Estrogen patch
An estrogen patch (oestrogen patch) is a transdermal delivery system for estradiol, which can be used as hormone replacement therapy to treat menopause symptoms, hypoestrogenism, and to prevent osteoporosis.[1] Transdermal preparations of estrogen are metabolized differently than oral preparations. Transdermal estrogens avoid first-pass metabolism which allow transdermal preparations to contain a range of lower doses of estrogen, and thus potentially reduce the risk of blood clotting and stroke.[2]
 Vivelle-dot, an estrogen patch | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Estradiol Transdermal Patch |
| Routes of administration | Transdermal |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Metabolites | Estriol |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H24O2 |
An estrogen patch is applied directly to the skin, preferably near the lower abdomen, hips, or buttocks, and is changed once or twice per week. For women who have not undergone a hysterectomy, it is often suggested that they take progestin in addition to an estrogen patch in order to protect the endometrium of the uterus.[1][2] Although it is uncommon, it is possible that women who have undergone a hysterectomy be recommended to take progestin as well.[1] Transdermal estrogens are not recommended for all women; there are important precautions and side effects that should be considered before use.[2]
Medical uses
Menopause
An estrogen patch may be recommended for women experiencing moderate to severe symptoms of menopause, such as vasomotor symptoms and vaginal atrophy. During menopause, the ovaries stop producing estrogen which causes estrogen levels to fall. The sudden change in estrogen levels may cause vasomotor symptoms, such as hot flashes. Research suggests that the estrogen patch can relieve both the frequency and severity of vasomotor symptoms by increasing estrogen levels. An estrogen patch may also be used to treat vulvar and vaginal atrophy, another symptom of menopause associated with the sudden change in estrogen levels.[1]
Hypoestrogenism
Hypoestrogenism, or estrogen deficiency, may suggest menopause is approaching for middle aged women. Other causes of hypoestrogenism are excessive exercise, restrictive diet, underactive pituitary gland, ovarian failure, Turner Syndrome, and kidney disease. Symptoms of hypoestrogenism may include pain during sex, irregular periods, mood swings, hot flashes, breast tenderness, headache, depression, fatigue, weak bones, and an increase risk of urinary tract infections. Estrogen therapies, including the use of an estrogen patch, can be used to alleviate these symptoms by increasing estrogen levels to a normal state. Premenopausal women may be recommended to take progestin with estrogen therapy.[2]
Prevention of osteoporosis
Estrogen patches may be effective in preventing osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Research suggests that estrogen patches can significantly increases bone mineral density and reduce risks of fractures in postmenopausal women by raising estrogen levels and avoiding first-pass metabolism.[3]
There is evidence that the combination of an estrogen patch with a progestin pill can improve bone mineral density in young, premenopausal amenorrheic athletes, and may be more effective than an oral estrogen with progestin.[4]
Patches with progestin

Taking progestin in addition to an estrogen patch should be considered for women who have not undergone a hysterectomy to regulate the thickness of the endometrial lining [2] and reduce the risk of endometrial cancer. Hysterectomized women rarely need progestin, however it may be considered if a history of endometriosis exists.[1] There are different types of delivery systems of progestin that can be used in addition to an estrogen patch, including pills, injections,[5] and patches.[6]
Research has suggested that estrogen plus progestin therapy may increase the risk of heart attacks, stroke, breast cancer, blot clots, and dementia in postmenopausal women. Taking the lowest effective dose of both estrogen and progestin may reduce risks.[1]
Administration
Depending on the brand, patches are applied to the skin once or twice weekly. Patches should be placed on clean skin where hair and moisture is not present. Preferred areas of application include lower abdomen, hip, and buttocks. Patches should never be applied to the breasts. To reduce the risk of the patch detaching from the skin and skin irritation, skin care products, sun exposure, damaged skin, and tight-fitting clothing should be avoided where the patch is placed.[2]
Side effects
Headache, breast tenderness, vaginal bleeding, spotting, abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, hair loss, fluid retention, vaginal infections, skin irritation are some common side effects that may occur while using an estrogen patch. More severe, but less common side effects may include heart attack, stroke, blood clotting, dementia, breast cancer, endometrial cancer, ovarian cancer, increased blood pressure, increased blood sugar, gallbladder disease, liver issues, abnormal thyroid hormone levels, and tumors in the uterus.
