Effingham County, Georgia
Effingham County is a county located in the U.S. state of Georgia. As of the 2010 census, the population was 52,250.[1] The seat is Springfield.[2]
Effingham County | |
|---|---|
 Effingham County Courthouse in Springfield | |
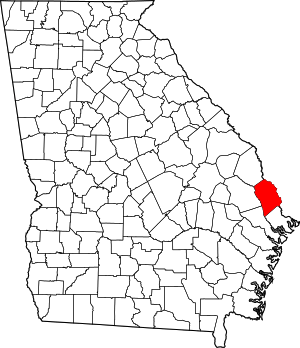 Location within the U.S. state of Georgia | |
 Georgia's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 32°22′N 81°20′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | February 5, 1777 |
| Named for | Thomas Howard, 3rd Earl of Effingham |
| Seat | Springfield |
| Largest city | Rincon |
| Area | |
| • Total | 483 sq mi (1,250 km2) |
| • Land | 478 sq mi (1,240 km2) |
| • Water | 5.2 sq mi (13 km2) 1.1%% |
| Population | |
| • Estimate (2019) | 64,296 |
| • Density | 109/sq mi (42/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional districts | 1st, 12th |
| Website | www |
Effingham County is included in the Savannah metropolitan area.
In 2008, Effingham County was ranked as the sixth-fastest-growing midsize county in the nation from 2000 to 2007 by the U.S. Census Bureau. The county had a 35.1% growth rate over that period.
History
Effingham was among the original counties of the state of Georgia, created February 5, 1777 during the American Revolution from the colonial parishes of St. Matthew and St. Phillip.[3] Its name honors Lord Effingham,[4] an English champion of colonial rights, who resigned his commission rather than fight against the rebel colonists during the American Revolution.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 483 square miles (1,250 km2), of which 478 square miles (1,240 km2) is land and 5.2 square miles (13 km2) (1.1%) is water.[5]
The entire western edge of Effingham County, from south of Newington to east of Guyton, then south to southwest of Meldrim, is located in the Lower Ogeechee River sub-basin of the Ogeechee River basin. The bulk of the rest of the county is located in the Lower Savannah River sub-basin of the Savannah River basin. A narrow rectangular portion of south Effingham County, from south of Pineora through Meldrim, is located in the Ogeechee Coastal sub-basin of the Ogeechee River basin.[6]
Major highways













Adjacent counties
- Hampton County, South Carolina (north)
- Jasper County, South Carolina (northeast)
- Chatham County (southeast)
- Bryan County (south)
- Bulloch County (west)
- Screven County (northwest)
National protected area
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 2,424 | — | |
| 1800 | 2,072 | −14.5% | |
| 1810 | 2,586 | 24.8% | |
| 1820 | 3,018 | 16.7% | |
| 1830 | 2,924 | −3.1% | |
| 1840 | 3,075 | 5.2% | |
| 1850 | 3,864 | 25.7% | |
| 1860 | 4,755 | 23.1% | |
| 1870 | 4,214 | −11.4% | |
| 1880 | 5,979 | 41.9% | |
| 1890 | 5,599 | −6.4% | |
| 1900 | 8,334 | 48.8% | |
| 1910 | 9,971 | 19.6% | |
| 1920 | 9,985 | 0.1% | |
| 1930 | 10,164 | 1.8% | |
| 1940 | 9,646 | −5.1% | |
| 1950 | 9,133 | −5.3% | |
| 1960 | 10,144 | 11.1% | |
| 1970 | 13,632 | 34.4% | |
| 1980 | 18,327 | 34.4% | |
| 1990 | 25,687 | 40.2% | |
| 2000 | 37,535 | 46.1% | |
| 2010 | 52,250 | 39.2% | |
| Est. 2019 | 64,296 | [7] | 23.1% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[8] 1790-1960[9] 1900-1990[10] 1990-2000[11] 2010-2019[1] | |||
2000 census
As of the 2000 United States Census,[12] there were 37,535 people, 13,151 households, and 10,494 families living in the county. The population density was 78 people per square mile (30/km2). There were 14,169 housing units at an average density of 30 per square mile (11/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 84.66% White, or European Americans, 12.99% Black or African American, 0.32% Native American, 0.45% Asian, 0.02% Pacific Islander, 0.52% from other races, and 1.04% from two or more races. About 1.41% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.
