68th United States Congress
The 68th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1923, to March 4, 1925, during the last months of Warren G. Harding's presidency, and the first years of the administration of his successor, Calvin Coolidge. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the Thirteenth Decennial Census of the United States in 1910. Both chambers had a Republican majority.
| 68th United States Congress | |
|---|---|
67th ← → 69th | |
 United States Capitol (1906) | |
| March 4, 1923 – March 4, 1925 | |
| Senate President | Calvin Coolidge (R) until August 2, 1923 Vacant from August 2, 1923 |
| Senate President pro tem | Albert B. Cummins (R) |
| House Speaker | Frederick H. Gillett (R) |
| Members | 96 senators 435 members of the House 5 non-voting delegates |
| Senate Majority | Republican |
| House Majority | Republican |
| Sessions | |
| 1st: December 3, 1923 – June 7, 1924 2nd: December 1, 1924 – March 3, 1925 | |
Major events
- August 2, 1923 – President Warren Harding died. Vice President Calvin Coolidge became President of the United States
Major legislation
* April 26, 1924: Seed and Feed Loan Act
- May 19, 1924: World War Adjusted Compensation Act (Bonus Bill), Sess. 1, ch. 157, 43 Stat. 121
- May 24, 1924: Rogers Act
- May 26, 1924: Immigration Act of 1924 (Johnson–Reed Act), Sess. 1, ch. 190, 43 Stat. 153
- May 29, 1924: Indian Oil Leasing Act of 1924 (Lenroot Act)
- June 2, 1924: Indian Citizenship Act of 1924 (Snyder Act), Sess. 1, ch. 233, 43 Stat. 253
- June 2, 1924: Revenue Act of 1924 (Simmons–Longworth Act), Sess. 1, ch. 234, 43 Stat. 253
- June 3, 1924: Inland Waterways Act of 1924 (Denison Act)
- June 7, 1924: Pueblo Lands Act of 1924
- June 7, 1924: Oil Pollution Act of 1924, Pub.L. 68–238, ch. 316, 43 Stat. 604
- June 7, 1924: Clarke–McNary Act, Sess. 1, ch. 348, 43 Stat. 653
- January 30, 1925: Hoch–Smith Resolution
- January 31, 1925: Special Duties Act
- February 2, 1925: Air Mail Act of 1925 (Kelly Act)
- February 12, 1925: Federal Arbitration Act
- February 16, 1925: Home Port Act of 1925
- February 24, 1925: Purnell Act
- February 27, 1925: Temple Act
- February 28, 1925: Classification Act of 1925
- February 28, 1925: Federal Corrupt Practices Act (Gerry Act)
- March 2, 1925: Judiciary Act of 1925
- March 3, 1925: River and Harbors Act of 1925
- March 3, 1925: Helium Act of 1925
- March 4, 1925: Establishment of the United States Navy Band
- March 4, 1925: Probation Act of 1925
Constitutional amendments
- June 2, 1924: Approved an amendment to the United States Constitution that would specifically authorize Congress to regulate "labor of persons under eighteen years of age", and submitted it to the state legislatures for ratification[1]
- This amendment, commonly known as the Child Labor Amendment, has not been ratified and is still pending before the states.[2]
Party summary
The count below identifies party affiliations at the beginning of the first session of this Congress, and includes members from vacancies and newly admitted states, when they were first seated. Changes resulting from subsequent replacements are shown below.
