Provinces of Indonesia
The provinces of Indonesia (provinsi) are the 34 largest subdivisions of the country and the highest tier of the local government (formerly called first-level region provinces or provinsi daerah tingkat I). Provinces are further divided into regencies and cities (formerly called second-level regions or kabupaten/kotamadya daerah tingkat II), which are in turn subdivided into districts (kecamatan).
| Provinces of Indonesia | |
|---|---|
| Category | Province |
| Location | Indonesia |
| Number | 34 provinces |
| Populations | Smallest: 622,350 (North Kalimantan) Largest: 43,053,732 (West Java) |
| Areas | Smallest: 664 km2 (256 sq mi) (Jakarta) Largest: 319,036 km2 (123,180 sq mi) (Papua) |
| Government | Governor |
| Subdivisions | Regencies and cities |
| This article is part of a series on |
| Subdivisions of Indonesia |
|---|
| Level 1 |
|
| Level 2 |
| (Full list; GDP; population) |
| Level 3 |
|
| Level 4 |
|
Background
Each province has a local government headed by a governor, and a legislative body. The governor and members of local representative bodies are elected by popular vote for five-year terms.
Current provinces
Indonesia has 34 provinces. Five provinces have special status:

.svg.png)


.svg.png)
The provinces are officially grouped into seven geographical units.[1]
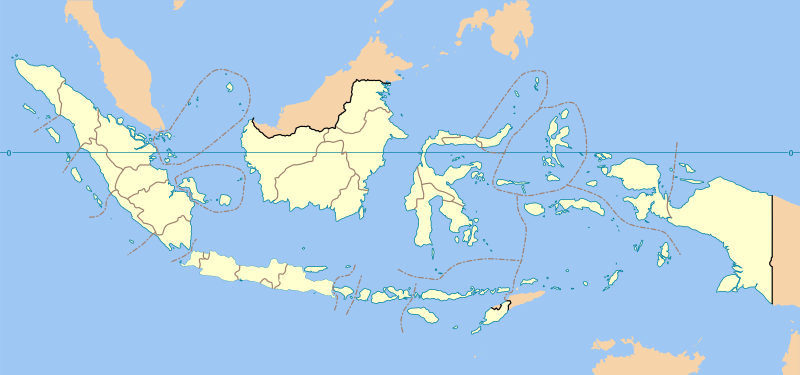
Table of provinces
| Arms | Province | Indonesian acronym | ISO[4] | Capital | Population (2015)[5] | Area (km²) | Population density per km² (2010) |
Geographical unit | Number of cities (kota) and regencies (kabupaten) |
Number of cities (kota) |
Number of regencies (kabupaten) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Aceh | Aceh | ID-AC | Banda Aceh | 4,993,385 | 57,956 | 77 | Sumatra | 23 | 5 | 18 |
 | Bali | Bali | ID-BA | Denpasar | 4,148,588 | 5,780 | 621 | Lesser Sunda Islands | 9 | 1 | 8 |
 | Bangka Belitung Islands | Babel | ID-BB | Pangkalpinang | 1,370,331 | 16,424 | 64 | Sumatra | 7 | 1 | 6 |
 | Banten | Banten | ID-BT | Serang | 11,934,373 | 9,662 | 909 | Java | 8 | 4 | 4 |
 | Bengkulu | Bengkulu | ID-BE | Bengkulu | 1,872,136 | 19,919 | 84 | Sumatra | 10 | 1 | 9 |
 | Central Java | Jateng | ID-JT | Semarang | 33,753,023 | 40,800 | 894 | Java | 35 | 6 | 29 |
 | Central Kalimantan | Kalteng | ID-KT | Palangka Raya | 2,490,178 | 153,564 | 14 | Kalimantan | 14 | 1 | 13 |
 | Central Sulawesi | Sulteng | ID-ST | Palu | 2,872,857 | 61,841 | 41 | Sulawesi | 13 | 1 | 12 |
 | East Java | Jatim | ID-JI | Surabaya | 38,828,061 | 47,799 | 828 | Java | 38 | 9 | 29 |
 | East Kalimantan[6] | Kaltim | ID-KI | Samarinda | 3,422,676 | 139,462 | 22 | Kalimantan | 10 | 3 | 7 |
 | East Nusa Tenggara | NTT | ID-NT | Kupang | 5,112,760 | 48,718 | 92 | Lesser Sunda Islands | 22 | 1 | 21 |
 | Gorontalo | Gorontalo | ID-GO | Gorontalo | 1,131,670 | 11,257 | 94 | Sulawesi | 6 | 1 | 5 |
