Alfuzosin
Alfuzosin, sold under the brand name Uroxatral among others, is a medication of the α1 blocker class. It is used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).[1]
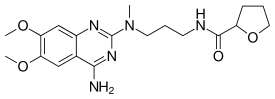 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ælˈfjuːzoʊsɪn/ al-FEW-zoh-sin |
| Trade names | Uroxatral, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a64002 |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth (tablets) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 49% |
| Protein binding | 82–90% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP3A4-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 10 hours |
| Excretion | Feces (69%) and Urine (24%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.108.671 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H27N5O4 |
| Molar mass | 389.456 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
As an antagonist of the α1 adrenergic receptor, it works by relaxing the muscles in the prostate and bladder neck, making it easier to urinate.
Alfuzosin was patented in 1978 and approved for medical use in 1988.[2] It was approved in the US for BPH in 2003. In 2017, it was the 266th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than one million prescriptions.[3][4]
Side effects
The most common side effects are dizziness (due to postural hypotension), upper respiratory tract infection, headache, fatigue, and abdominal disturbances. Side effects include stomach pain, heartburn, and congested nose.[5] Adverse effects of alfuzosin are similar to that of tamsulosin with the exception of retrograde ejaculation.[6]
Contraindications
Alfuzosin should be used with caution in patients with severe chronic kidney disease, and should not be prescribed to patients with a known history of QT prolongation or those who are taking medications known to prolong the QT interval.
Chemistry
Alfuzosin contains a stereocenter and is therefore chiral. There are two enantiomeric forms, (R)-alfuzosin and (S)-alfuzosin. The drug is used as a racemate, (RS)-alfuzosin, a 1: 1 mixture of the (R)- and (S)-forms.[7]
| Enantiomers of alfuzosin | |
|---|---|
-Alfuzosin_Structural_Formula_V2.svg.png) CAS number: 123739-69-5 |
-Alfuzosin_Structural_Formula_V2.svg.png) CAS number.: 123739-70-8 |
It is provided as the hydrochloride salt.
Brand names
It is marketed under the brand name Uroxatral and elsewhere under the tradenames Xat, Xatral, Prostetrol and Alfural.
References
- Lepor, Herbert (2016). "Alpha-blockers for the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia". Urologic Clinics of North America. 43 (3): 311–23. doi:10.1016/j.ucl.2016.04.009. PMC 2213889. PMID 27476124.
- Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 455. ISBN 9783527607495.
- "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- "Alfuzosin Hydrochloride - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- "Alfuzosin". MedlinePlus. United States National Library of Medicine. April 15, 2016.
- Hills, Robert K; Liu, Chenli; Zeng, Guohua; Kang, Ran; Wu, Wenqi; Li, Jiasheng; Chen, Kang; Wan, Show P. (2015). "Efficacy and Safety of Alfuzosin as Medical Expulsive Therapy for Ureteral Stones: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis". PLOS ONE. 10 (8): e0134589. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0134589. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 4526635. PMID 26244843.

- Rote Liste Service GmbH (Hrsg.): Rote Liste 2017 - Arzneimittelverzeichnis für Deutschland (einschließlich EU-Zulassungen und bestimmter Medizinprodukte). Rote Liste Service GmbH, Frankfurt/Main, 2017, Aufl. 57, S. 159, ISBN 978-3-946057-10-9.
External links
- Uroxatral (alfuzosin HCl) Extended-Release Tablets Prescribing Information
- Alfuzosin (General information from the NIH)