University of al-Qarawiyyin
The University of al-Qarawiyyin (Arabic: جامعة القرويين; Berber : ⵜⴰⵙⴷⴰⵡⵉⵜ ⵏ ⵍⵇⴰⵕⴰⵡⵉⵢⵢⵉⵏ; French: Université Al Quaraouiyine), also written Al-Karaouine or Al Quaraouiyine, is a university located in Fez, Morocco. It was founded as a mosque by Fatima al-Fihri in 859, and an associated madrasa subsequently became one of the leading spiritual and educational centers of the historic Muslim world. It was incorporated into Morocco's modern state university system in 1963 and was officially renamed "University of Al Quaraouiyine" two years later.[1] The mosque building itself is also a significant complex of historical Moroccan and Islamic architecture encompassing elements from many different periods of Moroccan history.[5]
جامعة القرويين ⵜⴰⵙⴷⴰⵡⵉⵜ ⵏ ⵍⵇⴰⵕⴰⵡⵉⵢⵢⵉⵏ | |
 | |
| Type | Madrasa and center of higher learning for non-vocational sciences (before 1963) State university since 1963[1][2][3] |
|---|---|
| Established | 859 (as a mosque)[4] |
Academic staff | 1,025 (2012) |
Administrative staff | 708 (2012) |
| Students | 8,120 (2012) |
| Location | , |
| Campus | Urban |
| Language | Arabic, Tamazight, French |
| Founder | Fatima al-Fihri |
| Colours | White |
| Website | uaq |
 | |
Scholars consider that the Qarawiyyin was founded[6][7] and run[3][8][9][10][11] as a madrasa until after World War II, and distinguish this status from the status of "university". They date the transformation of the madrasa of al-Qarawiyyin into a university to its modern reorganization in 1963.[1][2][3] Some sources, however, such as UNESCO and the Guinness World Records cite the Qarawiyyin as the oldest university or oldest continually operating higher-learning institution in the world,[12][13] although UNESCO also cites the University of Bologna as the oldest in the world[14].
Education at al-Qarawiyyin University concentrates on the Islamic religious and legal sciences with a heavy emphasis on, and particular strengths in, Classical Arabic grammar/linguistics and Maliki law, although lessons on other non-Islamic subjects are also offered to students. Teaching is delivered in the traditional method, in which students are seated in a semi-circle (halqa) around a sheikh who prompts them to read certain texts, asks them questions, and explains difficult points to them. The university is attended by students from all over Morocco and Muslim West Africa, with some also coming from further abroad.
Name
The Arabic name of the university, جَامِعَةُ الْقَرَوِيِّينَ pronounced [ʒaːmiʕtu lqarawijiːn] means "University of the People from Qairouan (القَيْرَوَان [alqajrawaːn])," the provenance of Fatima al-Fihriya's family in Tunisia .[15] The presence of the letter Qoph (ق), a voiceless uvular plosive which has no equivalent in European languages, as well as the ويّي ([awijiː]) triphthong in the university's name, in addition to the French colonization of Morocco, have introduced a number of different orthographies for the Romanization of the university's name, including al-Qarawiyyin, a standard anglicization; Al Quaraouiyine, following French orthography; and Al-Karaouine, another rendering using French orthography.
History of the institution
_(qarawiyyin_crop).jpg)
Mosque foundation and early history

According to the earliest source, the Rawd al-Qirtas by Ibn Abi Zar, Al-Qarawiyyin was founded as a mosque in 859 by Fatima al-Fihri[16][4][17][7], the daughter of a wealthy merchant named Mohammed Al-Fihri. The Al-Fihri family had migrated from Kairouan (hence the name of the mosque), Tunisia to Fes in the early 9th century, joining a community of other migrants from Kairouan who had settled in a western district of the city. Fatima and her sister Mariam, both of whom were well educated, inherited a large amount of money from their father. Fatima vowed to spend her entire inheritance on the construction of a mosque suitable for her community.[18]:48–49 Similarly, her sister Mariam is also reputed to have founded the Al-Andalusiyyin Mosque the same year.[19][18] At that time, the city of Fes was the capital of the Idrisid Dynasty, considered to be the first Moroccan Islamic state.[20]
Many scholars agree that some teaching and instruction took place at the Qarawiyyin Mosque from its very beginning.[21]:287[1]:71[22] Major mosques in the early Islamic period were typically multi-functional buildings where teaching and education took place alongside other religious and civic activities.[23][24] However, it is unclear at what time the Qarawiyyin Mosque began to act as an institution of formal education, in part because of the limited historical sources that pertain to its early period.[21][25] The earliest mentions of halaqat (circles) for learning and teaching may not have been until the 10th or the 12th Century.[26][21] The historian Abdelhadi Tazi indicated the earliest evidence of teaching at al-Qarawiyyin in 1121.[27] Moroccan historian Mohammed Al-Manouni believes that it was during the reign of the Almoravids (1040–1147) that the mosque acquired its function as a madrasa/university.[28][25] Other historians such as Abu al-Hasan Ali al-Jaznai[29] and Évariste Lévi-Provençal[30] date the beginning of the madrasa and teaching to the Marinid period (1244–1465).[31]
In the 10th century, the Idrisid dynasty fell from power and Fes became contested between the Fatimid and Cordoban Umayyad caliphates and their allies.[20] During this period, the Qarawiyyin progressively grew in prestige. At some point the khutba (Friday sermon) was transferred from the Shurafa Mosque of Idris II (today the Zawiya of Moulay Idris II) to the Qarawiyyin Mosque, thus granting it the status of Friday mosque (the community's main mosque). This transfer happened either in 919-18 or in 933, both dates which correspond to brief periods of Fatimid domination over the city, which suggests that the transfer may have occurred on Fatimid initiative.[5]:12 In any case, the mosque and its learning institution continued to enjoy the respect of political elites, with the mosque itself being significantly expanded by the Almoravids and repeatedly embellished under subsequent dynasties.[5] Tradition was established that all the other mosques of Fes based the timing of their call to prayer (adhan) according to that of the Qarawiyyin.[32]
Apogee during the Marinid period
Many scholars consider that the Qarawiyyin's high point as an intellectual and scholarly center was in the 13th-14th centuries, when the curriculum was at its broadest – including subjects like astronomy, mathematics, philosophy – and its prestige had reached new heights after centuries of expansion and elite patronage.[1][25]
Starting in the late 13th century, and especially in the 14th century, the Marinid dynasty was responsible for constructing a number of formal madrasas in the areas around the Qarawiyyin's main building. The first of these was the Saffarin Madrasa in 1271, followed by the al-Attarine in 1323 and the Mesbahiya Madrasa in 1346.[33] (A larger but much later madrasa, the Cherratine Madrasa, was also built nearby in 1670.[34]) These madrasas taught their own courses and sometimes became well-known institutions in their own right, but they usually had much narrower curriculums or specializations.[32]:141[35] One of their most important functions seems to have been to provide housing for students from other towns and cities – many of them poor – who needed a place to stay while studying at the Qarawiyyin.[36]:137[32]:110[18]:463 Thus, these buildings acted as complimentary or auxiliary institutions to the Qarawiyyin itself, which remained the center of intellectual life in the city.

