Pacritinib
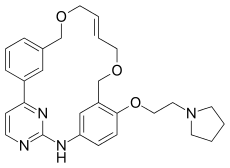
Pacritinib (INN[1]) is a macrocyclic Janus kinase inhibitor that is being developed for the treatment of myelofibrosis. It mainly inhibits Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) and Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3). The drug was in Phase III clinical trials as of 2013.[2] The drug was discovered in Singapore at the labs of S*BIO Pte Ltd. It is a potent JAK2 inhibitor with activity of IC50 = 23 nM for the JAK2WT variant and 19 nM for JAK2V617F with very good selectivity against JAK1 and JAK3 (IC50 = 1280 and 520 nM, respectively).[3][4]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | SB1518 |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C28H32N4O3 |
| Molar mass | 472.589 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
The drug was acquired by Cell Therapeutics, Inc. (CTI) and Baxter International and could effectively address an unmet medical need for patients living with myelofibrosis who face treatment-emergent thrombocytopenia on marketed JAK inhibitors.[5] When Shire Pharmaceuticals purchased Baxalta, a spin-off of Baxter Pharmaceuticals, they halted the development of the drug and ended their partnership with CTI.[6][7]
The drug was given fast-track status in 2014.[8] In 2016, the FDA placed a full clinical hold on pacritinib due to concerns about increased mortality in patients receiving the drug in the "PERSIST-2" trial.[9] The clinical hold was lifted in January 2017.[10]
References
- "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN) List 104" (PDF). WHO Drug Information. 24 (4): 386. 2010.
- "JAK-Inhibitoren: Neue Wirkstoffe für viele Indikationen". Pharmazeutische Zeitung (in German) (21). 2013.
- William AD, Lee AC, Blanchard S, Poulsen A, Teo EL, Nagaraj H, et al. (July 2011). "Discovery of the macrocycle 11-(2-pyrrolidin-1-yl-ethoxy)-14,19-dioxa-5,7,26-triaza-tetracyclo[19.3.1.1(2,6).1(8,12)]heptacosa-1(25),2(26),3,5,8,10,12(27),16,21,23-decaene (SB1518), a potent Janus kinase 2/fms-like tyrosine kinase-3 (JAK2/FLT3) inhibitor for the treatment of myelofibrosis and lymphoma". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 54 (13): 4638–58. doi:10.1021/jm200326p. PMID 21604762.
- Poulsen A, William A, Blanchard S, Lee A, Nagaraj H, Wang H, et al. (April 2012). "Structure-based design of oxygen-linked macrocyclic kinase inhibitors: discovery of SB1518 and SB1578, potent inhibitors of Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) and Fms-like tyrosine kinase-3 (FLT3)". Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design. 26 (4): 437–50. Bibcode:2012JCAMD..26..437P. doi:10.1007/s10822-012-9572-z. PMID 22527961.
- "Baxter licenses cancer drug from CTI in $172m deal". PMLiVE. 2013-11-18.
- "Pacritinib". CTI BioPharma Corp.
- "Shire ends pacritinib development deal with CTI post Baxalta merger". in-PharmaTechnologist. William Reed Business Media Ltd.
- Adams B (29 August 2016). "Struggling CTI reveals new pacritinib data, misses a primary endpoint". Fierce Biotech.
- "CTI BioPharma's (CTIC) Pacritinib Placed on Full Clinical Hold; NDA Withdrawn". StreetInsider. 10 February 2016.
- "CTI BioPharma Announces Removal Of Full Clinical Hold On Pacritinib". PR Newswire. Retrieved 18 April 2017.