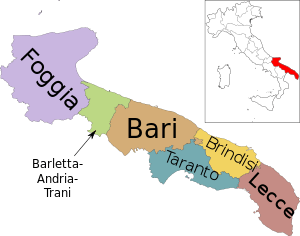
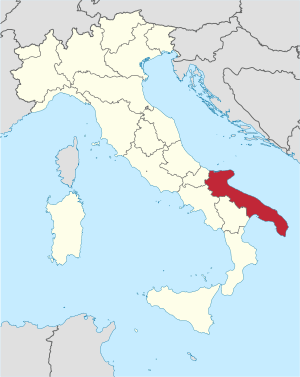
Apulia
Apulia (/əˈpuːliə/ ə-POO-lee-ə; Italian: Puglia [ˈpuʎːa]; Neapolitan: Pùglia [ˈpuʝːə];[lower-alpha 1] Albanian: Pulia; Ancient Greek: Ἀπουλία, romanized: Apoulía) is a region of Italy, located in the southern peninsular section of the country, bordering the Adriatic Sea to the east, the Ionian Sea to the southeast, and the Strait of Otranto and Gulf of Taranto to the south. The region comprises 19,345 square kilometers (7,469 sq mi), and its population is about four million.
Apulia | |
|---|---|
Region of Italy | |
 Coat of arms | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 41°0′31″N 16°30′46″E | |
| Country | Italy |
| Capital | Bari |
| Government | |
| • President | Michele Emiliano (PD) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 19,358 km2 (7,474 sq mi) |
| Population (31 December 2016) | |
| • Total | 4,063,888 |
| • Density | 210/km2 (540/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | English: Apulian Italian: Pugliese |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| ISO 3166 code | IT-75 |
| GDP (nominal) | €74.8 billion (2017)[1] |
| GDP per capita | €18,400 (2017)[2] |
| HDI (2017) | 0.844[3] very high · 18th of 21 |
| NUTS Region | ITF |
| Website | www.regione.puglia.it |
It is bordered by the other Italian regions of Molise to the north, Campania to the west, and Basilicata to the southwest. Its capital city is Bari.
Geography
.jpg)
Apulia's coastline is longer than that of any other mainland Italian region. In the north, the Gargano promontory extends out into the Adriatic like a 'sperone' ("spur"), while in the south, the Salento peninsula forms the 'tacco' ("heel") of Italy's boot.[4] The highest peak in the region is Mount Cornacchia (1,152 meters above sea level) within the Daunian Mountains, in the north along the Apennines.
It is home to two national parks, the Alta Murgia National Park and Gargano National Park.[5]
Outside national parks in the North and West, most of Apulia and particularly Salento is geographically flat with only moderate hills.
The climate is typically Mediterranean with hot, dry and sunny summers and mild, rainy winters. Snowfall, especially on the coast is rare but has occurred as recently as January 2019 (following on from snow in March 2018 and January 2017). Apulia is among the hottest and driest regions of Italy in summer with temperatures sometimes reaching up to and above 40 °C in Lecce and Foggia.
The coastal areas, particularly on the Adriatic and in the southern Salento region are frequently exposed to winds of varying strengths and directions, strongly affecting local temperatures and conditions, sometimes within the same day. The Northerly Bora wind from the Adriatic can lower temperatures, humidity and moderate summer heat while the Southerly Sirocco wind from North Africa can raise temperatures, humidity and occasionally drop red dust from the Sahara. On some days in spring and autumn, it can be warm enough to swim in Gallipoli and Porto Cesareo on the Ionian coast while at the same time, cool winds warrant jackets and sweaters in Monopoli and Otranto on the Adriatic coast.

History


Apulia is one of the richest archaeological regions in Italy. It was first colonized by Mycenaean Greeks.[6]
Some parts of the regions were conquered by the Muslim Saracens, and the Emirate of Bari was established for a brief period of time by Muhammad Abul Abbas of Sicily.