The Qarawiyyin also compiled a large selection of manuscripts that were kept at a library founded by the Marinid Sultan Abu Inan Faris in 1349. Among the most precious manuscripts currently housed in the library are volumes from the famous Al-Muwatta of Malik written on gazelle parchment, the Sirat Ibn Ishaq, a copy of the Qur'an given by Sultan Ahmad al-Mansur in 1602, and the original copy of Ibn Khaldun's book Al-'Ibar (including the Muqaddimah).[37][35] Among the subjects taught, alongside the Qur'an and Fiqh (Islamic jurisprudence), were grammar, rhetoric, logic, medicine, mathematics, astronomy.[25][21][1]
Students were male, but traditionally it has been said that “facilities were at times provided for interested women to listen to the discourse while accommodated in a special gallery (riwaq) overlooking the scholars’ circle.”[21] The twelfth century cartographer Mohammed al-Idrisi, whose maps aided European exploration in the Renaissance is said to have lived in Fes for some time, suggesting that he may have worked or studied at al-Qarawiyyin. The madrasa has produced numerous scholars who have strongly influenced the intellectual and academic history of the Muslim world. Among these are Ibn Rushayd al-Sabti (d. 1321), Mohammed Ibn al-Hajj al-Abdari al-Fasi (d. 1336), Abu Imran al-Fasi (d. 1015), a leading theorist of the Maliki school of Islamic jurisprudence, and Leo Africanus, a renowned traveler and writer. Pioneer scholars such as Al-Idrissi (d.1166 AD), Ibn al-Arabi (1165-1240 AD), Ibn Khaldun (1332-1395 AD), Ibn al-Khatib (d. 1374), Al-Bitruji (Alpetragius) (d. 1294), and Ibn Hirzihim (d. 1163) were all connected with the madrasa either as students or lecturers. Some Christian scholars also visited the al-Qarawiyyin, including the Flemish Nicolas Cleynaerts (d. 1542) and the Dutchman Golius (d. 1667),[37] as well as Gerbert d'Aurillac who later became Pope Sylvester II.[38][39][40][32]:138 (Although the story of Gerbert's visit to Fes is viewed as a legend by some modern scholars.[41])
Decline and reforms
The Qarawiyyin underwent a general decline in later centuries, along with a parallel relative decline of Fes itself. The strength of its teaching stagnated and its curriculum decreased in range and scope, becoming focused on traditional Islamic sciences and Arabic linguistic studies. Even some traditional Islamic specializations like tafsir (Qur'anic exegesis) were progressively neglected.[1][25] In 1788-89, the Alaouite sultan Muhammad ibn Abdallah introduced reforms which regulated the institution's program, but which also imposed stricter limits and excluded logic, philosophy, and the more radical Sufi texts from the curriculum.[21][25][42] Other subjects also disappeared over time, such as astronomy and medicine.[25] In 1845 Sultan Abd ar-Rahman carried out further reforms, but it's unclear if this had any significant effect in the long-term.[1][25] Between 1830 and 1906 the number of faculty decreased from 425 to 266 (of which, among the latter, only 101 were still teaching).[1]:71
By the 19th century, the mosque's library had also suffered from decline and neglect. Over time, a significant portion of its collection was lost, most likely due to books not being returned by borrowers and to less authoritative supervision. By the beginning of the 20th century, the collection had been reduced to around 1600 manuscripts and 400 printed books, though many valuable historic items were nonetheless retained.[25]
State University

At the time Morocco became a French protectorate in 1912, al-Qarawiyyin had witnessed a decline as a religious center of learning from its medieval prime.[1] However, it had retained some significance as an educational venue for the sultan's administration.[1] The student body was rigidly divided along social strata; ethnicity (Arab or Berber), social status, personal wealth and the geographic background (rural or urban) determined the group membership of the students who were segregated on the teaching facility as well as in their personal quarters.[1] The French administration implemented a number of structural reforms between 1914 and 1947, but did not modernize the contents of teaching likewise which were still dominated by the traditional worldviews of the ulama.[1] At the same time, the student numbers at al-Qarawiyyin dwindled to a total of 300 in 1922 as the Moroccan elite began to send its children instead to the new-found Western-style colleges and institutes elsewhere in the country.[1] In 1931 and 1933, on the orders of Muhammad V, the Qarawiyyin's teaching was reorganized into elementary, secondary, and higher education.[25][21][42]
In 1947, al-Qarawiyyin was integrated into the state educational system,[8] but it was only by royal decree after independence, in 1963, that the madrasa was finally transformed into a university under the supervision of the ministry of education.[1][3][2] The old madrasa was shut down and the new campus established at former French Army barracks.[1] While the dean took its seat at Fez, four faculties were founded in and outside the city: a faculty of Islamic law in Fez, a faculty of Arab studies in Marrakech and a faculty of theology in Tétouan, plus one near Agadir in 1979. Modern curricula and textbooks were introduced and the professional training of the teachers improved.[1][43] Following the reforms, al-Qarawiyyin was officially renamed "University of Al Quaraouiyine" in 1965.[1]
In 1975, the General Studies were transferred to the newly founded Sidi Mohamed Ben Abdellah University; al-Qarawiyyin kept the Islamic and theological courses of studies. In 1973, Abdelhadi Tazi published a three-volume history of the establishment entitled جامع القرويين (The al-Qarawiyyin Mosque).[44]
In 1988, after a hiatus of almost three decades, the teaching of traditional Islamic education at the madrasa of al-Qarawiyyin was resumed by king Hassan II in what has been interpreted as a move to bolster conservative support for the monarchy.[1]
Education and curriculum
Education at al-Qarawiyyin University concentrates on the Islamic religious and legal sciences with a heavy emphasis on, and particular strengths in, Classical Arabic grammar/linguistics and Maliki law, although a few lessons on other non-Islamic subjects such as French, English are also offered to students. Teaching is delivered in the traditional method, in which students are seated in a semi-circle (halqa) around a sheikh, who prompts them to read sections of a particular text, asks them questions on particular points of grammar, law, or interpretation, and explains difficult points. Students from all over Morocco and Islamic West Africa attend the Qarawiyyin, although a few might come from as far afield as Muslim Central Asia. Even Spanish Muslim converts frequently attend the institution, largely attracted by the fact that the sheikhs of the Qarawiyyin, and Islamic scholarship in Morocco in general, are heirs to the rich religious and scholarly heritage of Muslim al-Andalus.
Most students at the Qarawiyyin range from between the ages of 13 and 30, and study towards high school-level diplomas and university-level bachelor's degrees, although Muslims with a sufficiently high level of Arabic are also able to attend lecture circles on an informal basis, given the traditional category of visitors "in search of [religious and legal] knowledge" ("zuwwaar li'l-talab fii 'ilm"). In addition to being Muslim, prospective students of the Qarawiyyin are required to have memorized the Qur'an in full as well as several other shorter medieval Islamic texts on grammar and Maliki law, and in general to have a very good command of Classical Arabic. It is a common misconception that the university is open only to men; it is open to both men and women. Women were first admitted into the university in the 1940s.[45]
Architectural history of the mosque

Early history (9th-10th centuries)
_in_the_city_of_Fes%2C_Morocco_(Image_6_of_9).jpg)
The mosque was founded in 859 by Fatima al-Fihri, but its present form is the result of a long historical evolution over the course of more than 1,000 years. The original building, whose traces are preserved in the layout of the current mosque, occupied much of what is today the central area of the prayer hall, south of the courtyard.[5][46]:119 It had a rectangular floor plan measuring 36 by 32 metres, covering an area of 1520 square metres, and was composed of a prayer hall with four transverse aisles running roughly east–west, parallel to the southern qibla wall.[5][32]:135 It probably also had a courtyard of relatively small size, and the first minaret, also of small size, reportedly stood on the location now occupied by the wooden anaza (at the central entrance to the prayer hall from the courtyard).[5] Water for the mosque was initially provided by a well dug within the mosque's precinct.[5]
