Pacific Islands Forum
The Pacific Islands Forum (PIF) is an inter-governmental organization that aims to enhance cooperation between countries and territories of the Pacific Ocean, including formation of a trade bloc and regional peacekeeping operations. It was founded in 1971 as the South Pacific Forum (SPF), and changed its name in 1999 to "Pacific Islands Forum", so as to be more inclusive of the Forum's Oceania-spanning membership of both north and south Pacific island countries, including Australia. It is a United Nations General Assembly observer.[3]
Pacific Islands Forum | |
|---|---|
 Flag
 Logo
| |
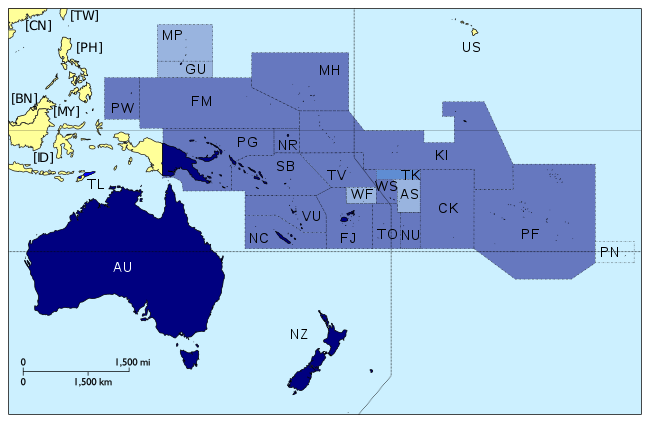 Membership (dark blue) of the Pacific Islands Forum. | |
| Seat of Secretariat | |
| Membership | |
| Leaders | |
• Forum Chair | Annual rotation |
| Establishment | |
• as South Pacific Forum | 1971 |
• renamed Pacific Islands Forum | 1999 |
| Area | |
• Total | 8,509,959[1] km2 (3,285,714 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2018 estimate | 38.759 million[2] |
• Density | 4/km2 (10.4/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2012 estimate |
• Total | US$ 1.689 trilliona |
• Per capita | US$ 40,000 |
| HDI (2007–2008) | high · 97tha |
| Currency | |
| Time zone | |
Website ForumSec.org | |
| |
The mission of the Pacific Islands Forum is "to work in support of Forum member governments, to enhance the economic and social well-being of the people of the South Pacific by fostering cooperation between governments and between international agencies, and by representing the interests of Forum members in ways agreed by the Forum". Its decisions are implemented by the Pacific Islands Forum Secretariat (PIFS), which grew out of the South Pacific Bureau for Economic Co-operation (SPEC). As well as its role in harmonising regional positions on various political and policy issues, the Forum Secretariat has technical programmes in economic development, transport and trade. The Pacific Islands Forum Secretary General is the permanent Chairman of the Council of Regional Organisations in the Pacific (CROP).[4]
Australia and New Zealand are generally larger and wealthier than the other countries that make up the rest of the Forum, with Australia's population being around twice that of the other 17 members combined and its economy is more than five times larger. They are significant aid donors and big markets for exports from the other island countries. Military and police forces as well as civilian personnel of Forum states, chiefly Australia and New Zealand, have recently been part of regional peacekeeping and stabilization operations in other states, notably in Solomon Islands (2003–) and Nauru (2004–2009), under Forum auspices. Such regional efforts are mandated by the Biketawa Declaration, which was adopted at the 31st Summit of Pacific Islands Forum Leaders, held at Kiribati in October 2000. The 50th meeting of the Forum took place in Tuvalu in August 2019.
The larger Pacific Community functions mainly to promote international development by providing technical and scientific advice and funding development projects, and does not consider security issues or function as a trade bloc.