 | Special Capital Region of Jakarta | DKI | ID-JK | Jakarta[lower-alpha 1] | 10,154,134 | 664 | 12,786 | Java | 6 | 5 | 1 |
 | Jambi | Jambi | ID-JA | Jambi | 3,397,164 | 50,058 | 57 | Sumatra | 11 | 2 | 9 |
 | Lampung | Lampung | ID-LA | Bandar Lampung | 8,109,601 | 34,623 | 226 | Sumatra | 15 | 2 | 13 |
 | Maluku | Maluku | ID-MA | Ambon | 1,683,856 | 46,914 | 32 | Maluku Islands | 11 | 2 | 9 |
 | North Kalimantan | Kaltara | ID-KU | Tanjung Selor | 639,639 | 72,275 | 10 | Kalimantan | 5 | 1 | 4 |
 | North Maluku | Malut | ID-MU | Sofifi | 1,160,275 | 31,982 | 31 | Maluku Islands | 10 | 2 | 8 |
 | North Sulawesi | Sulut | ID-SA | Manado | 2,409,921 | 13,851 | 162 | Sulawesi | 15 | 4 | 11 |
 | North Sumatra | Sumut | ID-SU | Medan | 13,923,262 | 72,981 | 188 | Sumatra | 33 | 8 | 25 |
 | Papua | Papua | ID-PA | Jayapura | 3,143,088 | 319,036 | 8 | Western New Guinea | 29 | 1 | 28 |
 | Riau | Riau | ID-RI | Pekanbaru | 6,330,941 | 87,023 | 52 | Sumatra | 12 | 2 | 10 |
 | Riau Islands | Kepri | ID-KR | Tanjungpinang | 1,968,313 | 8,201 | 208 | Sumatra | 7 | 2 | |
 | Southeast Sulawesi | Sultra | ID-SG | Kendari | 2,495,248 | 38,067 | 51 | Sulawesi | 17 | 2 | 15 |
 | South Kalimantan | Kalsel | ID-KS | Banjarmasin | 3,984,315 | 38,744 | 96 | Kalimantan | 13 | 2 | 11 |
 | South Sulawesi | Sulsel | ID-SN | Makassar | 8,512,608 | 46,717 | 151 | Sulawesi | 24 | 3 | 21 |
 | South Sumatra | Sumsel | ID-SS | Palembang | 8,043,042 | 91,592 | 86 | Sumatra | 17 | 4 | 13 |
 | West Java | Jabar | ID-JB | Bandung | 46,668,214 | 35,377 | 1,176 | Java | 27 | 9 | 18 |
 | West Kalimantan | Kalbar | ID-KB | Pontianak | 4,783,209 | 147,307 | 30 | Kalimantan | 14 | 2 | 12 |
 | West Nusa Tenggara | NTB | ID-NB | Mataram | 4,830,118 | 18,572 | 234 | Lesser Sunda Islands | 10 | 2 | 8 |
 | West Papua | Pabar | ID-PB[7] | Manokwari | 868,819 | 97,024 | 8 | Western New Guinea | 13 | 1 | 12 |
 | West Sulawesi | Sulbar | ID-SR | Mamuju | 1,279,994 | 16,787 | 73 | Sulawesi | 6 | 0 | 6 |
 | West Sumatra | Sumbar | ID-SB | Padang | 5,190,577 | 42,012 | 110 | Sumatra | 19 | 7 | 12 |
 | Special Region of Yogyakarta | DIY | ID-YO | Yogyakarta | 3,675,768 | 3,133 | 1,138 | Java | 5 | 1 | 4 |
Former provinces
.svg.png)
.svg.png)

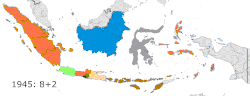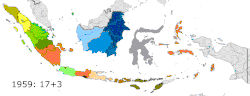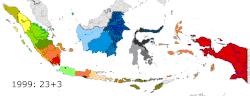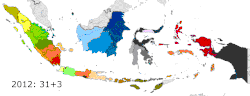
Upon the independence of Indonesia, eight provinces were established: West Java, Central Java, East Java, and Maluku still exist as of today despite later divisions, while Sumatra, Kalimantan, Sulawesi, and Lesser Sunda were fully liquidated. The province of Central Sumatra existed from 1948 to 1957, while East Timor was annexed as a province from 1976 until its power transfer to UNTAET in 1999 prior to its independence as a country in 2002.
