Masitinib
Masitinib is a tyrosine-kinase inhibitor used in the treatment of mast cell tumours in animals, specifically dogs.[1][2] Since its introduction in November 2008 it has been distributed under the commercial name Masivet. It has been available in Europe since the second part of 2009. Masitinib has been studied for several human conditions including melanoma, multiple myeloma, gastrointestinal cancer, pancreatic cancer, Alzheimer disease, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, mastocytosis, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.[3][4]
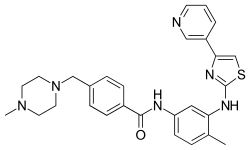 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Masivet, Kinavet |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C28H30N6OS |
| Molar mass | 498.65 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Mechanism of action
Masitinib inhibits the receptor tyrosine kinase c-Kit which is displayed by various types of tumour.[2] It also inhibits the platelet derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR), lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (Lck), focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3).[5]
References
- Hahn KA, Ogilvie G, Oglivie G, Rusk T, Devauchelle P, Leblanc A, et al. (2008). "Masitinib is safe and effective for the treatment of canine mast cell tumors". Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine. 22 (6): 1301–9. doi:10.1111/j.1939-1676.2008.0190.x. PMID 18823406.
- Information about Masivet at the European pharmacy agency website
- "Orphan designation EU/3/16/1722 for masitinib mesilate for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis". European Medicines Agency. 2018-09-17.
- Folch J, Petrov D, Ettcheto M, Pedrós I, Abad S, Beas-Zarate C, et al. (June 2015). "Masitinib for the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease". Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics. 15 (6): 587–96. doi:10.1586/14737175.2015.1045419. PMID 25961655.
- Gil da Costa RM (July 2015). "C-kit as a prognostic and therapeutic marker in canine cutaneous mast cell tumours: From laboratory to clinic". Veterinary Journal. 205 (1): 5–10. doi:10.1016/j.tvjl.2015.05.002. PMID 26021891.