF2α).[1] It is a potent luteolytic agent; this means that, within hours of administration, it causes the corpus luteum to stop production of progesterone, and to reduce in size over several days.[1] This effect is used in animals to induce estrus and to cause abortion.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Cyclomate, Estrumate |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular |
| ATCvet code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Excretion | 67% renal, 25% fecal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.050.009 100.207.142, 100.050.009 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H29ClO6 |
| Molar mass | 424.915 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
- Cooper, M. (1 January 1981). "Prostaglandins in veterinary practice". In Practice. 3 (1): 30–34. doi:10.1136/inpract.3.1.30.
- Plumb, DC (2015). "Cloprostenol Sodium". Plumb's Veterinary Drug Handbook (8th ed.). Wiley. ISBN 9781118911938.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.