As the city of Fes grew and as the mosque increased in prestige, the original building was insufficient for its religious and institutional needs.[5][32] During the 10th century, the Umayyad Caliphate of Cordoba (in Spain/Portugal) and the Fatimid Caliphate (in Tunisia) constantly vied for control over Fes and Morocco, seen as a buffer zone between the two.[20] Despite this uncertain period, the mosque received significant patronage and had its first expansions. The Zenata Berber amir Ahmed ibn Abi Said, one of the rulers of Fes during this period who was aligned with the Umayyads, wrote to the Caliph Abd al-Rahman III in Cordoba for permission and funds to expand the mosque.[5] The caliph approved, and the work was carried out or completed in 956.[5] This work expanded the mosque on three sides, encompassing the area of the present-day courtyard to the north and up to the current eastern and western boundaries of the building.[46] It also replaced the original minaret with a new, larger minaret still standing today. Its overall form, with a square shaft, was indicative of the subsequent development of North African (Maghrebi) and Andalusian minarets.[5][46] (Similar work was also carried out under Abd al-Rahman III at the same time on the other great mosque of Fes, the Andalusian Mosque.[46])
The mosque was again embellished when the Amirid ruler al-Muzaffar (son of al-Mansur) led a military expedition to Fes in 998. The embellishments included a new minbar and a new dome topped by talismans in the shape of a rat, a serpent, and a scorpion, but none of these works have survived.[5]
The Almoravid expansion (12th century)
One of the most significant expansions and renovations was carried out between 1135 and 1143 under the patronage of the Almoravid ruler Ali Ibn Yusuf, and the current form of the mosque owes much to this work.[5] The prayer hall was extended by dismantling the existing southern (qibla) wall and adding three more transverse aisles, bringing the number of these from 7 to 10, while essentially replicating the format of the existing arches of the mosque.[5][46] This expansion required the purchase and demolition of a number of neighbouring houses and structures, including some that were apparently part of the nearby Jewish neighbourhood (before the existence of the later Mellah of Fes).[5] The new expansion of the mosque involved not only a new mihrab (niche symbolizing the direction of prayer) in the middle of the new southern wall, but also the reconstruction or embellishment of the prayer hall's central "nave" (the arches along its central axis, in a line perpendicular to the southern wall and to the other rows of arches) leading from the courtyard to the mihrab. This involved not only embellishing some of the arches with new forms but also adding a series of highly elaborate cupola ceilings composed in muqarnas (honeycomb or stalactite-like) sculpting and further decorated with intricate reliefs of arabesques and Kufic letters.[5][47] Lastly, a new minbar (pulpit), in similar style and of similar artistic provenance as the famous (and slightly earlier) minbar of the Koutoubia Mosque, was completed and installed in 1144.[5] Made of wood in an elaborate work of marquetry, decorated with inlaid materials and intricately carved arabesque reliefs, it marked another highly accomplished work in a style that was emulated for later Moroccan minbars[5][47]
Elsewhere, many of the mosque's main entrances were given doors made of wood overlaid with ornate bronze fittings, which today count among the oldest surviving bronze artworks in Moroccan/Andalusian architecture.[36][5] Another interesting element added to the mosque was a small secondary oratory, known as the Jama' al-Gnaiz ("Funeral Mosque" or "Mosque of the Dead"), which was separated from the main prayer hall and dedicated to providing funerary rites for the deceased before their burial.[5] This annex is also decorated with a muqarnas cupola and a number of ornate archways and windows.[5]
Embellishment under subsequent dynasties (later 12th century and after)
Almohad period
Later dynasties continued to embellish the mosque or gift it with new furnishings, though no works as radical as the Almoravid expansion were undertaken again. The Almohads (later 12th century and 13th century) conquered Fes after a long siege in 1145–1146.[18][5] Historical sources (particularly the Rawd al-Qirtas) report a story claiming that the inhabitants of Fes, fearful that the "puritan" Almohads would resent the lavish decoration placed inside the mosque, hurriedly covered up some of the most ornate carvings and decorations from Ali ibn Yusuf's expansion near the mihrab.[5]:25–26 Although French scholar Henri Terrasse suggests this operation may have been carried out a few years later by the Almohad authorities themselves.[5] The Almoravid ornamentation was only fully uncovered again during renovations in the early 20th century.[48][5]
However, under the reign of Muhammad al-Nasir (ruled 1199-1213) the Almohads did add or upgrade a number of elements in the mosque, some of which were nonetheless marked with strong decorative flourishes. The ablutions facilities in the courtyard were upgraded, a separate mida'a (Arabic: ميضأة) or ablutions room was added to the north (of which only the rough layout has survived today), and a new underground storage room was created.[5] They also replaced the mosque's grand chandelier with a new and more ornate one in bronze, still hanging in the central nave of the mosque today.[5][46]
Marinid period

The Marinids, who were responsible for building many of the lavish madrasas around Fes, made various contributions to the mosque. In 1286 they restored and protected the 10th-century minaret, which had been made from poor-quality stone that was deteriorating, by covering it with whitewash.[5] At its southern foot they also built the Dar al-Muwaqqit, a chamber for the timekeeper of the mosque who was responsible for determining the precise times of prayer. The chamber was equipped with astrolabes and other scientific equipment of the era in order to aid in this task. Notably, a number of water clocks were built for it, the last of which, built on the orders of Sultan Abu Salim Ali II (ruled 1359-1361), is still partly preserved today.[46][49][50] The galleries around the nearby courtyard (sahn) were also rebuilt or repaired in 1283 and 1296–97, while at the entrance from the courtyard to the prayer hall (leading to the central nave of the mihrab), a decorative wooden screen, called the anaza, was installed in 1289 and acted as a symbolic "outdoor" or "summer" mihrab for prayers in the courtyard.[5] At the central outer entrance to the courtyard from the north, the gate called Bab al-Ward ("Gate of the Rose"), a decorative cupola and dome was installed over its vestibule in 1337, still visible today (with minor restorations).[5] A number of ornate metal chandeliers hanging in the mosque's prayer hall also date from the Marinid era. Three of them were made from church bells which Marinid craftsmen used as a base onto which they grafted ornate copper fittings. The largest of them, installed in the mosque in 1337, was a bell brought back from Gibraltar by the son of Sultan Abu al-Hasan, Abu Malik, after its reconquest from Spanish forces in 1333.[5]
Lastly, the mosque's library was officially founded by Sultan Abu Inan in 1349 (750 AH), as dated by an inscription over its doorway.[5]:64[39] This first Marinid library was located at the mosque's northeastern corner (as opposed to the library's current southern location).[39] In 1361, Sultan Abu Salim added to it a room which was built above and over the adjacent street and which was dedicated to readings of the Qur'an.[5]:64
Saadian and Alaouite period
The Saadians further embellished the mosque by adding two prominent pavilions to the western and eastern ends of the courtyard, each of which sheltered a new fountain. The famous Saadian sultan Ahmad al-Mansur was responsible for building the first pavilion to the east in 1587–88, while the western pavilion was added under his son, Muhammad al-Sheikh al-Ma'mun in 1609.[51] The pavilions emulate those found in the Court of Lions of the Alhambra palaces (in Granada, Spain).[5][51] This was the last major addition to the mosque's architecture. The Saadian sultan Ahmad al-Mansur also built a new room for the library on the south side of the mosque (around the library's current location), which was connected to the mosque via a door in the qibla wall.[52][39] The Alaouite dynasty, which has ruled Morocco from the 17th century onward, continued to effect minor additions and regular maintenance on the mosque, including another ribbed cupola in the central nave.[5] The present library building, continuously updated, now dates mainly from a major expansion and modification in the 20th century, particularly in the 1940s.[39][52]:174
Architectural description of the mosque
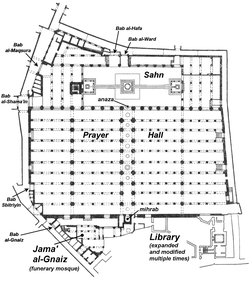
Successive dynasties expanded the Qarawiyyin mosque until it became the largest in Africa, with a capacity of 22,000 worshipers.[53] The present-day mosque thus covers an extensive area of about half an hectare.[32]:136 Broadly speaking, it consists of a large hypostyle interior space for prayers, a courtyard (sahn) with fountains, a minaret (at the courtyard's western end), and a number of annexes in addition to the main mosque itself.