Senate
| Party (shading shows control) |
Total | Vacant | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic (D) |
Farmer– Labor (FL) | Republican (R) | |||
| End of previous congress | 37 | 0 | 59 | 96 | 0 |
| Begin | 42 | 1 | 53 | 96 | 0 |
| End | 2 | 52 | |||
| Final voting share | 43.8% | 2.1% | 54.2% | ||
| Beginning of next congress | 40 | 1 | 55 | 96 | 0 |
House of Representatives
| Party (Shading indicates majority caucus) |
Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Democratic | Farmer–Labor | Socialist | Vacant | ||
| End of the previous Congress | 296 | 130 | 0 | 1 | 427 | 8 |
| Begin | 223 | 206 | 2 | 1 | 432 | 3 |
| End | 222 | 208 | 2 | 1 | 433 | 2 |
| Final voting share | 51.3% | 48.0% | 0.5% | 0.2% | ||
| Beginning of the next Congress | 247 | 183 | 3 | 1 | 434 | 1 |
Leadership

Senate
- President: Calvin Coolidge (R), until August 3, 1923; vacant thereafter.
- President pro tempore: Albert B. Cummins (R)
Majority (Republican) leadership
- Majority leader: Charles Curtis
- Majority whip: Wesley L. Jones
- Republican Conference Secretary: James Wolcott Wadsworth Jr.
- National Senatorial Committee Chair: George H. Moses
Minority (Democratic) leadership
- Minority leader: Joseph T. Robinson
- Minority whip: Peter G. Gerry
- Democratic Caucus Secretary: William H. King
House of Representatives
Majority (Republican) leadership
- Majority leader: Nicholas Longworth
- Majority Whip: Albert H. Vestal
- Republican Conference Chairman: Sydney Anderson
- Republican Campaign Committee Chairman: William R. Wood
Minority (Democratic) leadership
- Minority Leader: Finis J. Garrett
- Minority Whip: William Allan Oldfield
- Democratic Caucus Chairman: Henry Thomas Rainey
- Democratic Campaign Committee Chairman: Arthur B. Rouse
Members
This list is arranged by chamber, then by state. Senators are listed by class, and Representatives are listed by district.
Senate
Senators were elected every two years, with one-third beginning new six-year terms with each Congress. Preceding the names in the list below are Senate class numbers, which indicate the cycle of their election. In this Congress, Class 1 meant their term began in this Congress, requiring re-election in 1928; Class 2 meant their term ended with this Congress, requiring re-election in 1924; and Class 3 meant their term began in the last Congress, requiring re-election in 1926.
Alabama
Arizona
Arkansas
California
Colorado
Connecticut
Delaware
Florida
Georgia
Idaho
Illinois
Indiana
Iowa
Kansas
Kentucky
Louisiana
Maine
Maryland
Massachusetts
Michigan
Minnesota
Mississippi
Missouri
|
Montana
Nebraska
Nevada
New Hampshire
New Jersey
New Mexico
New York
North Carolina
North Dakota
Ohio
Oklahoma
Oregon
Pennsylvania
Rhode Island
South Carolina
South Dakota
Tennessee
Texas
Utah
Vermont
Virginia
Washington
West Virginia
Wisconsin
Wyoming
|
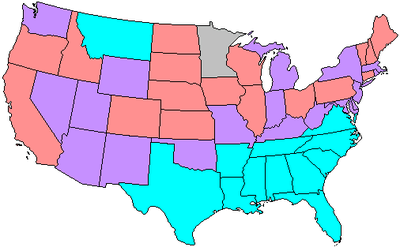 Senate composition, by party Senate majority leadership  Henry Cabot Lodge Republican leader (unofficial), until November 9, 1924  Charles Curtis Republican leader (unofficial, acting), from November 28, 1924 Republican whip, until November 28, 1924 .jpg) Wesley Jones Republican whip, from November 28, 1924 Senate minority leadership  Oscar Underwood Democratic leader, until December 3, 1923  Joseph T. Robinson Democratic leader, from December 3, 1923 .jpg) Peter G. Gerry Democratic whip
|
House of Representatives
The names of members of the House of Representatives elected statewide on the general ticket or otherwise at-large, are preceded by their district numbers.
Changes in membership
The count below reflects changes from the beginning of the first session of this Congress.