History
.jpg)
From 5–7 August 1971, the first meeting of the South Pacific Forum was initiated by New Zealand and held in Wellington, New Zealand, with attendants of the following seven countries: the President of Nauru, the Prime Ministers of Western Samoa, Tonga and Fiji, the Premier of the Cook Islands, the Australian Minister for External Territories, and the Prime Minister of New Zealand. It was a private and informal discussion of a wide range of issues of common concern, concentrating on matters directly affecting the daily lives of the people of the islands of the South Pacific, devoting particular attention to trade, shipping, tourism, and education. Afterwards this meeting was held annually in member countries and areas in turn. In 1999, the 30th South Pacific Forum decided to be renamed the organization to the Pacific Islands Forum, to better account for areas outside the south Pacific. Immediately after the forum's annual meeting at head of government level, the Post Forum Dialogue (PFD) is conducted at ministerial level with PFD development partners around the world.[5]
Suspension of Fiji
In August 2008, the Forum threatened to suspend Fiji if the latter did not commit to holding a general election by March 2009.[6] Subsequently, at a special leaders' meeting of the Pacific Islands Forum held in Papua New Guinea in January 2009, Forum leaders set a deadline of 1 May, by which date Fiji must set a date for elections before the end of the year. Fiji rejected the deadline. Consequently, on 2 May, Fiji was suspended indefinitely from participation in the Forum with immediate effect.[7][8] Toke Talagi, the Chair of the Pacific Islands Forum and Premier of Niue, described the suspension as "also particularly timely given the recent disturbing deterioration of the political, legal and human rights situation in Fiji since April 10, 2009".[9] He described Fiji as “a regime which displays such a total disregard for basic human rights, democracy and freedom” which he believed contravened membership of the Pacific Islands Forum.[9] Talagi emphasised, however, that Fiji had not been expelled and that it would be welcomed back into the fold when it returned to the path of "constitutional democracy, through free and fair elections".[9]
The 2009 suspension of Fiji marked the first time that a country had been suspended from the Pacific Islands Forum in the history of the then 38-year-old organization.[10]
Following the Fijian general election of 17 September 2014, the Forum lifted the suspension of Fiji on 22 October 2014.[11]
Membership
In September 2011, the U.S. territories of American Samoa, Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands were granted observer status in the Pacific Islands Forum,[12] while in September 2016 the French territories of French Polynesia and New Caledonia were granted full membership.[13] All Pacific island nations and territories in Oceania are either members or observer states of the Pacific Islands Forum with the exception of the British Overseas Territory of the Pitcairn Islands. In addition East Timor is an observer despite usually being regarded as part of South East Asia.
|
| ||||
| Member states[14] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Associate members | Observers | |||
| Asian Development Bank | Commonwealth of Nations | WCPFC | ||
| World Bank | ||||
| For abbreviations, see ISO 3166-1. | ||||
| Dialogue partners | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Development Partner | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Statistics
| Member | Land area (km2)[18] | Population[19][20] (2018) | GDP Millions USD (2010)[21] | GDP Per Capita USD (2010) | Human Development Index (2016) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7,741,220 | 24,898,152 | 1,293,201 | 58,350 | 0.939 | |
| 236 | 17,518 | 255 | 12,579 | — | |
| 18,274 | 883,483 | 8,800 | 3,652 | 0.736 | |
| 4,167 | 277,679 | 6,081 | 22,684 | — | |
| 811 | 115,847 | 153 | 1,493 | 0.588 | |
| 181 | 58,413 | 164 | 3,124 | — | |
| 702 | 112,640 | 297 | 2,867 | 0.638 | |
| 21 | 10,670 | 62 | 6,234 | — | |
| 18,575 | 279,993 | 9,355 | 37,976 | — | |
| 268,838 | 4,743,131 | 146,584 | 33,551 | 0.915 | |
| 260 | 1,620 | — | — | — | |