The exterior

The Qarawiyyin's exterior does not generally present a monumental appearance and is integrated with the dense urban fabric around it. By one count there are 18 separate gates and entrances distributed around its perimeter.[32] The gates vary from small rectangular doorways to enormous horseshoe arches with huge doors preceded by wooden roofs covering the street in front of them.[5] While the doors are generally made of wood, some of the gates have extensive ornate bronze overlays crafted during the Almoravid period.[5] The most ornate and best-preserved examples include the doors of the principal northern gate, Bab al-Ward (which opens onto the courtyard), the western gate called Bab Sbitriyyin (whose current doors, however, are replicas replacing the originals now kept by the Dar Batha Museum[46]), and the southwestern gate Bab al-Gna'iz which leads to the Jama' al-Gna'iz or Funeral Mosque.[5][47] The much more monumental northwestern gates of the mosque, Bab al-Shama'in (or Bab Chemaine) and Bab al-Maqsura, also have heavy bronze fittings, including some ornate knockers, which date from the Almoravid period.[5]
Adjacent to Bab al-Ward, on its west side, is another doorway, Bab al-Hafa ("Gate of the Barefooted"), from the Almohad era, which is distinguished by a small water channel across the floor just inside it. This water allowed for worshipers entering the mosque to wash their feet on the way in, helping with initial ablutions.[34][5]
Also next to the mosque is a tower known as the Borj Neffara (برج النفارة , "Tower of the Trumpeters"), an observation tower that is sometimes confused as a minaret but was actually part of another Dar al-Muwaqqit (timekeeper's house).[54][36]:150
The prayer hall (interior)
.jpg)
The interior hypostyle prayer hall takes up most of the mosque's area. Like the interior of most traditional mosques in Moroccan architecture, it is a relatively austere space, with mostly plain walls, wooden roofs, and rows upon rows of arches. The main area, south of the courtyard, is a vast space divided into ten transverse aisles by rows of arches running parallel to the southern wall.[5] The southern wall of this hall also marks the qibla or direction of prayer for Muslim worshipers. The central axis of the prayer hall, perpendicular to the qibla wall, is marked by a central "nave" running between two extra lines of arches along this axis, perpendicular to the other arches.[5] This nave leads towards the mihrab: a niche in the qibla wall which symbolizes the direction of prayer, and in front of which the imam usually leads prayers and delivers sermons. This overall layout (a hypostyle hall with a central nave emphasized against the others) is a familiar layout for North African mosques generally.[5][52]
The mihrab area, which dates from the Almoravid (12th-century) expansion, is decorated with carved and painted stucco, as well as several windows of coloured glass. The mihrab niche itself is a small alcove which is covered by a small dome of muqarnas (stalactite or honeycomb-like sculpting).[47] The central nave that runs along the axis of the mihrab is distinguished from the rest of the mosque by a number of architectural embellishments. The arches that run along it are of varying shapes, including both horseshoe arches and multi-lobed arches.[5] Instead of the plain timber ceilings, most sections of the nave are covered by a series of intricate muqarnas ceilings and cupolas, each slightly different from the other, as well as two "ribbed" dome cupolas (similar to the domes of the Great Mosque of Cordoba and Cristo de la Luz Mosque in Toledo) dating from the Almoravid and Alaouite periods.[5] Many of the muqarnas compositions are further decorated with intricate reliefs of arabesques and Arabic inscriptions in both Kufic and cursive letters.[5][47] Additionally, there are several elaborately carved bronze chandeliers hanging in the nave which were gifted to the mosque during the Almohad and Marinid eras; at least three of which were made from bells (probably church bells) brought back from victories in Spain.[5][55]
To the right of the mihrab is the minbar (pulpit) of the mosque, which could also be stored in a small room behind a door in the qibla wall here. The minbar is most likely of similar origins as the famous Almoravid minbar of the Koutoubia Mosque, made by a workshop in Cordoba not long after the latter and installed in the Qarawiyyin Mosque in 1144 (at the end of the Almoravid works on the mosque).[5] It is another exceptional work of marquetry and woodcarving, decorated with geometric compositions, inlaid materials, and arabesque reliefs.[5][47]
Aside from the embellishments of the central nave, the rest of the mosque is architecturally quite uniform, but there are some minor irregularities in the floor plan. For example, the arches in the western half of the prayer hall are shorter than those of the eastern half, and some of the transverse aisles are slightly wider than others. These anomalies have not been fully explained but they appear to have been present since the early centuries of the mosque; they may be due to early reconstructions or alterations which have gone unrecorded in historical chronicles.[5]
The courtyard
The courtyard (sahn) is rectangular, surrounded by the prayer hall on three sides and by a gallery to the north. The floor is paved with typical Moroccan mosaic tiles (zellij) and at the center is a fountain.[52] From outside the mosque, the courtyard is accessed by the main northern gate, called Bab al-Ward, whose vestibule is covered by a Marinid-era white dome which is fluted on the outside and covered in painted and carved stucco on the inside.[5] Opposite this gate, situated on the mihrab axis, is the central entrance to the interior prayer hall, guarded by a carved and painted wooden screen called the anaza which also acted as a symbolic "outdoor" or "summer" mihrab for prayers taking place in the courtyard.[5] (These features are visible to visitors standing outside the gate.) Both this entrance to the prayer hall and the outer gate across from it have facades decorated with carved and painted stucco.[5]
At the western and eastern ends of the courtyard stand two ornate Saadian pavilions each sheltering another fountain. The pavilions have pyramidal domes and emulate the pavilions in the Court of Lions in the Alhambra (Spain).[5] They are decorated with carved wood and stucco, mosaic-tiled walls, and marble columns.[51] Behind these pavilions are extensions of the main prayer hall divided into four naves by rows of arches.[5] The gallery and arched hall on the northeastern sides of the courtyard are a prayer space reserved for women.[5]
The minaret

The minaret was constructed in the 10th century by the Umayyad caliph of Cordoba, and overlooks the courtyard from the west. It was constructed in local limestone of relatively poor quality and was covered in whitewash by the Marinids in the 13th century in order to protect it from deterioration. It has a square shaft and is topped by a dome, as well as a parapet from which the muezzin historically issued the call to prayer (adhan). The full structure is 26.75 meters tall.[5] One curious feature of the minaret is the lower window on its southern facade, which is shaped like a "triple" horseshoe arch, elongated vertically, which is unique to this structure.[46] On the minaret's southern side, just above the gallery of the courtyard, is a room known as the Dar al-Muwaqqit, devoted to determining the times of prayer in a precise manner.[5]
The funerary annex (Jama' al-Gnaiz)
A number of annexes are attached around the mosque, serving various functions. The northwestern edge of the building is occupied by latrines.[5] Behind the southern qibla wall, to the west of the mihrab axis, is an area known as the Jama' al-Gnaiz ("Funeral Mosque", or sometimes translated as "Mosque of the Dead"), which served as a separate oratory reserved for funerary rites. This type of facility was not particularly common in the Islamic world but there are several examples in Fez, including at the Chrabliyine and Bab Guissa Mosques. It was kept separate from the main mosque in order to preserve the purity of the latter as a regular prayer space, which in principle could be soiled by the presence of a dead body.[5][47] This oratory dates back to the Almoravid period and also features embellishments such as a muqarnas cupola and a number of ornate archways in varying forms.[5][47]
The library
Also behind the southern wall of the mosque, but to the east of the mihrab axis, is the historic library of the mosque and university.[5] It is sometimes cited as the world's oldest surviving library, and was recently restored by Aziza Chaouni and reopened in 2016.[56][57] The first purpose-built library structure was added to the mosque by the Marinid sultan Abu Inan Faris in 1349 CE, though it was located at the mosque's northeastern corner instead of to the south.[58][5] This first structure still exists today, embedded near the women's section of the mosque, and consists of a square chamber measuring 5.4 meters per side. Its entrance is covered by a wooden screen from the Marinid period which features an inscription carved in cursive Arabic above the doorway recording Abu Inan's foundation of the library.[5]:64