A number of castles were built in the area by Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II, including Castel del Monte,[7] sometimes called the "Crown of Apulia".[8]
Apulia was an autonomous duchy until 1130 when its duke became king of Sicily. After 1282, when the kingdom lost the island of Sicily itself, Apulia remained part of the remnant Kingdom of Naples (confusingly known also as the Kingdom of Sicily), and remained so until the unification of Italy in 1861. This kingdom was independent under the House of Anjou from 1282 to 1442, then was part of Aragon until 1458, after which it was again independent under a cadet branch of the House of Trastámara until 1501. As a result of the French–Spanish war of 1501–1504, Naples again came under the rule of Aragon and the Spanish Empire from 1504 to 1714. When Barbary pirates of North Africa sacked Vieste in 1554, they took an estimated 7,000 slaves.[9] The coast of Apulia was occupied at times by the Turks and at other times by the Venetians.[10]
In 1861 the region became part of the Kingdom of Italy.[11]
Economy
The region's contribution to Italy's gross value added was around 4.6% in 2000, while its population was 7% of the total. The per capita GDP is low compared to the national average and represents about 68.1% of the EU average.[12]
The share of gross value added by the agricultural and services sectors was above the national average in 2000. The region has industries specialising in particular areas, including food processing and vehicles in Foggia; footwear and textiles in the Barletta area, and wood and furniture in the Murge area to the west.[13]
Between 2007 and 2013 the economy of Apulia expanded more than that of the rest of southern Italy.[14] Such growth, over several decades, is a severe challenge to the hydrogeological system.[15]
Apulia's thriving economy is articulated into numerous sectors boasting several leading companies: Aerospace (Sitael, Blackshape, Leonardo S.p.A.); Agriculture (Casillo Group, G.C. Partecipazioni), Automotive (Getrag, a subsidiary of Magna International); Food and Beverage (De Carlo, Divella, Quarta Caffé); Furniture (Natuzzi); ICT (Exprivia); Mechanics (Isotta Fraschini Motori, MERMEC); Publishing (Laterza), Tourism (Nicolaus tour).
Unemployment
The unemployment rate stood at 18.8% in 2017 and was higher than the national average.[16]
| Year | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unemployment rate (in %) |
12.6% | 11.1% | 11.6% | 12.6% | 13.5% | 13.2% | 15.7% | 19.7% | 21.5% | 19.7% | 19.4% | 18.8% | 16% |
Olive cultivars
There are an estimated 50 to 60 million olive trees in Apulia, and the region accounts for 40% of Italy's olive oil production. There are four specific Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) covering the whole region.[17] Olive varieties include: Baresane, Biancolilla, Brandofino (Castiglione), Buscionetto (Biancolilla), Carolea, Cellina di Nardò, Cerasuola (Ogliara), Cerignola (Bella di Cerignola), Cima di Bitonto, Cima di Mola, Coratina,[18] also grown in Corning, CA., a 2018 Gold Medal New York International Olive Oil Competition (NYIOOC) winner,[19] Frantoio, Garganica, La Minuta, Leccino, Moresca, Nocellara Etnea, Nocellara Messinese, Ogliarola, Ogliarola Barese, Ogliara Messinese, Ottobratica, Peranzana that is produced as "Certified Ultra-Premium Extra Virgin Olive Oil",[20] Rotondella, Santagatese, Saracena, Tonda Iblea, and Verdello (subspecies of San Benedetto).[21][22]
Xylella fastidiosa disease
The olive oil industry in Apulia is under threat from the pathogen Xylella fastidiosa, a disease which inhibits the uptake of water and nutrients by the trees. The south-eastern part of the region is at the centre of the epidemic.
Transport
The region has a good network of roads, but the railway network is less comprehensive, particularly in the south.[13] The region is crossed northwest to southeast by the A14 highway (Bologna–Taranto), which connects the region capital, Bari, to Taranto, the second most populous city in the region. The A14 also connects Foggia and points further north along the Adriatic coast to Pescara, Ancona, Rimini and eventually, Bologna. The only other highway in the region is the A16 (Napoli–Canosa), which crosses the Italian peninsula east–west and links the region with Napoli.