| 459 | 17,907 | 186 | 9,084 | 0.788 | |
| 462,840 | 8,606,323 | 14,205 | 2,074 | 0.516 | |
| 2,831 | 196,129 | 679 | 3,651 | 0.704 | |
| 28,896 | 652,857 | 720 | 1,368 | 0.515 | |
| 12 | 1,319 | — | — | — | |
| 747 | 103,197 | 374 | 3,597 | 0.721 | |
| 26 | 11,508 | 32 | 3,239 | — | |
| 12,189 | 292,680 | 701 | 2,966 | 0.597 | |
| Total | 8,546,152 | 40,250,245 | 1,481,849 | 36,816 | 0.696 |
1 Associate member
Secretaries General
The Secretary General of the Pacific Islands Forum Secretariat is appointed to a three-year term by the leaders of the member states.[22] The Secretary General reports directly to the national leaders and the Forum Officials' Committee (FOC).[22] The Secretary General also automatically serves as the permanent chairman of the Council of Regional Organisations in the Pacific (CROP).[22]
| # | Name | Country | Took office | Left office |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Directors of the South Pacific Bureau for Economic Co-operation | ||||
| 1 | Mahe Tupouniua | November 1972 | 1980 | |
| 2 | Gabriel Gris | 1980 | 1982 (died in office) | |
| John Sheppard (acting) | 1982 | January 1983 | ||
| 3 | Mahe Tupouniua | January 1983 | January 1986 | |
| 4 | Henry Naisali | January 1986 | September 1988 | |
| Secretary General of the Pacific Islands Forum | ||||
| Henry Naisali | September 1988 | January 1992 | ||
| 5 | Ieremia Tabai | January 1992 | January 1998 | |
| 6 | Noel Levi | February 1998 | 16 May 2004 | |
| 7 | Greg Urwin | 16 May 2004 | 2 May 2008 (resigned) | |
| Feleti Teo (acting) | 2 May 2008 | 13 October 2008 | ||
| 8 | Tuiloma Neroni Slade | 13 October 2008 | 4 December 2014 | |
| 9 | Meg Taylor | 4 December 2014 | Incumbent | |
Institutions and legal framework

The Pacific Islands Forum Secretariat was established initially as a trade bureau in 1972 and later became the South Pacific Bureau for Economic Co-operation (SPEC). The name South Pacific Forum Secretariat was approved by member governments in 1988 and changed to Pacific Islands Forum Secretariat in 2000.
There are four divisions in the Pacific Islands Forum Secretariat, and each of these divisions has direct responsibility for a range of programs designed to improve the capacity of the Forum member countries and to co-ordinate action on matters of common interest:
- Development and Economic Policy
- Trade and Investment
- Political, International and Legal Affairs
- Corporate Services
The Forum Economic Ministers Meeting (FEMM) established in 1995, plays a key role in assessing regional economic developments.[24]
Pacific Island Countries Trade Agreement
The Pacific Island Countries Trade Agreement[25] (PICTA) aims to establish a free-trade area between 14 of the Pacific Islands Forum countries. As of 2013, it had been signed by 12 states:[26]
- Cook Islands
- Fiji
- Kiribati
- Micronesia
- Nauru
- Niue
- Papua New Guinea
- Samoa
- Solomon Islands
- Tonga
- Tuvalu
- Vanuatu
It has not been signed by either Palau or the Marshall Islands. All of the signing states have ratified the treaty, with the exception of Micronesia. As of March 2008, six countries had announced that domestic arrangements had been made enabling them to trade under the agreement:[26] Cook Islands, Fiji, Niue, Samoa, Solomon Islands,[27] Vanuatu.[28]
After the trade agreement goes into force, countries commit to removing tariffs on most goods by 2021. As of April 2008, The Forum Island Countries are also negotiating an Economic Partnership Agreement (EPA) with the European Union. It is important to note that the PICTA discussed here covers only the trade of goods. At the Forum Island Leaders Meeting held in Rarotonga, Cook Islands on 28 August 2012, nine members signed the Pacific Island Countries Trade Agreement Trade in Services (PICTA TIS).[29] As of April 2008, there is an ongoing negotiation to design and agree on a protocol to include trade in services and the temporary movement of natural persons (a broader concept than the GATS's Mode 4).[30]
The Office of the Chief Trade Adviser was established on 29 March 2010 to provide independent advice and support to the Pacific Forum Island Countries (FICs) in the PACER Plus trade negotiations with Australia and New Zealand.