Senate
- replacements: 7
- Democratic: 1 seat net gain
- Republican: 2 seat net loss
- Farmer–Labor: 1 seat net gain
- deaths: 7
- resignations: 0
- vacancy: 0
- Total seats with changes: 8
| State | Senator | Reason for Vacancy | Successor | Date of Successor's Installation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorado (3) |
Samuel D. Nicholson (R) | Died March 24, 1923. Successor was appointed. |
Alva B. Adams (D) | May 17, 1923 |
| Minnesota (2) |
Knute Nelson (R) | Died April 28, 1923. Successor was elected. |
Magnus Johnson (FL) | July 16, 1923 |
| Vermont (3) |
William P. Dillingham (R) | Died July 12, 1923. Successor was elected. |
Porter H. Dale (R) | November 7, 1923 |
| Rhode Island (2) |
LeBaron Bradford Colt (R) | Died August 18, 1924. Successor was elected. |
Jesse H. Metcalf (R) | November 5, 1924 |
| Connecticut (3) |
Frank B. Brandegee (R) | Died October 14, 1924. Successor was elected December 17, 1924. |
Hiram Bingham III (R) | January 8, 1925[3] |
| Massachusetts (1) |
Henry Cabot Lodge (R) | Died November 9, 1924. Successor was appointed. |
William M. Butler (R) | November 13, 1924 |
| Colorado (3) |
Alva B. Adams (D) | Interim appointee retired. Successor was elected November 4, 1924. |
Rice W. Means (R) | December 1, 1924 |
| Illinois (2) |
Joseph M. McCormick (R) | Died February 25, 1925. Successor was appointed, having already been elected to the next term. |
Charles S. Deneen (R) | February 26, 1925 |
House of Representatives
- replacements: 22
- Democratic: 1 seat net gain
- Republican: 1 seat net loss
- deaths: 15
- resignations: 6
- contested election: 0
- Total seats with changes: 24
| District | Vacator | Reason for Vacancy | Successor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Illinois 2nd | Vacant | Rep. James R. Mann died during previous congress | Morton D. Hull (R) | April 3, 1923 |
| California 10th | Vacant | Rep. Henry Z. Osborne died during previous congress | John D. Fredericks (R) | May 1, 1923 |
| New York 16th | Vacant | Rep. William Bourke Cockran died during previous congress | John J. O'Connor (D) | November 6, 1923 |
| Alabama 2nd | John R. Tyson (D) | Died March 27, 1923 | Lister Hill (D) | August 14, 1923 |
| Michigan 3rd | John M. C. Smith (R) | Died March 30, 1923 | Arthur B. Williams (R) | June 19, 1923 |
| Iowa 8th | Horace M. Towner (R) | Resigned April 1, 1923, after being appointed Governor of Puerto Rico | Hiram K. Evans (R) | June 4, 1923 |
| New York 11th | Daniel J. Riordan (D) | Died April 28, 1923 | Anning S. Prall (D) | November 6, 1923 |
| Illinois 4th | John W. Rainey (D) | Died May 4, 1923 | Thomas A. Doyle (D) | November 6, 1923 |
| Arkansas 6th | Lewis E. Sawyer (D) | Died May 5, 1923 | James B. Reed (D) | October 6, 1923 |
| Washington 5th | J. Stanley Webster (R) | Resigned May 8, 1923, after being appointed to United States District Court for the Eastern District of Washington | Samuel B. Hill (D) | September 25, 1923 |
| North Carolina 2nd | Claude Kitchin (D) | Died May 31, 1923 | John H. Kerr (D) | November 6, 1923 |
| New York 32nd | Luther W. Mott (R) | Died July 10, 1923 | Thaddeus C. Sweet (R) | November 6, 1923 |
| Vermont 2nd | Porter H. Dale (R) | Resigned August 11, 1923, after becoming a candidate for the US Senate | Ernest Willard Gibson (R) | November 6, 1923 |
| Kentucky 7th | J. Campbell Cantrill (D) | Died September 2, 1923 | Joseph W. Morris (D) | November 30, 1923 |