The current library building dates in part from a Saadian construction by Ahmad al-Mansur (late 16th century), who built a chamber called al-Ahmadiyya just behind the qibla wall. Most of the building, however, now dates from a major 20th-century expansion. This expansion included the current grand reading room, which measures 23 metres long and features an ornately-painted wooden ceiling.[39]
Status as world's oldest university
According to UNESCO,[13] and a number of other scholars, al-Qarawiyyin is considered to have been a university since its founding and therefore that it is the oldest university in the world.[59][60][32] In some sources, the medieval madrasa is described as a "university".[60][61] Although UNESCO also cites the University of Bologna as the oldest university in the world.[62] According to Yahya Pallavicini, the university model did not spread in Europe until the 12th century, and was found throughout the Muslim world from the founding of al-Qarawiyyin in the 9th century until at least European colonialism.[63] According to Encyclopædia Britannica, universities had existed in parts of Asia and Africa prior to the founding of the first medieval European universities.[64]
A number of other scholars, however, consider the medieval university (from Latin universitas) to be an institution unique to Christian Europe, arguing that the first universities were located in Western Europe with Paris and Bologna often cited as the earliest examples.[65][66][67][68][69][70][71] Jacques Verger says that while the term 'university' is occasionally applied by scholars to the madrasa out of convenience, the European university marked a major disruption between earlier institutions of higher learning and were the earliest true modern university.[72] Several scholars consider that al-Qarawiyyin was founded[4][7] and run[3][8] as a madrasa (Arabic: مدرسة) until after World War II. They consider institutions like al-Qarawiyyin to be higher education colleges of Islamic law where other subjects were only of secondary importance.[9][73][74] They also consider that the University was only adopted outside the West, including into the Islamic world, in the course of modernization programs since the beginning of the 19th century.[75][76][72][77] Organization at the pre-modern al-Qarawiyyin differed from both that of European universities and of Cairo and Tunis in that there was no defined scholastic year, registration was not imposed, duration of the studies were not fixed, and there was no examination to ratify studies (although a simple certificate called idjaza was handed to students who had given proff of a certain ability).[78] They date the transformation of the madrasa of al-Qarawiyyin into a university to its modern reorganization in 1963.[1][2][3] In the wake of these reforms, al-Qarawiyyin was officially renamed "University of Al Quaraouiyine" two years later.[1]
Some scholars, noting certain parallels between such madrasas and European medieval universities, have proposed that the latter may have been influenced by the madrasas of Islamic Spain and the Emirate of Sicily.[79] Other scholars have questioned this, citing the lack of evidence for an actual transmission from the Islamic world to Christian Europe and highlighting the differences in the structure, methodologies, procedures, curricula and legal status of the "Islamic college" (madrasa) versus the European university.[75][80][81]
The earliest date of formal teaching at al-Qarawiyyin is also uncertain.[25] In the Rawd al-Qirtas, Ibn Abi Zar mentions the mosque but not its educational function. The earliest mentions of learning or teaching may not have been until the 10th or the 12th Century.[82][83] The historian Abdelhadi Tazi indicated the earliest evidence of teaching at al-Qarawiyyin in 1121.[84] Historian Mohammed Al-Manouni believes that the madrasa was added to the mosque during the reign of the Almoravids (1040–1147), Évariste Lévi-Provençal and Abu al-Hasan Ali al-Jaznai the Marinid period (1244–1465), although al-Jaznai affirms that it was the religious heart of the Maghreb since the Idrissid era.[85] [86][87] [88] Moroccan historian Abdelhadi Tazi indicated the earliest evidence of teaching at al-Qarawiyyin in 1121.[89] Upon reviewing this evidence in Abdelhadi Tazi's work, Abdul Latif Tibawi claims that:
This is considerably later than the beginning of instruction at the al-Azhar under the Fatimids. So it is very difficult to sustain the claim that the University of Qarawiyyin is the "oldest university", and not only in the Muslim world! The mosque school or college did not assume the name of university until 1960 when in a ceremony Muhammad V invested it with that dignified title. [90]
Famous alumni
A number of well-known philosophers, scholars, and politicians in the history of Morocco and the western Mediterranean have either studied or taught at the Qarawiyyin since its founding. The most notable persons are listed here.
List of alumni:
- Gerbert of Aurillac (946–1003), scholar and the later Pope Sylvester II[38][39][32] (though his travels to Fez and attendance at the Qarawiyyin is considered a legend by other scholars[41])
- Muhammad al-Idrisi (1100–1165), geographer[91][92]
- Maimonides (1135/1138–1204), Jewish philosopher[1][91]
- Ibn Arabi (1165–1240), Sufi philosopher[91]
- Ibn Khaldun (1332–1406), historian and philosopher[1][91][35]
- Nicolas Cleynaerts (1495–1542), Flemish grammarian and traveler[91][92]
- Leo Africanus (1494–1554), author[91]
- Imam al-Bannani (1727–1780), faqīh (Muslim jurist)
- Ahmad ibn Idris (1760–1837), Moroccan Sufi scholar[93]
- Muhammad al-Kattani (1873–1909), writer and political leader[94]
- Abd el-Krim el-Khattabi (1882–1963), Morocan political and military leader[95]
- Allal al-Fassi (1910–1974), Moroccan politician[96]
- Muhammad Taqi-ud-Din al-Hilali (1893–1987), translator
- Abdullah al-Ghumari (1910–1993), faqīh (Muslim jurist)[97]
- Fatima al-Kabbaj (1932–), Member of High Council of Knowledge (Islamic council)[98]
See also
- Dar al-Muwaqqit (the "timekeeper's house" in Moroccan mosques)
- Borj Neffara (observation tower next to the mosque)
- List of universities in Morocco
- Education in Morocco
- History of Medieval Arabic and Western European domes
References and notes
- Lulat, Y. G.-M.: A History Of African Higher Education From Antiquity To The Present: A Critical Synthesis, Greenwood Publishing Group, 2005, ISBN 978-0-313-32061-3, pp. 154–157
- Park, Thomas K.; Boum, Aomar: Historical Dictionary of Morocco, 2nd ed., Scarecrow Press, 2006, ISBN 978-0-8108-5341-6, p. 348
al-qarawiyin is the oldest university in Morocco. It was founded as a mosque in Fès in the middle of the ninth century. It has been a destination for students and scholars of Islamic sciences and Arabic studies throughout the history of Morocco. There were also other religious schools like the madras of ibn yusuf and other schools in the sus. This system of basic education called al-ta'lim al-aSil was funded by the sultans of Morocco and many famous traditional families. After independence, al-qarawiyin maintained its reputation, but it seemed important to transform it into a university that would prepare graduates for a modern country while maintaining an emphasis on Islamic studies. Hence, al-qarawiyin university was founded in February 1963 and, while the dean's residence was kept in Fès, the new university initially had four colleges located in major regions of the country known for their religious influences and madrasas. These colleges were kuliyat al-shari's in Fès, kuliyat uSul al-din in Tétouan, kuliyat al-lugha al-'arabiya in Marrakech (all founded in 1963), and kuliyat al-shari'a in Ait Melloul near Agadir, which was founded in 1979.
- Belhachmi, Zakia: "Gender, Education, and Feminist Knowledge in al-Maghrib (North Africa) – 1950–70", Journal of Middle Eastern and North African Intellectual and Cultural Studies, Vol. 2–3, 2003, pp. 55–82 (65):
The Adjustments of Original Institutions of the Higher Learning: the Madrasah. Significantly, the institutional adjustments of the madrasahs affected both the structure and the content of these institutions. In terms of structure, the adjustments were twofold: the reorganization of the available original madaris and the creation of new institutions. This resulted in two different types of Islamic teaching institutions in al-Maghrib. The first type was derived from the fusion of old madaris with new universities. For example, Morocco transformed Al-Qarawiyin (859 A.D.) into a university under the supervision of the ministry of education in 1963.
- Petersen, Andrew: Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, Routledge, 1996, ISBN 978-0-415-06084-4, p. 87 (entry "Fez"):
The Quaraouiyine Mosque, founded in 859, is the most famous mosque of Morocco and attracted continuous investment by Muslim rulers.
- Terrasse, Henri (1968). La Mosquée al-Qaraouiyin à Fès; avec une étude de Gaston Deverdun sur les inscriptions historiques de la mosquée. Paris: Librairie C. Klincksieck.
- Petersen, Andrew: Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, Routledge, 1996, ISBN 978-0-415-06084-4, p. 87 (entry "Fez"):
The Quaraouiyine Mosque, founded in 859, is the most famous mosque of Morocco and attracted continuous investment by Muslim rulers.