There are two international airports, Karol Wojtyla Airport in Bari (IATA: BRI) and Brindisi Airport (IATA: BDS), which serves as the principal logistical hub for the United Nations Global Service Center headquartered in Brindisi. With the approval of a redevelopment project in 2018, the Grottaglie Airfield (IATA: TAR) will host a spaceport for the Italian Space Agency and Virgin Galactic.
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1861 | 1,335,000 | — |
| 1871 | 1,440,000 | +7.9% |
| 1881 | 1,609,000 | +11.7% |
| 1901 | 1,987,000 | +23.5% |
| 1911 | 2,195,000 | +10.5% |
| 1921 | 2,365,000 | +7.7% |
| 1931 | 2,508,000 | +6.0% |
| 1936 | 2,642,000 | +5.3% |
| 1951 | 3,220,000 | +21.9% |
| 1961 | 3,421,000 | +6.2% |
| 1971 | 3,583,000 | +4.7% |
| 1981 | 3,872,000 | +8.1% |
| 1991 | 4,032,000 | +4.1% |
| 2001 | 4,021,000 | −0.3% |
| 2011 | 4,091,000 | +1.7% |
| 2017 | 4,063,888 | −0.7% |
| Source: ISTAT 2001 | ||
Emigration from the region's depressed areas to northern Italy and the rest of Europe was very intense in the years between 1956 and 1971. Subsequently, the trend declined, as economic conditions improved, to the point where there was net immigration in the years between 1982 and 1985. Since 1986 the stagnation in employment has led to a new inversion of the trend, caused by a decrease in immigration.[23]
Government and politics
Since 1 June 2015, former judge and mayor of Bari Michele Emiliano of the Democratic Party has served as President of the Apulian region.[24][25]
Culture
Cuisine
Cuisine plays an important role throughout Apulia. The key locally produced ingredients used there include olive oil, artichokes, tomatoes, aubergine, asparagus, and mushrooms.[26] In summer it is very common to use also the carosello, a variety of muskmelon which is often consumed in an immature state. Several PDO and PGI products are made in Apulia; among can be found some types of cheese like the Canestrato Pugliese PDO and Burrata di Andria PGI, of olive oil like the Collina di Brindisi PDO, Dauno PDO, Terra d'Otranto PDO, Terre Tarentine PDO and Terra di Bari PDO, some fruits and vegetables like the Arancia del Gargano PGI, Carciofo Brindisino PGI, Cipolla bianca di Margherita PGI, Clementine del Golfo di Taranto PGI, La Bella della Daunia PDO, Limone femminello del Gargano PGI, Patata novella di Galatina PGI and Uva di Puglia PGI. Moreover, also a type of bread, Pane di Altamura PDO and a legume called Lenticchia di Altamura PGI are present in the list.
Language
As with the other regions of Italy, the national language (since 1861) is Italian. However, because of its long and varied history, other historical languages have been used in this region for centuries. In isolated pockets of the southern part of Salento, a dialect of Greek called Griko is still spoken by a few thousand people.[27] In addition, rare dialects of the Franco-Provençal language called Faetar and the closely related Cellese are spoken by a dwindling number of individuals in the mountain villages of Faeto and Celle di San Vito, in the Province of Foggia.[28] The Arbëreshë dialect of the Albanian language has been spoken by a small community since refugees settled there in the 15th century.[29]
See also
Notes
-
Also:
Neapolitan:
Sicilian:
- Salentino: Puia [ˈpuːja]
References
- "Regional gross domestic product by NUTS 2 regions - million". Eurostat. Archived from the original on 4 November 2013. Retrieved 8 September 2013.
- "Regional GDP per capita ranged from 31% to 626% of the EU average in 2017" (Press release). ec.europa.eu. Archived from the original on 2 September 2019. Retrieved 2 September 2019.
- "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Archived from the original on 23 September 2018. Retrieved 13 September 2018.
- "Introducing Puglia". Lonely Planet. Archived from the original on 1 July 2017. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- "Holiday guide to Puglia, southern Italy: the best towns, restaurants and hotels". The Guardian. Guardian Media Group. 4 July 2015. Archived from the original on 16 November 2016. Retrieved 15 November 2016.