| New York 24th | James V. Ganly (D) | Died September 7, 1923 | Benjamin L. Fairchild (R) | November 6, 1923 |
| Mississippi 3rd | Benjamin G. Humphreys II (D) | Died October 16, 1923 | William Y. Humphreys (D) | November 27, 1923 |
| Kentucky 9th | William J. Fields (D) | Resigned December 11, 1923 | Fred M. Vinson (D) | January 24, 1924 |
| Louisiana 2nd | H. Garland Dupré (D) | Died February 21, 1924 | James Z. Spearing (D) | April 22, 1924 |
| Illinois 14th | William J. Graham (R) | Resigned June 7, 1924, after being appointed to the United States Court of Customs Appeals | Seat remained vacant until next Congress | |
| Kansas 2nd | Edward C. Little (R) | Died June 27, 1924 | Ulysses S. Guyer (R) | November 4, 1924 |
| North Dakota 2nd | George M. Young (R) | Resigned September 2, 1924, after being appointed to the Board of General Appraisers | Thomas Hall (R) | November 4, 1924 |
| Massachusetts 15th | William S. Greene (R) | Died September 22, 1924 | Robert M. Leach (R) | November 4, 1924 |
| Maryland 5th | Sydney E. Mudd II (R) | Died October 11, 1924 | Stephen W. Gambrill (D) | November 4, 1924 |
| California 4th | Julius Kahn (R) | Died December 18, 1924 | Seat remained vacant until next Congress | |
Committees
Lists of committees and their party leaders, for members (House and Senate) of the committees and their assignments, go into the Official Congressional Directory at the bottom of the article and click on the link (5 links), in the directory after the pages of terms of service, you will see the committees of the Senate, House (Standing with Subcommittees, Select and Special) and Joint and after the committee pages, you will see the House/Senate committee assignments in the directory, on the committees section of the House and Senate in the Official Congressional Directory, the committee's members on the first row on the left side shows the chairman of the committee and on the right side shows the ranking member of the committee.
Senate
- Agriculture and Forestry (Chairman: George W. Norris; Ranking Member: Ellison D. Smith)
- Alien Property Custodian's Office (Select)
- Appropriations (Chairman: Francis E. Warren; Ranking Member: Lee S. Overman)
- Audit and Control the Contingent Expenses of the Senate (Chairman: Henry W. Keyes; Ranking Member: Kenneth McKellar)
- Banking and Currency (Chairman: George P. McLean; Ranking Member: Duncan U. Fletcher)
- Civil Service (Chairman: James Couzens then Porter H. Dale; Ranking Member: Kenneth McKellar)
- Claims (Chairman: Rice W. Means; Ranking Member: Park Trammell)
- Commerce (Chairman: Wesley L. Jones; Ranking Member: Duncan U. Fletcher)
- District of Columbia (Chairman: Arthur Capper; Ranking Member: William H. King)
- Education and Labor (Chairman: Lawrence C. Phipps; Ranking Member: Andrieus A. Jones)
- Enrolled Bills (Chairman: Frank L. Greene; Ranking Member: Coleman L. Blease)
- Expenditures in Executive Departments (Chairman: David A. Reed; Ranking Member: Oscar W. Underwood)
- Finance (Chairman: Reed Smoot; Ranking Member: Furnifold M. Simmons)
- Foreign Relations (Chairman: William E. Borah; Ranking Member: Claude Swanson)
- Immigration (Chairman: Hiram W. Johnson; Ranking Member: William H. King)
- Indian Affairs (Chairman: John W. Harreld; Ranking Member: Henry F. Ashurst)
- Internal Revenue Bureau (Select)