| Province | Capital | Period | Successor(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sumatra[8] | Bukittinggi / Medan | 1945–1948 | Central Sumatra North Sumatra South Sumatra |
| Kalimantan[9] | Banjarmasin | 1945–1956 | East Kalimantan South Kalimantan West Kalimantan |
| Nusa Tenggara (formerly Lesser Sunda (Sunda Kecil))[10] |
Singaraja | 1945–1958 | Bali East Nusa Tenggara West Nusa Tenggara |
| Sulawesi[11] | Makassar / Manado | 1945–1960 | North-Central Sulawesi South-Southeast Sulawesi |
| Central Sumatra (Sumatera Tengah)[8][12] |
Bukittinggi | 1948–1957 | Jambi Riau West Sumatra |
| North-Central Sulawesi (Sulawesi Utara-Tengah)[13] |
Manado | 1960–1964 | North Sulawesi Central Sulawesi |
| South-Southeast Sulawesi (Sulawesi Selatan-Tenggara)[13] |
Makassar | 1960–1964 | South Sulawesi Southeast Sulawesi |
| East Timor (Timor Timur)[14] |
Dili | 1976–1999 | Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste |
New provinces made from currently-existing provinces
.svg.png)
.svg.png)
| New province (current name) |
Year | New province (then name) |
Province of origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aceh | 1956 | Aceh | North Sumatra |
| Central Kalimantan | 1958 | Central Kalimantan | South Kalimantan |
| Lampung | 1964 | Lampung | South Sumatra |
| Central Sulawesi | 1964 | Central Sulawesi | North Sulawesi |
| Southeast Sulawesi | 1964 | Southeast Sulawesi | South Sulawesi |
| Bengkulu | 1967 | Bengkulu | South Sumatra |
| West Papua | 1999 | West Irian Jaya | Irian Jaya |
| North Maluku | 1999 | North Maluku | Maluku |
| Banten | 2000 | Banten | West Java |
| Bangka Belitung Islands | 2000 | Bangka Belitung Islands | South Sumatra |
| Gorontalo | 2000 | Gorontalo | North Sulawesi |
| Riau Islands | 2002 | Riau Islands | Riau |
| West Sulawesi | 2004 | West Sulawesi | South Sulawesi |
| North Kalimantan | 2012 | North Kalimantan | East Kalimantan |
Provinces renaming
| Year | Old name (Indonesian) |
Old name (English) |
New name (Indonesian) |
New name (English) |
Current name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1959 | Aceh | Aceh | Daerah Istimewa Aceh | Aceh Special Region | Aceh |
| 1973 | Irian Barat | West Irian | Irian Jaya | Irian Jaya | Papua |
| 1990 | Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta Raya | Greater Jakarta Special Capital Region | Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta | Jakarta Special Capital Region | Jakarta Special Capital Region |
| 2001 | Daerah Istimewa Aceh | Aceh Special Region | Nanggroë Aceh Darussalam | State of Aceh, the Abode of Peace | Aceh |
| 2002 | Irian Jaya | Irian Jaya | Papua | Papua | Papua |
| 2007 | Irian Jaya Barat | West Irian Jaya | Papua Barat | West Papua | West Papua |
| 2009 | Nanggroë Aceh Darussalam | State of Aceh, the Abode of Peace | Aceh | Aceh | Aceh |
See also
- List of Indonesian provinces by Human Development Index
- List of Indonesian provinces by GRP per capita
- List of Indonesian floral emblems
- List of Indonesian animal emblems
- Armorial of Indonesia
General:
Notes
- Jakarta is a provincial-level city
References
- ISO 3166-2:ID
- "Data Wilayah – Kementerian Dalam Negeri – Republik Indonesia". Archived from the original on 2012-02-22. Retrieved 2011-02-16.