- Elizabeth A. Fisher, The Mycenaeans and Apulia. An Examination of Aegean Bronze Age Contacts with Apulia in Eastern Magna Grecia, Astrom, 1998
- "Italy: Puglia". Rough Guides. Archived from the original on 12 December 2013. Retrieved 8 December 2013.
- Heinz Götze, Castel Del Monte: Geometric Marvel of the Middle Ages (1998), p. 89
- Asaolu, Richard Oluseyi (n.d.). Slavery:Abolition. Mainz: Pedia. p. 50. Retrieved 3 June 2017.
- Dursteler, Eric R., ed. (2013). A Companion to Venetian History, 1400-1797. Leiden: Koninklejke. pp. 142–43. ISBN 978-9004252516. Retrieved 3 June 2017.CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
- David Gilmour, The Pursuit of Italy: A History of a Land, Its Regions and their Peoples (2012), p. 24
- "Eurostat". Greenreport. Archived from the original on 24 April 2014. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- "Puglia - Economy". Portrait of the Regions. Eurostat. March 2004. Archived from the original on 21 August 2009. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- Massimo Monteduro, Pierangelo Buongiorno, Saverio Di Benedetto, Law and Agroecology: A Transdisciplinary Dialogue (2015), p. 176
- Amílcar Soares, Maria João Pereira, Roussos Dimitrakopoulos! geoENV VI – Geostatistics for Environmental Application (2008), p. 191: "The approach highlighted the widespread degradation of water resources in the Apulian groundwater. ... Above all the rapid socio-economic growth over the last decades has caused severe stress to the Apulian hydrogeological system."
- "Regional Unemployment by NUTS2 Region". Eurostat. Archived from the original on 5 November 2018.
- PDO status Archived 6 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine- Retrieved 6 July 2018
- Coratina olive Archived 6 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine- Retrieved 5 July 2019
- Coratina olives in Ca. Archived 6 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine- Retrieved 5 July 2018
- Peranzana olive oil- Retrieved 5 July 2018
- Apulia region cultivars Archived 6 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine- Retrieved 20180-7-05
- Puglia olive cultivars Archived 6 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine- Retrieved 5 July 2018
- "Eurostat". c.europa.eu. Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved 22 April 2010.
- "Scheda Personale". Sito web Istituzionale della Regione Puglia (in Italian). Archived from the original on 5 September 2015. Retrieved 17 October 2015.
- "BIOGRAFIA" (PDF). CompletaMente.org (in Italian). Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 5 September 2015.
- Around Italy: A look at Apulia the cuisine Archived 1 October 2016 at the Wayback Machine at sacla.se, accessed 22 July 2016
- "Ethnologue report for language code:ell". Ethnologue.com. Archived from the original on 28 May 2010. Retrieved 22 April 2010.
- Nagy, Naomi (2011). "A Multilingual Corpus to Explore Variation in Language Contact Situations" (PDF). Rassegna Italiana di Linguistica Applicata. 43 (1–2): 3. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 February 2017. Retrieved 3 February 2017.
- "Ethnologue report for language code:aae". Ethnologue.com. Archived from the original on 2 October 2012. Retrieved 13 July 2016.
Further reading
See also: Bibliography of the history of Apulia (in Italian)
- Desmond Seward, An Armchair Traveller's History of Apulia (Haus Publishing, 2013)
- Stefania Mola, Apulia: the Cathedrals (Adda, 2008)
- Francesco Carofiglio, Apulia, a Tourist's Guide to the Culture of Apulia (1988)
- Susanna Gelmetti, Italian Country Cooking: Recipes from Umbria & Apulia (1996), ISBN 1872803229
- Apulia: A Film Tourism Guide (Laterza, 2009, 246 pp)
- Tessa Garton, Early Romanesque Sculpture in Apulia (Courtauld Institute, 1984)
- "Apulia", Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.), New York, 1910, OCLC 14782424
- Roy Domenico (2002). "Apulia". Regions of Italy: a Reference Guide to History and Culture. Greenwood. ISBN 0313307334.
External links
![]()
![]()
- Official website (in Italian)
- Accademia Apulia (in Italian)
- Environmental League Puglia (in Italian)