- Interoceanic Canals (Chairman: Walter Evans Edge; Ranking Member: Thomas J. Walsh)
- Interstate Commerce (Chairman: James Eli Watson; Ranking Member: Ellison D. Smith)
- Irrigation and Reclamation (Chairman: Charles L. McNary; Ranking Member: Morris Sheppard)
- Judiciary (Chairman: Albert B. Cummins; Ranking Member: Lee S. Overman)
- Library (Chairman: Simeon D. Fess; Ranking Member: Kenneth McKellar)
- Manufactures (Chairman: William B. McKinley; Ranking Member: Ellison D. Smith)
- Military Affairs (Chairman: James W. Wadsworth, Jr.; Ranking Member: Duncan U. Fletcher)
- Mines and Mining (Chairman: Tasker L. Oddie; Ranking Member: Thomas J. Walsh)
- Naval Affairs (Chairman: Frederick Hale; Ranking Member: Claude A. Swanson)
- Patents (Chairman: William M. Butler; Ranking Member: Ellison D. Smith)
- Pensions (Chairman: Peter Norbeck; Ranking Member: Peter G. Gerry)
- Post Office and Post Roads (Chairman: George H. Moses; Ranking Member: Kenneth McKellar)
- Printing (Chairman: George W. Pepper; Ranking Member: Duncan U. Fletcher)
- Privileges and Elections (Chairman: Richard P. Ernst; Ranking Member: William H. King)
- Public Buildings and Grounds (Chairman: Bert M. Fernald; Ranking Member: James A. Reed)
- Public Lands and Surveys (Chairman: Robert Nelson Stanfield; Ranking Member: Key Pittman)
- Rules (Chairman: Charles Curtis; Ranking Member: Lee S. Overman)
- Senatorial Elections (Select)
- Tariff Commission (Select)
- Territories and Insular Possessions (Chairman: Frank B. Willis; Ranking Member: Key Pittman)
- War Finance Corporation Loans (Select)
- Whole
House of Representatives
- Accounts (Chairman: Clarence MacGregor; Ranking Member: Ralph Waldo Emerson Gilbert)
- Agriculture (Chairman: Gilbert N. Haugen; Ranking Member: James B. Aswell)
- Alcoholic Liquor Traffic (Chairman: Grant M. Hudson; Ranking Member: William D. Upshaw)
- Appropriations (Chairman: Martin B. Madden; Ranking Member: Joseph W. Byrns)
- Banking and Currency (Chairman: Louis T. McFadden; Ranking Member: Otis Wingo)
- Census (Chairman: E. Hart Fenn; Ranking Member: John E. Rankin)
- Civil Service (Chairman: Frederick R. Lehlbach; Ranking Member: Lamar Jeffers)
- Claims (Chairman: Charles L. Underhill; Ranking Member: John C. Box)
- Coinage, Weights and Measures (Chairman: Randolph Perkins; Ranking Member: Bill G. Lowrey)
- Disposition of Executive Papers (Chairman: Edward H. Wason; Ranking Member: Arthur B. Rouse)
- District of Columbia (Chairman: Frederick N. Zihlman; Ranking Member: Christopher D. Sullivan)
- Education (Chairman: Daniel A. Reed; Ranking Member: Bill G. Lowrey)
- Election of the President, Vice President and Representatives in Congress (Chairman: Hays B. White; Ranking Member: Lamar Jeffers)
- Elections No.#1 (Chairman: Don B. Colton; Ranking Member: C.B. Hudspeth)
- Elections No.#2 (Chairman: Bird J. Vincent; Ranking Member: Gordon Browning)
- Elections No.#3 (Chairman: Charles L. Gifford; Ranking Member: Guinn Williams)
- Enrolled Bills (Chairman: Guy E. Campbell; Ranking Member: Thomas L. Blanton)
- Expenditures in the Agriculture Department (Chairman: Edward J. King; Ranking Member: Frank Gardner)
- Expenditures in the Commerce Department (Chairman: Henry R. Rathbone; Ranking Member: Miles C. Allgood)
- Expenditures in the Interior Department (Chairman: William Williamson; Ranking Member: Sol Bloom)
- Expenditures in the Justice Department (Chairman: Willis G. Sears; Ranking Member: Frank Oliver)