- Lulat, Y. G.-M.: A History Of African Higher Education From Antiquity To The Present: A Critical Synthesis Studies in Higher Education, Greenwood Publishing Group, 2005, ISBN 978-0-313-32061-3, p. 70:
As for the nature of its curriculum, it was typical of other major madrasahs such as al-Azhar and Al Quaraouiyine, though many of the texts used at the institution came from Muslim Spain...Al Quaraouiyine began its life as a small mosque constructed in 859 C.E. by means of an endowment bequeathed by a wealthy woman of much piety, Fatima bint Muhammed al-Fahri.
- Shillington, Kevin: Encyclopedia of African History, Vol. 2, Fitzroy Dearborn, 2005, ISBN 978-1-57958-245-6, p. 1025:
Higher education has always been an integral part of Morocco, going back to the ninth century when the Karaouine Mosque was established. The madrasa, known today as Al Qayrawaniyan University, became part of the state university system in 1947.
They consider institutions like al-Qarawiyyin to be higher education colleges of Islamic law where other subjects were only of secondary importance. - Pedersen, J.; Rahman, Munibur; Hillenbrand, R.: "Madrasa", in Encyclopaedia of Islam, 2nd edition, Brill, 2010:
Madrasa, in modern usage, the name of an institution of learning where the Islamic sciences are taught, i.e. a college for higher studies, as opposed to an elementary school of traditional type (kuttab); in mediaeval usage, essentially a college of law in which the other Islamic sciences, including literary and philosophical ones, were ancillary subjects only.
- Meri, Josef W. (ed.): Medieval Islamic Civilization: An Encyclopedia, Vol. 1, A–K, Routledge, ISBN 978-0-415-96691-7, p. 457 (entry "madrasa"):
A madrasa is a college of Islamic law. The madrasa was an educational institution in which Islamic law (fiqh) was taught according to one or more Sunni rites: Maliki, Shafi'i, Hanafi, or Hanbali. It was supported by an endowment or charitable trust (waqf) that provided for at least one chair for one professor of law, income for other faculty or staff, scholarships for students, and funds for the maintenance of the building. Madrasas contained lodgings for the professor and some of his students. Subjects other than law were frequently taught in madrasas, and even Sufi seances were held in them, but there could be no madrasa without law as technically the major subject.
- Makdisi, George: "Madrasa and University in the Middle Ages", Studia Islamica, No. 32 (1970), pp. 255–264 (255f.):
In studying an institution which is foreign and remote in point of time, as is the case of the medieval madrasa, one runs the double risk of attributing to it characteristics borrowed from one's own institutions and one's own times. Thus gratuitous transfers may be made from one culture to the other, and the time factor may be ignored or dismissed as being without significance. One cannot therefore be too careful in attempting a comparative study of these two institutions: the madrasa and the university. But in spite of the pitfalls inherent in such a study, albeit sketchy, the results which may be obtained are well worth the risks involved. In any case, one cannot avoid making comparisons when certain unwarranted statements have already been made and seem to be currently accepted without question. The most unwarranted of these statements is the one which makes of the "madrasa" a "university".
- "Oldest higher-learning institution, oldest university". Guinness World Records. Retrieved 30 July 2020.
- "Medina of Fez". UNESCO. Retrieved 31 July 2012.
- mondial, UNESCO Centre du patrimoine. "The Porticoes of Bologna - UNESCO World Heritage Centre". UNESCO Centre du patrimoine mondial (in French). Retrieved 16 August 2020.
- "مَوْسُوعَةُ الْجَزِيرَةِ | جَامِعَةُ الْقَرَوِيِّينَ - AJNET Encyclopedia | al-Qarawiyyin University". learning.aljazeera.net. Retrieved 15 July 2019.
- ʻAlī ibn ʻAbd Allāh Ibn Abī Zarʻ al-Fāsī (1964). Rawd Al-Qirtas. Valencia [Impreso por J. Nácher].
- Meri, Josef W. (ed.): Medieval Islamic Civilization: An Encyclopedia, Vol. 1, A–K, Routledge, ISBN 978-0-415-96691-7, p. 257 (entry "Fez")
- Le Tourneau, Roger (1949). Fès avant le protectorat: étude économique et sociale d'une ville de l'occident musulman. Casablanca: Société Marocaine de Librairie et d'Édition.
- Terrasse, Henri (1942). La mosquée des Andalous à Fès. Paris: Les Éditions d'art et d'histoire.
- Abun-Nasr, Jamil (1987). A history of the Maghrib in the Islamic period. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521337674.
- Tibawi, A. L. (Summer 1980). "Reviewed Work: Jami' al-Qarawiyyin: al-Masjid wa'l-Jami'ah bi Madinat Fas (Mausu'ah li-Tarikhiha al-Mi'mari wa'l-Fikri). Al Qaraouiyyine: la Mosquée-Université de Fès (histoire architecturale et intellectuelle) by Abdul-Hadi at-Tazi". Arab Studies Quarterly. 2 (3): 286-288.
- Esposito, John, ed. (2003). "Universities (Islamic)". The Oxford Dictionary of Islam. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-1951-2559-7.
- Pedersen, J.; Makdisi, G.; Rahman, Munibur; Hillenbrand, R. (2012). "Madrasa". Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition. Brill.
- "mosque | Parts, Features, Architecture, & Information". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- Deverdun, Gaston (2012). "al-Ḳarawiyyīn". Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition. Brill.
- "Al-Qarawiyyin University in Fes: Brainchild of a Muslim Woman". Inside Arabia. 15 September 2019. Retrieved 11 August 2020.
- Tazi, Abdelhadi (1972). Jami' al-Qarawiyyin: al-Masjid wa'l-Jami'ah bi Madinat Fas (Mausu'ah li-Tarikhiha al-Mi'mari wa'l-Fikri). Al Qaraouiyyine: la Mosquée-Université de Fès (histoire architecturale et intellectuelle). Beirut: Dar al Kitab ab Lubnani. p. 112.
- Deverdun, Gaston (1971). Encyclopédie de l'Islam volume IV. Leyde/Paris: E.J.Brill/Maisonneuve & Larose.
- Al-Jaznaï,, Zahrat al-Âs; Bel, Alfred (1923). "Publications de la faculté des lettres d'Alger, fascicule 59" (PDF): 7. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help)CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) - Les historiens des Chorfa; essai sur la littérature historique et biographique au Maroc du XVIe au XXe siècle. Paris,: Maisonneuve & Larose. 2001. ISBN 9782706815072.CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link)
- Al-Jaznaï,, Zahrat al-Âs; Bel, Alfred (1923). "Publications de la faculté des lettres d'Alger, fascicule 59": 7. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help)CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) - Gaudio, Attilio (1982). Fès: Joyau de la civilisation islamique. Paris: Les Presse de l'UNESCO: Nouvelles Éditions Latines. ISBN 2723301591.
- Kubisch, Natascha (2011). "Maghreb - Architecture". In Hattstein, Markus; Delius, Peter (eds.). Islam: Art and Architecture. h.f.ullmann. pp. 312–313.
- Marçais, Georges (1954). L'architecture musulmane d'Occident. Paris: Arts et métiers graphiques.
- Irwin, Robert (2019). Ibn Khaldun: An Intellectual Biography. Princeton University Press. p. 29.
- Parker, Richard B. (1981). A practical guide to Islamic Monuments in Morocco. Charlottesville, VA: The Baraka Press.
- see R. Saoud article on http://muslimheritage.com/topics/default.cfm?ArticleID=447,
- Crowe, Felicity; Goddard, Jolyon; Hollingum, Ben; MacEachern, Sally; Russell, Henry, eds. (2011). Modern Muslim Societies. Muslim World. New York, NY: Marshall Cavendish Reference. p. 93. ISBN 978-0-7614-7927-7. Retrieved 24 November 2015.
- Touri, Abdelaziz; Benaboud, Mhammad; Boujibar El-Khatib, Naïma; Lakhdar, Kamal; Mezzine, Mohamed (2010). Le Maroc andalou : à la découverte d'un art de vivre (2 ed.). Ministère des Affaires Culturelles du Royaume du Maroc & Museum With No Frontiers. ISBN 978-3902782311.
- Messier, Ronald A. (2010). The Almoravids and the Meanings of Jihad. ABC-CLIO. p. 45.
