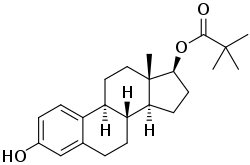
Estradiol pivalate
Estradiol pivalate, also known as estradiol trimethyl acetate (E2-TMA) and sold under the brand name Estrotate, is an estrogen medication and an estrogen ester; specifically, the C3 pivalic acid (trimethylacetic acid) ester of estradiol.[1][2][3] It was marketed as an oil solution for intramuscular injection in the 1940s and 1950s.[1][3] A combination of estradiol pivalate (1 mg/mL) and progesterone (10 mg/mL) in oil solution for intramuscular injection was available in 1949.[4][5][6]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Estrotate, Estrotate with Progesterone, Menotrope |
| Other names | E2-TMA; Estradiol trimethyl acetate; Trimethyl estradiol acetate; Estradiol 17-(2,2-dimethylpropanoate) |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intramuscular injection |
| Drug class | Estrogen; Estrogen ester |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H32O3 |
| Molar mass | 356.506 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
The duration of biological effect of estradiol pivalate in women has been studied.[7] It has been found to stimulate the vaginal epithelium in postmenopausal women, with a minimally effective dose of 0.16 mg and a maximally effective dose of 0.5 mg, both by intramuscular injection.[7] Its effect lasted for about 4 weeks at a dose of 0.16 mg and for more than 7 weeks at a dose of 3.3 mg.[7]
Menotrope was an oral tablet that contained 0.33 mg estradiol pivalate, 80 mg choline bitartrate, 0.46 mg folic acid, and 1.25 μg cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) and was used in menopausal hormone therapy.[8][9][10][11][12]

References
- Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. p. 898. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- Negwer M (1994). Organic-chemical Drugs and Their Synonyms: (an International Survey). Akademie Verlag. p. 2235. ISBN 978-3-05-500156-7.
- Wilson CO, Gisvold O (1956). Textbook of Organic Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry. Lippincott. p. 578.
A trimethylacetic acid ester of α-estradiol in sesame oil solution [...]
- "New Drugs and Instruments". Postgraduate Medicine. McGraw-Hill. 5 (5): 434–6. 1949.
Estrotate and Estrotate With Progesterone purpose: Steroid hormone therapy. composition: Estrotate is the trimethyl acetic acid ester of alpha-estradiol. indications for use: Control of menopausal syndrome, functional uterine [...]
- Howard ME (1949). Modern Drug Encyclopedia and Therapeutic Index. Drug Publications.
[...] Supply: ESTROTATE—Vials, multi dose 10 cc. Combination: ESTROTATE WITH PROGESTERONE—Each cc contains 1 mg estradiol trimethyl acetate and 10 mg progesterone. For the simultaneous administration where both natural ovarian [...]
- Tyler ET (February 1949). "Use and misuse of endocrine therapy in sterility". Journal of the American Medical Association. 139 (9): 560–4. doi:10.1001/jama.1949.02900260006002. PMID 18123546.
Both hormones may be given in one injection with a preparation which contains 10 mg. of progesterone and 1 mg. of [estradiol] trimethyl acetate per cubic centimeter.15 One cubic centimeter is given three times weekly. [...] Supplied as Estrotate® (trimethyl acetic acid ester of alpha [estradiol] in sesame oil) with progesterone.
- Brown WE, Bradbury JT (August 1949). "The use of the human vaginal smear in the assay of estrogens". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 9 (8): 725–35. doi:10.1210/jcem-9-8-725. PMID 18133489.
- Unlisted Drugs. Unlisted Drugs. 1952. p. 58.
a Menotrope C. each tablet contains: choline bitartrate, 80 mg ; Estrota te (estradiol 3 -trimethylacetate j , 0,33 mg . ; folic acid, 0.46 mg.; and vitamin B12 U.S. P., 1.25 micrograms N. Lakeside Labs , A. for menopausal therapy R.
- American Practitioner and Digest of Treatment. Lippincott. July 1952. p. 604.
- Medical Times. Romaine Pierson Pub. 1952. pp. 390, 514.
- Medical Economics. Medical Economics, Incorporated. 1952. p. 61.
- American Professional Pharmacist. American Professional Pharmacist, Incorporated. 1952. pp. 633, 780.