- Expenditures in the Labor Department (Chairman: Carroll L. Beedy; Ranking Member: Thomas L. Blanton)
- Expenditures in the Navy Department (Chairman: George F. Brumm; Ranking Member: Charles L. Abernethy)
- Expenditures in the Post Office Department (Chairman: Philip D. Swing; Ranking Member: Guinn Williams)
- Expenditures in the State Department (Chairman: J. Will Taylor; Ranking Member: George C. Peery)
- Expenditures in the Treasury Department (Chairman: Ernest W. Gibson; Ranking Member: Heartsill Ragon)
- Expenditures in the War Department (Chairman: Thaddeus C. Sweet; Ranking Member: Arthur H. Greenwood)
- Expenditures on Public Buildings (Chairman: Elmer O. Leatherwood; Ranking Member: Samuel Dickstein)
- Flood Control (Chairman: Frank R. Reid; Ranking Member: Riley J. Wilson)
- Foreign Affairs (Chairman: Stephen G. Porter; Ranking Member: J. Charles Linthicum)
- Immigration and Naturalization (Chairman: Albert Johnson; Ranking Member: Adolph J. Sabath)
- Indian Affairs (Chairman: John W. Harreld; Ranking Member: Carl Hayden)
- Industrial Arts and Expositions (Chairman: George A. Welsh; Ranking Member: Fritz G. Lanham)
- Inquiry into Operation of the United States Air Services (Select) (Chairman: N/A)
- Insular Affairs (Chairman: Scott Leavitt; Ranking Member: Mell G. Underwood)
- Interstate and Foreign Commerce (Chairman: James S. Parker; Ranking Member: Alben W. Barkley)
- Invalid Pensions (Chairman: Charles E. Fuller; Ranking Member: Mell G. Underwood)
- Irrigation and Reclamation (Chairman: Addison T. Smith; Ranking Member: Carl Hayden)
- Judiciary (Chairman: George S. Graham; Ranking Member: Hatton W. Sumners)
- Labor (Chairman: William F. Kopp; Ranking Member: William D. Upshaw)
- Library (Chairman: Robert Luce; Ranking Member: Ralph Waldo Emerson Gilbert)
- Merchant Marine and Fisheries (Chairman: Frank D. Scott; Ranking Member: Ladislas Lazaro)
- Mileage (Chairman: Carroll L. Beedy; Ranking Member: John W. Moore)
- Military Affairs (Chairman: John M. Morin; Ranking Member: Percy E. Quin)
- Mines and Mining (Chairman: John M. Robsion; Ranking Member: Daniel Sutherland)
- Naval Affairs (Chairman: Thomas S. Butler; Ranking Member: Carl Vinson)
- Patents (Chairman: Albert H. Vestal; Ranking Member: Fritz G. Lanham)
- Pensions (Chairman: Harold Knutson; Ranking Member: William D. Upshaw)
- Post Office and Post Roads (Chairman: William W. Griest; Ranking Member: Thomas M. Bell)
- Printing (Chairman: Edward M. Beers; Ranking Member: William F. Stevenson)
- Public Buildings and Grounds (Chairman: Richard N. Elliott; Ranking Member: Fritz G. Lanham)
- Public Lands (Chairman: Nicholas J. Sinnott; Ranking Member: John E. Raker then John M. Evans)
- Railways and Canals (Chairman: Oscar E. Keller; Ranking Member: William C. Lankford)
- Revision of Laws (Chairman: Roy G. Fitzgerald; Ranking Member: Alfred L. Bulwinkle)
- Rivers and Harbors (Chairman: S. Wallace Dempsey; Ranking Member: Joseph J. Mansfield)
- Roads (Chairman: Cassius C. Dowell; Ranking Member: Edward B. Almon)
- Rules (Chairman: Bertrand H. Snell; Ranking Member: Edward W. Pou)
- Standards of Official Conduct
- Territories (Chairman: Charles F. Curry; Ranking Member: William C. Lankford)
- War Claims (Chairman: James G. Strong; Ranking Member: Bill G. Lowrey)
- Ways and Means (Chairman: William R. Green; Ranking Member: John N. Garner)