There were 13,151 households out of which 43.00% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 64.30% were married couples living together, 11.10% had a female householder with no husband present, and 20.20% were non-families. 16.90% of all households were made up of individuals and 6.00% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.84 and the average family size was 3.18.
In the county, the population was spread out with 29.90% under the age of 18, 8.20% from 18 to 24, 32.10% from 25 to 44, 21.70% from 45 to 64, and 8.00% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 34 years. For every 100 females, there were 98.70 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 96.20 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $46,505, and the median income for a family was $50,351. Males had a median income of $39,238 versus $23,814 for females. The per capita income for the county was $18,873. About 7.10% of families and 9.30% of the population were below the poverty line, including 10.80% of those under age 18 and 12.60% of those age 65 or over.
2010 census
As of the 2010 U.S. Census, there were 52,250 people, 18,092 households, and 14,139 families living in the county.[13] The population density was 109.4 inhabitants per square mile (42.2/km2). There were 19,884 housing units at an average density of 41.6 per square mile (16.1/km2).[14] The racial makeup of the county was 82.6% white, 13.5% black or African American, 0.8% Asian, 0.3% American Indian, 0.8% from other races, and 1.9% from two or more races. Those of Hispanic or Latino origin made up 2.9% of the population.[13] In terms of ancestry, 17.6% were German, 17.0% were Irish, 14.0% were English, and 10.2% were American.[15]
Of the 18,092 households, 43.6% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 60.1% were married couples living together, 12.7% had a female householder with no husband present, 21.8% were non-families, and 17.3% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.85 and the average family size was 3.22. The median age was 35.1 years.[13]
The median income for a household in the county was $56,903 and the median income for a family was $63,277. Males had a median income of $49,646 versus $34,554 for females. The per capita income for the county was $23,465. About 8.0% of families and 10.3% of the population were below the poverty line, including 13.2% of those under age 18 and 11.6% of those age 65 or over.[16]
Economy
In the early years of the 1900s, agriculture was the mainstay of the county economy. The chief agricultural products were Irish potatoes and sweet potatoes. The county farmers raised so many Irish potatoes in the early 1920s that they were shipped out numerous railroad boxcars, full of potatoes, during the summer months of those years.
Small businesses, such as the Effingham Canning Company and Potato Barrel manufacturing mills, became big businesses. The Effingham Canning Company did not last long. It was established in 1918 at the site of the former Savannah Atlanta Railroad Locomotive Repair Shop in Springfield. This site today would be located across the road from Georgia Highway Department Maintenance Building on Georgia Highway 21, south of Springfield. A later canning company operated in the 1940s at the old elementary school grounds in Springfield.
In the early 21st century, Effingham County has had unprecedented demand for industrial locations. Interest in industrial development has been spurred by the area's high population growth, tremendous growth at the Georgia ports and the ever-growing economy of coastal Georgia. Contributors include the military, aerospace industry and a diversified manufacturing base. The Savannah area is home to Gulfstream Aerospace and Hunter Army Airfield.
The Effingham County Industrial Park has announced several new tenants since 2005. In 2007 it became the site of EFACEC Group, a Portuguese-based transformer manufacturer for their North and Central America operations. The U.S. factory is located in Rincon, Georgia and produces both core and shell technology power transformers. Other businesses include the Flint River Services refrigerated storage, ValuePart distribution center, as well as expansions of several existing industries in the park. The site is ideally located on a four-lane divided highway only 10 miles (16 km) from Interstate 95 and within 15 miles (24 km) of the Georgia Ports, the Savannah International Airport and the historic City of Savannah.
The Effingham Industrial Development Authority acquired approximately 4,000 acres (16 km2) for development. The acquisitions include a tract of approximately 200 acres (0.81 km2) adjacent to Interstate 16 and an additional 1,550-acre (6.3 km2) tract on Interstate 16 seven miles from Interstate 95. Both tracts are within 15 miles (24 km) of the Georgia Ports Authority, and within 10 miles (16 km) of the Chatham County Mega-Site (formerly known as the DaimlerChrysler site) at the strategic intersection of Interstates 95 and 16.
A potential of 10,000,000 square feet (930,000 m2) of light manufacturing and/or Distribution Center/ Warehousing space exists at this site. Another recent acquisition is the former Research Forest Tract. Approximately 2,300 acres (9.3 km2) in size, this will be a "legacy" development to include commercial, executive office, heavy industrial, light industrial, professional service, research and recreational land uses. The site comprises three separate tracts of land six rail miles from the Georgia Ports Authority, with planned access to the Savannah River Parkway, Norfolk Southern mainline rail and CSX mainline rail. The property is being master planned. The development is planned to attract research and development, assembly operations, headquarters and other low-impact operations.