- Buku Induk—Kode dan Data Wilayah Administrasi Pemerintahan per Provinsi, Kabupaten/Kota dan Kecamatan Seluruh Indonesia (PDF) (in Indonesian), Kementerian Dalam Negeri [Ministry of Home Affairs], archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-11-19
- ISO 3166-2:ID (ISO 3166-2 codes for the provinces of Indonesia)
- Badan Pusat Statistik/Statistics Indonesia (November 2015). Hasil Survei Penduduk Antas Sensus 2015/Result of the 2015 Intercensal Population Census (PDF) (in Indonesian and English). ISBN 978-979-064-912-5. Retrieved 10 June 2018.CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link)
- Figures adjusted to take account of the separation of Tarakan city and four regencies, as confirmed by Badan Pusat Statistik, to form the new province of North Kalimantan, listed separately in this table.
- West Papua was created from the western portion of Papua province in February 2003, initially under the name of Irian Jaya Barat, and was renamed Papua Barat (West Papua) on 7 February 2007. The split remains controversial. In November 2004, the Constitutional Court of Indonesia ruled that the split violated Papua's autonomy laws. However, since the western province had already been created, it should remain separate from Papua. The ruling also aborted the creation of another proposed province, Central Irian Jaya, because the split was not yet completed. As of June 2008, an ISO 3166-2 code has not yet been published for West Papua. If one were to follow precedent, it would be ID-PB. Note: ISO 3166-2 Newsletter II-1 (corrected 2010-02-19) page 18-19 confirms this as ID-PB. See http://www.iso.org/iso/iso_3166-2_newsletter_ii-1_corrected_2010-02-19.pdf . The code ID-IJ now refers to the larger geographical region including Papua and West Papua.
- "Peraturan Pemerintah Nomor 21 Tahun 1950" [Government Regulation Number 21 of 1950] (PDF), hukum.unsrat.ac.id (in Indonesian), archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-12-11, retrieved 1 May 2020
- "Undang-Undang Nomor 25 Tahun 1956" [Act Number 25 of 1956], hukumonline.com (in Indonesian), retrieved 14 November 2018
- "Undang-Undang Nomor 64 Tahun 1958" [Act Number 64 of 1958], hukumonline.com (in Indonesian), Republic of Indonesia, retrieved 14 November 2018
- "Peraturan Pemerintah Pengganti Undang-Undang Nomor 47 Tahun 1960" [Government Regulation in Lieu of Law Number 47 of 1960], hukumonline.com (in Indonesian), retrieved 14 November 2018
- "Undang-Undang Darurat Nomor 19 Tahun 1957" [Emergency Act Number 19 Year 1957], hukumonline.com (in Indonesian), retrieved 14 November 2018
- "Undang-Undang Nomor 13 Tahun 1964" [Act Number 13 of 1964]. hukumonline.com (in Indonesian). Retrieved 29 January 2020.
- Undang-Undang Republik Indonesia Nomor 7 Tahun 1976 [Act of the Republic of Indonesia Number 7 of 1976] (PDF) (in Indonesian), archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-11-14, retrieved 2018-11-14
External links
- Daftar 34 Provinsi Di Indonesia (in Indonesian)
- Map at Indonesian Wikipedia