- "Qantara - Gerbert d'Aurillac". www.qantara-med.org. Retrieved 23 June 2020.
- Esposito, John, ed. (2003). "Qarawiyin University". The Oxford Dictionary of Islam. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-1951-2559-7.
- Park, Thomas K.; Boum, Aomar: Historical Dictionary of Morocco, 2nd ed., Scarecrow Press, 2006, ISBN 978-0-8108-5341-6, p. 348
- Tazi, Abdelhadi. جامع القرويين [The al-Qarawiyyin Mosque] (in Arabic). ISBN 9981-808-43-1.
- Ahmed, Sumayya (2016). "Learned Women: Three Generations of Female Islamic Scholarship in Morocco". The Journal of North African Studies. 21 (3): 470–484. doi:10.1080/13629387.2016.1158110.
- Lintz, Yannick; Déléry, Claire; Tuil Leonetti, Bulle (2014). Le Maroc médiéval: Un empire de l'Afrique à l'Espagne. Paris: Louvre éditions. ISBN 9782350314907.
- Salmon, Xavier (2018). Maroc Almoravide et Almohade: Architecture et décors au temps des conquérants, 1055-1269. Paris: LienArt.
- Terrasse, Henri (1957). "La Mosquée d'Al-Qarawīyīn à Fès et l'Art des Almoravides". Ars Orientalis. 2: 135–147.
- Hill, Donald R. (1997). "Clocks and watches". In Selin, Helaine (ed.). Encyclopaedia of the History of Science, Technology, and Medicine in Non-Westen Cultures. Kluwer Academic Publishers. p. 209.
- "La clepsydre d'Al Lajaï 763/1361"". Mémorial du Maroc. 3: 66–69.
- Salmon, Xavier (2016). Marrakech: Splendeurs saadiennes: 1550-1650. Paris: LienArt. ISBN 9782359061826.
- Métalsi, Mohamed (2003). Fès: La ville essentielle. Paris: ACR Édition Internationale. ISBN 978-2867701528.
- Fauzi M. Najjar (April 1958). "The Karaouine at Fez". The Muslim World. 48 (2): 104–112. doi:10.1111/j.1478-1913.1958.tb02246.x.
- "La magnifique rénovation des 27 monuments de Fès – Conseil Régional du Tourisme (CRT) de Fès" (in French). Retrieved 10 January 2020.
- Mezzine, Mohamed (2019). "Qarawiyyin Mosque". Discover Islamic Art - Museum With No Frontiers. Retrieved 22 May 2020.
- Shaheen, Kareem (19 September 2016). "World's oldest library reopens in Fez: 'You can hurt us, but you can't hurt the books'". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 14 December 2019.
- Carrington, Daisy (29 September 2016). "This 1,157-year-old library gets a facelift". CNN Travel. Retrieved 14 December 2019.
- Lulat, Y. G.-M. A History of African Higher Education from Antiquity to the Present: A Critical Synthesis: A Critical Synthesis. ABC-CLIO. p. 71. ISBN 978-0-313-06866-9.
- Seelinger, Lani. "The 13 Oldest Universities In The World". Culture Trip. Retrieved 30 May 2017.
- Esposito, John (2003). The Oxford Dictionary of Islam. Oxford University Press. p. 328. ISBN 978-0-1951-2559-7.
- Joseph, S, and Najmabadi, A. Encyclopedia of Women & Islamic Cultures: Economics, education, mobility, and space. Brill, 2003, p. 314.
- mondial, UNESCO Centre du patrimoine. "The Porticoes of Bologna - UNESCO World Heritage Centre". UNESCO Centre du patrimoine mondial (in French).
- Pallavicini, Yahya Sergio Yahe (2009), "Islamic Knowledge in Italy", in Aslan, Ednan (ed.), Islamic Education in Europe, Wiener islamisch-religionspädagogische Studien, 1, Böhlau Verlag Wien, pp. 220–221, ISBN 9783205783107,
The Muslim community maintained, favoured, and organized the institutions for higher education that became the new centres for the diffusion of Islamic knowledge. These centres were places where teachers and students of that time would meet and also where all intellectuals would gather and take part in extremely important scientific debates. It is not a coincidence that around the 9th century the first university in the world, the Qarawiyyin University in Fez, was established in the Muslim world followed by az-Zaytuna in Tunis and Al-Azhar in Cairo. The university model, that in the West was widespread starting only from the 12th century, had an extraordinary fortune and was spread throughout the Muslim world at least until the colonial period.
- Encyclopædia Britannica: "University", 2012, retrieved 26 July 2012
- Ferruolo, Stephen C.: The Origins of the University: The Schools of Paris and Their Critics, 1100–1215, Stanford University Press, 1985, ISBN 978-0-8047-1266-8, p. 5
- Pace, Edward: "Universities", The Catholic Encyclopedia, Vol. 15, Robert Appleton Company, New York, 1912, retrieved 27 July 2012)
- Brill's New Pauly: "University", Brill, 2012)
- Lexikon des Mittelalters: "Universität. Die Anfänge", Vol. 8, Cols 1249–1250, Metzler, Stuttgart, [1977]–1999
- Vauchez, André; Dobson, Richard Barrie; Lapidge, Michael (eds.): Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages, Vol. 1, Routledge, 2000, ISBN 978-1-57958-282-1, p. 1484 (entry "university")
- Verger, Jacques: "Patterns", in: Ridder-Symoens, Hilde de (ed.): A History of the University in Europe. Vol. I: Universities in the Middle Ages, Cambridge University Press, 2003, ISBN 978-0-521-54113-8, pp. 35–76 (35)
- Makdisi, George: "Madrasa and University in the Middle Ages", Studia Islamica, No. 32 (1970), pp. 255–264
- Verger, Jacques: "Patterns", in: Ridder-Symoens, Hilde de (ed.): A History of the University in Europe. Vol. I: Universities in the Middle Ages, Cambridge University Press, 2003, ISBN 978-0-521-54113-8, pp. 35–76 (35):
No one today would dispute the fact that universities, in the sense in which the term is now generally understood, were a creation of the Middle Ages, appearing for the first time between the twelfth and thirteenth centuries. It is no doubt true that other civilizations, prior to, or wholly alien to, the medieval West, such as the Roman Empire, Byzantium, Islam, or China, were familiar with forms of higher education which a number of historians, for the sake of convenience, have sometimes described as universities.Yet a closer look makes it plain that the institutional reality was altogether different and, no matter what has been said on the subject, there is no real link such as would justify us in associating them with medieval universities in the West. Until there is definite proof to the contrary, these latter must be regarded as the sole source of the model which gradually spread through the whole of Europe and then to the whole world. We are therefore concerned with what is indisputably an original institution, which can only be defined in terms of a historical analysis of its emergence and its mode of operation in concrete circumstances.
- Meri, Josef W. (ed.): Medieval Islamic Civilization: An Encyclopedia, Vol. 1, A–K, Routledge, ISBN 978-0-415-96691-7, p. 457 (entry "madrasa"):
A madrasa is a college of Islamic law. The madrasa was an educational institution in which Islamic law (fiqh) was taught according to one or more Sunni rites: Maliki, Shafi'i, Hanafi, or Hanbali. It was supported by an endowment or charitable trust (waqf) that provided for at least one chair for one professor of law, income for other faculty or staff, scholarships for students, and funds for the maintenance of the building. Madrasas contained lodgings for the professor and some of his students. Subjects other than law were frequently taught in madrasas, and even Sufi seances were held in them, but there could be no madrasa without law as technically the major subject.
- Makdisi, George: "Madrasa and University in the Middle Ages", Studia Islamica, No. 32 (1970), pp. 255–264 (255f.):
In studying an institution which is foreign and remote in point of time, as is the case of the medieval madrasa, one runs the double risk of attributing to it characteristics borrowed from one's own institutions and one's own times. Thus gratuitous transfers may be made from one culture to the other, and the time factor may be ignored or dismissed as being without significance. One cannot therefore be too careful in attempting a comparative study of these two institutions: the madrasa and the university. But in spite of the pitfalls inherent in such a study, albeit sketchy, the results which may be obtained are well worth the risks involved. In any case, one cannot avoid making comparisons when certain unwarranted statements have already been made and seem to be currently accepted without question. The most unwarranted of these statements is the one which makes of the "madrasa" a "university".