Recent works
An “open skies” policy has been under work by a number of nations. The Pacific Islands Air Services Agreement or PIASA would allow member nations to have more access for their airlines to other member countries. To date there have been ten signatories, Cook Islands, Kiribati, Nauru, Niue, Papua New Guinea, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Tuvalu and Vanuatu, while only six have ratified the agreement. These six are Cook Islands, Nauru, Niue, Samoa, Tonga and Vanuatu.
At the 19–20 August 2008 Pacific Islands Forum meeting in Niue, the leaders discussed Pacific Plan priorities including, “fisheries, energy, trade and economic integration, climate change and transport, in addition to information and communication technology, health, education, and good governance.” Leaders also discussed the impacts of climate change and adopted the Niue Declaration on Climate Change. Restoration of democratic governance in Fiji was discussed as were consequences should the interim government fail to meet established deadlines.[31] Regional assistance to the Solomon Islands and Nauru was discussed, followed by discussion of radioactive contamination in the Marshall Islands from US government tests. Regional institutional framework issues and WTO Doha round developments were discussed, followed by discussion of country-initiatives and the Pacific Region Infrastructure Facility launched 19 August 2008 to provide up to A$200 million over four years to help improve infrastructure in Kiribati, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Tuvalu and Vanuatu.[14] The United Nations announced that it would partner with Samoa to develop an Inter-Agency Climate Change Centre to help Pacific island nations combat the impacts of climate change in the region.[32] In the 2013 forum, the Marshall Islands, supported by all other Pacific nations, claimed compensation from the United States for the nuclear tests conducted on the islands during the 1940s and 1950s.[33][34]
In the Nadi Bay declaration of 30 July 2019, the Pacific Islands Forum warned that coral atoll nations could be uninhabitable as early as 2030, expressed their deeply concern about a lack of "comprehension, ambition or commitment" from developed nations and called for an immediate reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.[35][36]
Prospects
There has been a call from within both the Australian and New Zealand business communities to extend the CER (Closer Economic Relations) to other Pacific island nations, moving towards a single market and allowing the free movement of people and goods. A Pacific Union has been theorized as the next step of the forum.
In September 2016, the Pacific Islands Association of Non-Governmental Organisations (PIANGO) regional network, encouraged member states’ leaders to include in the organisation's agenda the issue of human rights violations in West Papua.[37]
See also
- Forum Fisheries Agency
- Melanesian Spearhead Group
- Micronesian Chief Executives
- Pacific Community
- Pacific Forum Line – a regional shipping company owned by 12 Pacific Islands Forum member countries
- Pacific Games
- Pacific Islands Private Sector Organisation (PIPSO)
- Pacific Trade Invest
- Pacific Union
- Polynesian Leaders Group
- Trade bloc
References
- Corresponds to the terrestrial surface. Including the Exclusive Economic Zones of each member state, the total area is 37 894 287 km².
- https://web.archive.org/web/20170716183647/http://prism.spc.int/regional-data-and-tools/population-statistics. Archived from the original on 16 July 2017. Retrieved 14 January 2017. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - https://www.un.org/en/sections/member-states/intergovernmental-organizations/index.html
- Unattributed. "About Us". Pacific Islands Forum web site. Pacific Islands Forum. Retrieved 2008-08-23.
- The Pacific Islands Forum (Former South Pacific Forum)- Pacific Regional Order, pp 58-80, by Dave Peebles- Retrieved 2017-01-08
- "Solomon's Prime Minister says all Forum members backed suspension threat". Radio New Zealand International. 24 August 2008. Retrieved 1 November 2011.
- Statement by Forum Chair on suspension of the Fiji military regime from the Pacific Islands Forum Archived 2012-03-24 at the Wayback Machine; PIFS Press Statement 21/09, 2 May 2009
- "Chair of Pacific Islands Forum says Fiji has been suspended". Radio New Zealand International. 2 May 2009. Retrieved 1 November 2011.
- "Fiji suspended from Pacific Islands Forum". Xinhua News Agency. 2009-05-02. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- "Fiji isolated after election deadline expires". Australia Broadcasting Corporation. 2009-05-01. Retrieved 2009-05-03.