Seeing a health professional regularly, taking progestin, having pelvic and breast exams, lowering blood pressure, and lowering cholesterol may reduce the likelihood of developing severe side effects while using an estrogen patch.[1]
Precautions
Women that have experienced vaginal bleeding post menopause, certain cancers, stroke, heart attack, blood clotting, or uncontrollable bleeding, and women who are pregnant or allergic to ingredients in estrogen patches should not use an estrogen patch as serious adverse effects may occur.[1]
Formulations
| Brand name |
Forms (µg/day) | Duration | Type | Size (cm2)a | Estradiol (mg) | Levels (pg/mL) |
Launch (year) |
Hits | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alora | 25, 50, 75, 100 | 3–4 days | Matrix | 9, 18, 27, 36 | 0.77, 1.5, 2.3, 3.1 | 43–144 | 1996 | 42,300 | |
| Climara | 25, 37.5, 50, 60, 75, 100 | 7 days | Matrix | 6.5, 9.375, 12.5, 15, 18.75, 25 | 2, 2.85, 3.8, 4.55, 5.7, 7.6 | 17–174 | 1994 | 110,000 | |
| Climara Prob | E2 (45) + LNG (15) | 7 days | Matrix | 22 | 4.4 | 27–54 | 2003 | 23,400 | |
| CombiPatchb | E2 (50) + NETA (14, 25) | 3–4 days | Matrix | 9, 16 | 0.62, 0.51 | 27–71 | 1998 | 33,500 | |
| Estradiolc | 25, 37.5, 50, 75, 100 | 3–4 days | Matrix | 2.5, 3.75, 5, 7.5, 10 | 0.41, 0.62, 0.82, 1.23, 1.64 | 30–145 | 1996 | – | |
| Estradiolc | 25, 37.5, 50, 75, 100 | 7 days | Matrix | 7.75, 11.625, 15.5, 18.6, 23.25, 31 | 0.97, 1.46, 1.94, 2.33, 2.91, 3.88 | 17–174 | 2000 | – | |
| Menostar | 14 | 7 days | Matrix | 3.25 | 1 | 13–21 | 2004 | 21,300 | |
| Minivelle | 25, 37.5, 50, 75, 100 | 3–4 days | Matrix | 1.65, 2.48, 3.3, 4.95, 6.6 | 0.41, 0.62, 0.83, 1.24, 1.65 | 30–117 | 2012 | 15,100 | |
| Vivelle | 3–4 days | Matrix | 30–145 | 2000 | 91,900 | ||||
| Vivelle-Dot | 25, 37.5, 50, 75, 100 | 3–4 days | Matrix | 2.5, 3.75, 5, 7.5, 10 | 0.39, 0.585, 0.78, 1.17, 1.56 | 30–145 | 1996 | 68,900 | |
| Abbreviations: E2 = Estradiol. LNG = Levonorgestrel. NETA = Norethisterone acetate. EtOH = Ethanol. Notes: | |||||||||
Estrogen levels
_in_postmenopausal_women.png) Levels of estradiol at steady-state over a period of 4 days with different dosages of Vivelle-type (Vivelle, Vivelle-Dot, Mylan generic) twice-weekly transdermal estradiol matrix patches applied to the abdomen and worn until day 4 in postmenopausal women.
Levels of estradiol at steady-state over a period of 4 days with different dosages of Vivelle-type (Vivelle, Vivelle-Dot, Mylan generic) twice-weekly transdermal estradiol matrix patches applied to the abdomen and worn until day 4 in postmenopausal women._in_postmenopausal_women.png) Levels of estradiol over a period of 7.5 days after a single application of different dosages of a Climara-type (Climara, Menostar, Mylan generic) once-weekly transdermal estradiol matrix patch to the abdomen and removed on day 7 in postmenopausal women.
Levels of estradiol over a period of 7.5 days after a single application of different dosages of a Climara-type (Climara, Menostar, Mylan generic) once-weekly transdermal estradiol matrix patch to the abdomen and removed on day 7 in postmenopausal women._in_women.png) Levels of estradiol over a period of 8 days after a single application of a 50 or 100 μg/day Climara-type (Climara, Menostar, Mylan generic) once-weekly transdermal estradiol matrix patch to the abdomen and removed on day 7 in postmenopausal women.
Levels of estradiol over a period of 8 days after a single application of a 50 or 100 μg/day Climara-type (Climara, Menostar, Mylan generic) once-weekly transdermal estradiol matrix patch to the abdomen and removed on day 7 in postmenopausal women.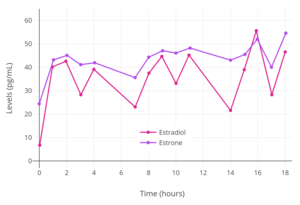 Levels of estradiol and estrone with application of a single 50 µg/day estradiol transdermal reservoir patch (Estraderm) in postmenopausal women.