- Makdisi, George: "Madrasa and University in the Middle Ages", Studia Islamica, No. 32 (1970), pp. 255-264 (264):
Thus the university, as a form of social organization, was peculiar to medieval Europe. Later, it was exported to all parts of the world, including the Muslim East; and it has remained with us down to the present day. But back in the Middle Ages, outside of Europe, there was nothing anything quite like it anywhere.
- Rüegg, Walter: "Foreword. The University as a European Institution", in: Ridder-Symoens, Hilde de (ed.): A History of the University in Europe. Vol. I: Universities in the Middle Ages, Cambridge University Press, 1992, ISBN 0-521-36105-2, pp. XIX–XX:
The university is a European institution; indeed, it is the European institution par excellence. There are various reasons for this assertion. As a community of teachers and taught, accorded certain rights, such as administrative autonomy and the determination and realization of curricula (courses of study) and of the objectives of research as well as the award of publicly recognized degrees, it is a creation of medieval Europe, which was the Europe of papal Christianity...
No other European institution has spread over the entire world in the way in which the traditional form of the European university has done. The degrees awarded by European universities – the bachelor's degree, the licentiate, the master's degree, and the doctorate – have been adopted in the most diverse societies throughout the world. The four medieval faculties of artes – variously called philosophy, letters, arts, arts and sciences, and humanities –, law, medicine, and theology have survived and have been supplemented by numerous disciplines, particularly the social sciences and technological studies, but they remain none the less at the heart of universities throughout the world.
Even the name of the universitas, which in the Middle Ages was applied to corporate bodies of the most diverse sorts and was accordingly applied to the corporate organization of teachers and students, has in the course of centuries been given a more particular focus: the university, as a universitas litterarum, has since the eighteenth century been the intellectual institution which cultivates and transmits the entire corpus of methodically studied intellectual disciplines.
- Sanz, Nuria; Bergan, Sjur (eds.): The Heritage of European Universities, Council of Europe, 2002, ISBN 978-92-871-4960-2, p. 119:
In many respects, if there is any institution that Europe can most justifiably claim as one of its inventions, it is the university. As proof thereof and without wishing here to recount the whole history of the birth of universities, it will suffice to describe briefly how the invention of universities took the form of a polycentric process of specifically European origin.
- Deverdun, G. (1960–2009). "al-Ḳarawiyyīn". The encyclopaedia of Islam (New ed.). Leiden: Brill. ISBN 9789004161214. Retrieved 17 August 2020.CS1 maint: date format (link)
- Alatas, S. F. (2006), "From Jami'ah to University: Multiculturalism and Christian–Muslim Dialogue", Current Sociology, 54 (1): 112–132 [123–4], doi:10.1177/0011392106058837
- The scholarship on these differences is summarized in Toby Huff, Rise of early modern science, 2nd ed. p. 149-159; p. 179-189.
- Norman Daniel: Review of "The Rise of Colleges. Institutions of Learning in Islam and the West by George Makdisi", Journal of the American Oriental Society, Vol. 104, No. 3 (Jul. - Sep., 1984), pp. 586-588 (587)
- "Al-Qarawiyyin University in Fes: Brainchild of a Muslim Woman". Inside Arabia. 15 September 2019. Retrieved 11 August 2020.
- Tibawi, A. L. (Summer 1980). "Reviewed Work: Jami' al-Qarawiyyin: al-Masjid wa'l-Jami'ah bi Madinat Fas (Mausu'ah li-Tarikhiha al-Mi'mari wa'l-Fikri). Al Qaraouiyyine: la Mosquée-Université de Fès (histoire architecturale et intellectuelle) by Abdul-Hadi at-Tazi". Arab Studies Quarterly. 2 (3): 286-288.
- Tazi, Abdelhadi (1972). Jami' al-Qarawiyyin: al-Masjid wa'l-Jami'ah bi Madinat Fas (Mausu'ah li-Tarikhiha al-Mi'mari wa'l-Fikri). Al Qaraouiyyine: la Mosquée-Université de Fès (histoire architecturale et intellectuelle). Beirut: Dar al Kitab ab Lubnani. p. 112.
- Deverdun, Gaston (1971). Encyclopédie de l'Islam volume IV. Leyde/Paris: E.J.Brill/Maisonneuve & Larose.
- Al-Jaznaï,, Zahrat al-Âs; Bel, Alfred (1923). "Publications de la faculté des lettres d'Alger, fascicule 59": 7. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help)CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) - Les historiens des Chorfa; essai sur la littérature historique et biographique au Maroc du XVIe au XXe siècle. Paris,: Maisonneuve & Larose. 2001. ISBN 9782706815072.CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link)
- Al-Jaznaï,, Zahrat al-Âs; Bel, Alfred (1923). "Publications de la faculté des lettres d'Alger, fascicule 59": 85. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help)CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) - Tazi, Abdelhadi (1972). Jami' al-Qarawiyyin: al-Masjid wa'l-Jami'ah bi Madinat Fas (Mausu'ah li-Tarikhiha al-Mi'mari wa'l-Fikri). Al Qaraouiyyine: la Mosquée-Université de Fès (histoire architecturale et intellectuelle). Beirut: Dar al Kitab ab Lubnani. p. 112.
- Tibawi, A. L. (1980). "Review of Jami' al-Qarawiyyin: al-Masjid wa'l-Jami'ah bi Madinat Fas (Mausu'ah li-Tarikhiha al-Mi'mari wa'l-Fikri). Al Qaraouiyyine: la Mosquée-Université de Fès (histoire architecturale et intellectuelle)". Arab Studies Quarterly. pp. 286–288. Retrieved 12 August 2020.
- Bhattacharyya, Shilpa; Guha, Debjani (2016). "Scholastic Excellence of Nalanda and Nalanda Contemporary (415 A.D. – 1200 A.D.) Al-Qarawiyyin: A Comparative Evaluation". INSIGHT Journal of Applied Research in Education. 21 (1): 343–351.
- Fry, Tatiana; Clevel; University, State; Curnow, Kathy. "Al-Qarawiyyin - University, Library, and Mosque in One". Bright Continent. Retrieved 9 August 2020.
- Radtke, Bernd R. (2012). "Aḥmad b. Idrīs". Encyclopaedia of Islam (3rd ed.). Brill.
- "الموسوعة العربية | الكتاني (محمد بن عبد الكبير-)". arab-ency.com.sy. Retrieved 9 August 2020.
- Pennell, C.R. (2004). "Muḥammad b. ʿAbd al-Karīm". In Bearman, P.; Bianquis, Th.; Bosworth, C.E.; van Donzel, E.; Heinrichs, W.P. (eds.). Encyclopaedia of Islam. XII (2nd ed.). Leiden, Netherlands: E. J. BRILL. p. 634. ISBN 9004139745.
- Dennerlein, Bettina (2018). "al-Fāsī family". Encyclopaedia of Islam (3rd ed.). Brill.
- "The Biography of Abu al_Fadl ^Abdullah bin as-Siddiq al-Ghumari". www.riadnachef.org. Retrieved 9 August 2020.
- Ahmed, Sumayya (2016). "Learned Women: Three Generations of Female Islamic Scholarship in Morocco". The Journal of North African Studies. 21 (3): 470–484. doi:10.1080/13629387.2016.1158110.
Further reading
- Tazi, Abdelhadi. جامع القرويين [The al-Qarawiyyin Mosque] (in Arabic).
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Al-Qarawiyyin. |
- ISESCO: Fez 2007
- UNIVERSITE QUARAOUIYINE - Fes (French)
- Al Qaraouiyine Rehabilitation at ArchNet (includes pictures of the interior, the minbar, and other architectural elements)
_in_the_city_of_Fes%2C_Morocco_(Image_8_of_9).jpg)


_in_the_city_of_Fes%2C_Morocco_(Image_7_of_9).jpg)

_(edited).jpg)