- Woman Suffrage (Chairman: Wallace H. White, Jr.; Ranking Member: John E. Raker then Christopher D. Sullivan)
- World War Veterans' Legislation (Chairman: Royal C. Johnson; Ranking Member: Carl Hayden)
- Whole
Joint committees
- Civil Service Retirement Act
- Conditions of Indian Tribes (Special)
- Disposition of (Useless) Executive Papers
- Determine what Employment may be Furnished Federal Prisoners (Chairman: Rep. George S. Graham)
- Investigation of Northern Pacific Railroad Land Grants (Chairman: Rep. Nicholas J. Sinnott)
- Muscle Shoals
- The Library (Chairman: Sen. Simeon D. Fess)
- Printing (Chairman: Sen. George H. Moses; Vice Chairman: Rep. Edgar R. Kiess)
- Taxation (Chairman: Rep. William R. Green)
Caucuses
- Democratic (House)
- Democratic (Senate)
Employees
Legislative branch agency directors
- Architect of the Capitol: Elliott Woods, until May 22, 1923
- David Lynn, from August 22, 1923
- Comptroller General of the United States: John R. McCarl
- Librarian of Congress: Herbert Putnam
- Public Printer of the United States: George H. Carter
Senate
- Chaplain: John J. Muir Baptist
- Secretary: George A. Sanderson
- Librarian: Edward C. Goodwin
- Sergeant at Arms: David S. Barry
House of Representatives
- Chaplain: James S. Montgomery Methodist
- Clerk: William T. Page
- Doorkeeper: Bert W. Kennedy
- Clerk at the Speaker’s Table: Lehr Fess
- Reading Clerks: Patrick Joseph Haltigan (D) and Alney E. Chaffee (R)
- Postmaster: Frank W. Collier
- Sergeant at Arms: Joseph G. Rodgers
See also
- United States elections, 1922 (elections leading to this Congress)
- United States Senate elections, 1922
- United States Senate elections, 1923
- United States House of Representatives elections, 1922
- United States elections, 1924 (elections during this Congress, leading to the next Congress)
- 1924 United States presidential election
- United States Senate elections, 1924 and 1925
- United States House of Representatives elections, 1924
References
- Huckabee, David C. (September 30, 1997). "Ratification of Amendments to the U.S. Constitution" (PDF). Congressional Research Service reports. Washington D.C.: Congressional Research Service, The Library of Congress.
- "Four amendments that almost made it into the constitution". Constitution Daily. Philadelphia: The National Constitution Center. March 23, 2014. Archived from the original on March 5, 2017. Retrieved March 3, 2017.
- "A chronological list of senators since the First Congress in 1789" (PDF). United States Senate.
- Martis, Kenneth C. (1989). The Historical Atlas of Political Parties in the United States Congress. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company.
- Martis, Kenneth C. (1982). The Historical Atlas of United States Congressional Districts. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company.
External links
- Biographical Directory of the U.S. Congress
- U.S. House of Representatives: House History
- U.S. Senate: Statistics and Lists
- Official Congressional Directory for the 68th Congress, 1st Session.
- Official Congressional Directory for the 68th Congress, 1st Session (1st Revision).
- Official Congressional Directory for the 68th Congress, 1st Session (2nd Revision).
- Official Congressional Directory for the 68th Congress, 2nd Session.
- Official Congressional Directory for the 68th Congress, 2nd Session (Revision).
.jpg)


.jpg)