Industry in Effingham County includes paper manufacturing—Georgia Pacific (Savannah River Mill), high-precision turbine blade production—Doncasters, aluminum geodesic dome production—Temcor, concrete pipe manufacturing—Hanson, customized business jet interiors—Edward's Interiors, electrical distribution power transformer production—EFACEC PT, among many others.
Education
Politics
Effingham County has been a reliably Republican county from 1984 onward. While it began voting Republican earlier than most Georgia counties, albeit by very narrow margins, it voted in line with most other rural Deep South counties from 1964–1972. The last Democratic Party candidate to win the county was Jimmy Carter, who won it convincingly in his statewide landslide in 1976, but only narrowly in 1980.
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 76.2% 17,874 | 20.7% 4,853 | 3.1% 731 |
| 2012 | 74.8% 15,596 | 23.7% 4,947 | 1.5% 311 |
| 2008 | 74.9% 15,230 | 24.3% 4,936 | 0.9% 175 |
| 2004 | 77.3% 12,503 | 22.3% 3,613 | 0.4% 66 |
| 2000 | 68.8% 7,326 | 30.4% 3,232 | 0.9% 92 |
| 1996 | 56.8% 5,022 | 34.3% 3,031 | 9.0% 795 |
| 1992 | 47.9% 3,814 | 33.8% 2,690 | 18.3% 1459 |
| 1988 | 67.1% 3,933 | 32.5% 1,905 | 0.4% 21 |
| 1984 | 67.5% 4,266 | 32.5% 2,055 | |
| 1980 | 47.0% 2,528 | 51.8% 2,783 | 1.2% 66 |
| 1976 | 36.3% 1,654 | 63.7% 2,906 | |
| 1972 | 86.5% 3,175 | 13.5% 497 | |
| 1968 | 19.4% 769 | 16.0% 635 | 64.6% 2,561 |
| 1964 | 79.7% 2,676 | 20.3% 680 | |
| 1960 | 50.1% 885 | 49.9% 880 | |
| 1956 | 51.0% 637 | 49.0% 611 | |
| 1952 | 50.9% 829 | 49.1% 800 | |
| 1948 | 60.3% 779 | 26.8% 347 | 12.9% 167 |
| 1944 | 45.7% 365 | 54.3% 433 | |
| 1940 | 26.4% 227 | 73.6% 633 | |
| 1936 | 18.8% 142 | 81.1% 612 | 0.1% 1 |
| 1932 | 14.8% 90 | 84.9% 518 | 0.3% 2 |
| 1928 | 79.4% 627 | 20.6% 163 | |
| 1924 | 9.6% 39 | 83.0% 337 | 7.4% 30 |
| 1920 | 14.0% 118 | 86.0% 726 | |
| 1916 | 12.3% 64 | 86.2% 450 | 1.5% 8 |
| 1912 | 1.8% 7 | 97.2% 375 | 1.0% 4 |
Communities
External links
- Effingham County Government Official Webpage
- Effingham Now - News and Information
- Effingham Today, the website of Effingham County, Georgia
- Effingham County Chamber of Commerce
- Effingham Industrial Development Authority
- EffinghamTalk - The voice of Effingham County
- Effingham County historical marker
- Effingham County Methodist Camp Ground historical marker
- Bethany historical marker
- Goshen Church historical marker
- Historic Taverns on this Road historical marker
References
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 3, 2011. Retrieved June 22, 2014.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on July 12, 2012. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- "1140". Archived from the original on February 1, 2014. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- Gannett, Henry (1905). The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States. Govt. Print. Off. pp. 115.
- "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. February 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2011.
- "Georgia Soil and Water Conservation Commission Interactive Mapping Experience". Georgia Soil and Water Conservation Commission. Retrieved November 22, 2015.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved May 21, 2020.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 22, 2014.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved June 22, 2014.
- "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 22, 2014.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 22, 2014.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved May 14, 2011.
- "DP-1 Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved December 29, 2015.
- "Population, Housing Units, Area, and Density: 2010 - County". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved December 29, 2015.
- "DP02 SELECTED SOCIAL CHARACTERISTICS IN THE UNITED STATES – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved December 29, 2015.
- "DP03 SELECTED ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved December 29, 2015.
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved March 19, 2018.