- Statement by Forum Chair on lifting the suspension of Fiji from the Pacific Islands Forum Archived 2014-10-27 at the Wayback Machine. Forumsec.org (2014-10-24). Retrieved on 2015-01-07.
- "American Samoa's Tulafono pleased to be part of Pacific family". Radio New Zealand International. 2011-09-09. Retrieved 2011-09-16.
- "Forum Communiqué, Pohnpei, Federated States of Micronesia" (PDF). Forty-Seventh Pacific Islands Forum. Pacific Islands Forum Secretariat. 2016-09-10. Retrieved 2016-09-15.
- "Forum Communiqué, Alofi, Niue" (PDF). Thirty-Ninth Pacific Islands Forum. Pacific Islands Forum Secretariat. 2008-08-20. Retrieved 2008-08-22. The Niue Declaration on Climate Change is Appendix B of this document.
- "Tokelau happy as forum associate member". Pacific News. Radio New Zealand International. 2016-09-27. Retrieved 27 September 2016.
- Unattributed (2008-08-22). "Decision on Wallis bid to join Forum (as Associate Member) deferred". Latest Pacific News Headlines. Radio New Zealand International. Retrieved 2008-08-22.
- 國際組織參與現狀
- "Land area rankings". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved May 9, 2018.
- ""World Population prospects – Population division"". population.un.org. United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved November 9, 2019.
- ""Overall total population" – World Population Prospects: The 2019 Revision" (xslx). population.un.org (custom data acquired via website). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved November 9, 2019.
- "United Nations" (2010 Data).
- Vula, Timoci (2011-09-09). "Slade back at the helm". Fiji Times. Archived from the original on 2014-08-08.CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link)
- Fisher, Mue (2011-09-09). "Forum Leaders endorse Slade's second term as SG". PRESS STATEMENT (83/11). Forum Secretariat. Archived from the original on 2014-02-25.CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link)
- Dave Peebles -Pacific Regional Order 2005 1920942467- Page 141 "As discussed in Chapter Four, in 1995 the Forum instituted a new annual meeting, the Forum Economic Ministers Meeting (FEMM). According to the Forum Secretariat, the FEMM 'plays a key role in assessing regional economic developments, ...
- "Page Not Found - Pacific Islands Forum Secretariat" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 May 2013. Retrieved 14 January 2017.
- "Page Not Found - Pacific Islands Forum Secretariat" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 May 2013. Retrieved 14 January 2017.
- "Solomon Islands Ready to Trade Under PICTA", Pacific Islands Forum Secretariat
- "Vanuatu ready to trade under PICTA", People's Daily Online
- Protocol
- Pacific Trade in Services Negotiations - First Round, Pacific Island Forum Secretariat
- Gao (2008-08-22). "Fiji ministers "angry" at Pacific Islands Forum's suspension warning". World. Xinhuanet. Retrieved 2008-08-23. "Australian Prime Minister Kevin Rudd said Pacific leaders were losing patience with Fiji's interim government. He said Australia will mobilize any resources necessary to restore democracy to Fiji."
- Unattributed (2008-08-19). "UN to Help Pacific Island States Fight Climate Change". Environment News Service. Archived from the original on 2014-08-30.CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link)
- Unattributed (2013-09-19). "Nuclear contamination still an issue for Marshall Islands". Radio Australia. Retrieved 2013-09-19.
- Unattributed (2013-09-19). "Marshall Islands minister unhappy with John Key nuclear response". Radio New Zealand International. Retrieved 2013-09-19.
- Adam Morton (2019-08-01). "Pacific leaders plead with Australia to drop plans to carry over emissions credits". The Guardian. Retrieved 2019-08-30.
- "Nadi Bay Declaration on the Climate Change Crisis in the Pacific". 2019-07-30. Retrieved 2019-08-30.
- "Geo Politics At Play Over Leader's Lack of Expressed Commitment on West Papua". PIANGO. Retrieved 30 September 2016.