Levels of estradiol and estrone with application of a single 50 µg/day estradiol transdermal reservoir patch (Estraderm) in postmenopausal women._with_and_without_an_ethanol_injection_in_postmenopausal_women.png) Estradiol level with a single 100 µg/day estradiol reservoir patch (Estraderm) with and without ethanol added in postmenopausal women. This patch has a 3- to 4-day duration and is designed for twice-weekly application. In one group, ethanol was injected into the area between the patch and the skin on day 3. This gave significantly higher and prolonged estradiol levels.
Estradiol level with a single 100 µg/day estradiol reservoir patch (Estraderm) with and without ethanol added in postmenopausal women. This patch has a 3- to 4-day duration and is designed for twice-weekly application. In one group, ethanol was injected into the area between the patch and the skin on day 3. This gave significantly higher and prolonged estradiol levels.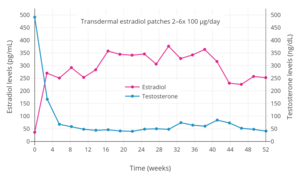 Estradiol and testosterone levels with high-dosage transdermal estradiol in the form of two to six 100 µg/day estradiol patches (Progynova TS forte) in men with prostate cancer.
Estradiol and testosterone levels with high-dosage transdermal estradiol in the form of two to six 100 µg/day estradiol patches (Progynova TS forte) in men with prostate cancer.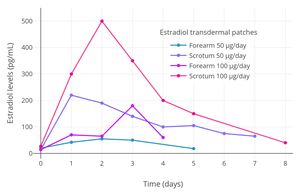 Estradiol levels with 50 to 100 μg/day transdermal estradiol patches applied to the forearm and to the scrotum in a crossover study in 2 men with prostate cancer. In 35 men treated continuously with one 100 μg/day estradiol patch scrotally, the mean estradiol level was ~500 pg/mL (range ~125–1,200 pg/mL).
Estradiol levels with 50 to 100 μg/day transdermal estradiol patches applied to the forearm and to the scrotum in a crossover study in 2 men with prostate cancer. In 35 men treated continuously with one 100 μg/day estradiol patch scrotally, the mean estradiol level was ~500 pg/mL (range ~125–1,200 pg/mL).
Brand names
The following are brand names of estradiol patches in the United States and United Kingdom:[7][8]
- United States
- Alora
- Climara
- Climara Pro (with levonorgestrel)
- CombiPatch (with norethisterone acetate)
- Elleste Solo
- Esclim (discontinued)
- Estraderm (discontinued)
- FemPatch
- Menostar
- Minivelle
- Twirla (with levonorgestrel)
- Vivelle
- Vivelle-Dot
- United Kingdom
- Dermestril
- Elleste Solo MX
- Estracombi (with norethisterone acetate)
- Estraderm MX
- Estraderm TTS
- Estradot
- Estrapak (pack with oral norethisterone acetate tablets)
- Evorel
- Evorel Conti (with norethisterone acetate)
- Evorel-Pak (pack with oral norethisterone acetate tablets)
- Femapak (pack with oral dydrogesterone tablets)
- Fematrix
- FemSeven
- Nuvelle TS (with cyclical levonorgestrel)
- Progynova TS
References
- "ESTRADIOL TRANSDERMAL SYSTEM- estradiol patch". dailymed.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2020-02-07.
- Beck KL, Anderson MC, Kirk JK (August 2017). "Transdermal estrogens in the changing landscape of hormone replacement therapy". Postgraduate Medicine. 129 (6): 632–636. doi:10.1080/00325481.2017.1334507. PMID 28540770. S2CID 205452835.
- Abdi F, Mobedi H, Bayat F, Mosaffa N, Dolatian M, Ramezani Tehrani F (2017). "The Effects of Transdermal Estrogen Delivery on Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women: A Meta-analysis". Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. 16 (1): 380–389. PMC 5423263. PMID 28496491.
- Ackerman KE, Singhal V, Baskaran C, Slattery M, Campoverde Reyes KJ, Toth A, et al. (February 2019). "Oestrogen replacement improves bone mineral density in oligo-amenorrhoeic athletes: a randomised clinical trial". British Journal of Sports Medicine. 53 (4): 229–236. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2018-099723. PMC 6686188. PMID 30301734.
- "Progestin-Only Hormonal Birth Control: Pill and Injection - ACOG". www.acog.org. Retrieved 2020-02-10.
- "Sequidot". Drugs.com. Retrieved 1 March 2014.
- "Drugs@FDA: FDA Approved Drug Products". United States Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 5 May 2019.
- "Available Forms of HRT (UK)".
External links
- "Estradiol". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Estradiol mixture with levonorgestrel". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Estradiol mixture with norethindrone acetate". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
-solution.jpg)