Lithuanian calendar
The Lithuanian calendar is unusual among Western countries in that neither the names of the months nor the names of the weekdays are derived from Greek or Norse mythology. They were formalized after Lithuania regained independence in 1918, based on historic names, and celebrate natural phenomena; three months are named for birds, two for trees, and the remainder for seasonal activities and features. The days of the week are simply ordinal numbers.
History

Ancient Baltic cosmological schemes have been found on burial urns dated from 600-200 BC. As with other Bronze Age cultures, there were megaliths associated with the summer and winter solstices; hill enclaves with solar calendars have been discovered at Birutė Mountain near Palanga,[1] and at the Purmaliai mound near Klaipėda. A modern interpretation of the ancient solar calendar was created in 2002 at the Kretinga Museum.
Lithuanian calendar shows some similarities with Slavic calendar, and so may have roots in Proto-Balto-Slavic era.
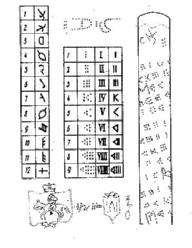
The Gediminas Sceptre, discovered in 1680, indicates that during his reign the year started in April and was divided into 12 months, varying in length from 29 to 31 days. Each month began with a new moon; the weeks were nine days long [2] The month names on this artifact are expressed in symbols, based on natural phenomena and agricultural cycles.[3] (i.e. the sidereal month was divided into three parts).[4]
The Julian calendar was used in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania; the Gregorian calendar was adopted by the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1586, a few years after its promulgation in 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII. In 1800, following Lithuania's annexation by the Russian Empire, the Julian calendar again became the norm, although a part of ethnic Lithuania left of Nemunas River (Suvalkija) retained the Gregorian calendar (see Aleksotas).[5] The Russian Revolution of 1917 re-instated the Gregorian calendar, which had been the Western European standard for over a century, in January 1918. These changes caused some confusion before their usage became familiar.[6]
Names of the months
The standardization of month names was made difficult by the fact that publication in the Lithuanian language was illegal from 1864 to 1904 (see Lithuanian press ban) and some drift in the usages occurred.
Month names are not capitalized in the Lithuanian language, reflecting their secular origins.
- Sausis (January) derives from the adjective sausas, "dry". At this point in Lithuania's winter, precipitation is usually in the form of fine, dry snowflakes, and indoor humidity is very low. Its historic names included ragas, didysis ragutis, siekis, sausinis, and pusčius.
- Vasaris (February) derives from the noun vasara, "summer". At this point, the days have begun to lengthen, there are occasional thaws, and thoughts and plans of summer reawaken. Its historic names were ragutis, kovinis, and pridėtinis.
- Kovas (March) may derive from either the noun kovas, the rook, or the noun kova, meaning battle. Rooks increase their activity at this time, building their nests and mating. The alternate derivation refers to the struggle between winter and spring. It was formerly known as morčius and karvelinis.
- Balandis (April) is derived from balandis, the dove, which at this point has begun to coo, nest and mate. Earlier names included žiedų, sultekis, gegužinis, karvelinis, biržėtas, and Velykų.
- Gegužė (May) is derived from gegužė, the cuckoo. Its call is felt to herald the final arrival of spring. Several folk beliefs are associated with this event. It was earlier known as gegužinis, sėtinis, sėmenis, žiedžius, žiedų, berželis, sultekis, milčius, and mildinis.
- Birželis (June) is derived from beržas, the birch, which flowers during this month. Birch branches are used as decorations during Pentecost. Its earlier names were visjavis, jaunius, žienpjovys, sėmenis, kirmėlių, biržis, mėšlinis, and pūdymo.
- Liepa (July) is derived from liepa, the linden tree, which flowers during this month; the flowers pleasantly scent the air, are used to make herbal teas, and attract honeybees. Older names for the month were liepinis, liepžiedis, plaukjavis, plūkis, šienpjūtis, and šienpjūvis.
- Rugpjūtis (August) is derived from rugiai, rye, and the verb pjauti, to cut. This staple Lithuanian grain is harvested then; before mechanization, this was performed with sickles. It was also known as degėsis, paukštlėkis, and pjūties.
- Rugsėjis (September) is also derived from rugiai, with the suffix sėti, to sow. The grain is sown at this time, germinates, and overwinters in the fields, resuming growth in the spring. Other names for this month were rudenio, vėsulinis, paukštlėkis, šilų, rujos, strazdinis, rudugys, viržių, sėjos, veselinis, and vesulis.
- Spalis (October) is derived from spaliai, flax hards. The plant was harvested at this time; it was and is used for fiber, food, and as a cash crop. The historic names for this month were vėlinis, spalinis, lapkristys, visagalis, and septintinis.
- Lapkritis (November) is derived from lapas, leaf, and kristi, to fall. Its older names include vėlių, vėlius, spalinis, lapkrėstys, lapkristys, grodis, gruodinis, and vilkų.
- Gruodis (December) is derived from the noun gruodas, which has no direct English equivalent; it may be described as "a frozen clod". Its older names include sausinis, vilkinis, vilkų, and Kalėdų.
Days of the week
The days of the week are named in sequence, beginning with Monday. They are pirmadienis ("first day"), antradienis, trečiadienis, ketvirtadienis, penktadienis, šeštadienis, and sekmadienis. They are not capitalized.
See also
- History of Lithuania
- Symbols of Lithuania
- Slavic calendar
- Germanic calendar
- Archaeoastronomy
References
- Lithuanian archeoastronomy Archived 2007-02-02 at the Wayback Machine
- Libertas Klima. "Zmogus ir gamta etninëje kultûroje" (PDF). Lietuvos kultūros darbuotojų tobulinimosi centras. Retrieved 2009-01-21.
- Cosmology of the ancient Balts
- Straižys, Vytautas; Klimka, Libertas. "Natural rhythms and calendar". Cosmology of the Ancient Balts. Global Lithuanian Net. Retrieved 2009-01-21.
- Timeline of Lithuanian history
- Lithuanian calendar from the 13th to 20th centuries Archived 2007-03-02 at the Wayback Machine

