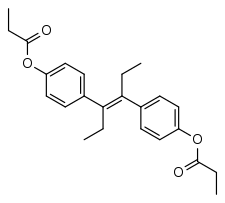
Diethylstilbestrol dipropionate
Diethylstilbestrol dipropionate (DESDP) (brand names Agostilben, Biokeral, Clinestrol, Cyclen, Estilbin, Estril, Neobenzoestrol, Orestol, Oroestrol, Ostregenin, Prostilbene, Stilbestriol DP, Stilboestrolum Dipropionicum, Stilboestrol, Synestrin, Willestrol, others), or diethylstilbestrol dipropanoate, also known as stilboestrol dipropionate (BANM), is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group that was formerly marketed widely throughout Europe.[1][2] It is an ester of diethylstilbestrol with propionic acid,[1] and is more slowly absorbed in the body than diethylstilbestrol.[3] The medication has been said to be one of the most potent estrogens known.[4]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | DESDP; Diethylstilbestrol dipropanoate; Stilboestrol dipropionate; Stilbestrol dipropionate |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
| Drug class | Nonsteroidal estrogen; Estrogen ester |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H28O4 |
| Molar mass | 380.484 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
The medication has been available in both oral and intramuscular formulations.[5]
| Estrogen | Type | Class | ETD (2–3 weeks) | EPD (2–3 weeks) | MSD (2–3 weeks) | MSD (daily) | OID (daily) | TSD (daily) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estradiol (non-micronized) | Bioidentical | Steroidal | 30 mg | ≥120–300 mg | 120 mg | 6 mg | ? | ? |
| Estradiol (micronized) | Bioidentical | Steroidal | 6–12 mg | 60–80 mg | 14–42 mg | 1–2 mg | >5 mg | >8 mg |
| Estradiol valerate | Bioidentical | Steroidal | 6–12 mg | 60–80 mg | 14–42 mg | 1–2 mg | ? | >8 mg |
| Estradiol benzoate | Bioidentical | Steroidal | ? | 60–140 mg | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| Estriol | Bioidentical | Steroidal | 20 mga | 120–150 mgb | 28–126 mg | 1–6 mg | >5 mg | ? |
| Estriol succinate | Bioidentical | Steroidal | ? | 140–150 mgb | 28–126 mg | 2–6 mg | ? | ? |
| Estrone sulfate | Bioidentical | Steroidal | 12 mg | 60 mg | 42 mg | 2 mg | ? | ? |
| Conjugated estrogens | Natural | Steroidal | 5–12 mg | 60–80 mg | 8.4–25 mg | 0.625–1.25 mg | >3.75 mg | 7.5 mg |
| Ethinylestradiol | Synthetic | Steroidal | 200 μg | 1–2 mg | 280 μg | 20–40 μg | 100 μg | 100 μg |
| Mestranol | Synthetic | Steroidal | 300 μg | 1.5–3.0 mg | 300–600 μg | 25–30 μg | >80 μg | ? |
| Quinestrol | Synthetic | Steroidal | 300 μg | 2–4 mg | 500 μg | 25–50 μg | ? | ? |
| Methylestradiol | Synthetic | Steroidal | ? | 2 mg | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| Diethylstilbestrol | Synthetic | Nonsteroidal | 2.5 mg | 20–30 mg | 11 mg | 0.5–2.0 mg | >5 mg | 3 mg |
| Diethylstilbestrol dipropionate | Synthetic | Nonsteroidal | ? | 15–30 mg | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| Dienestrol | Synthetic | Nonsteroidal | 5 mg | 30–40 mg | 42 mg | 0.5–4.0 mg | ? | ? |
| Dienestrol diacetate | Synthetic | Nonsteroidal | 3–5 mg | 30–60 mg | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| Hexestrol | Synthetic | Nonsteroidal | ? | 70–110 mg | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| Chlorotrianisene | Synthetic | Nonsteroidal | ? | >100 mg | ? | ? | >48 mg | ? |
| Methallenestril | Synthetic | Nonsteroidal | ? | 400 mg | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| Footnotes: a = Very variable, often higher. b = In divided doses, 3x/day; irregular and atypical proliferation. Sources: See template. | ||||||||
| Estrogen | Form | Major brand name(s) | EPD (14 days) | Duration | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diethylstilbestrol (DES) | Oil solution | Metestrol | 20 mg | 1 mg ≈ 2–3 days; 3 mg ≈ 3 days | |
| Diethylstilbestrol dipropionate | Oil solution | Cyren B | 12.5–15 mg | 2.5 mg ≈ 5 days | |
| Aqueous suspension | ? | 5 mg | ? mg = 21–28 days | ||
| Dimestrol (DES dimethyl ether) | Oil solution | Depot-Cyren, Depot-Oestromon, Retalon Retard | 20–40 mg | ? | |
| Fosfestrol (DES diphosphate)a | Aqueous solution | Honvan | ? | <1 day | |
| Dienestrol diacetate | Aqueous suspension | Farmacyrol-Kristallsuspension | 50 mg | ? | |
| Hexestrol dipropionate | Oil solution | Hormoestrol, Retalon Oleosum | 25 mg | ? | |
| Hexestrol diphosphatea | Aqueous solution | Cytostesin, Pharmestrin, Retalon Aquosum | ? | Very short | |
| Note: All by intramuscular injection unless otherwise noted. Footnotes: a = By intravenous injection. Sources: See template. | |||||
See also
References
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. p. 397. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 332–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- Charles Owens Wilson; Ole Gisvold (1949). Organic Chemistry in Pharmacy. J. B. Lippincott. p. 168.
- G. Dallenbach-Hellweg (6 December 2012). Histopathology of the Endometrium. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 200–. ISBN 978-3-642-96249-3.
- Heinrich Kahr (8 March 2013). Konservative Therapie der Frauenkrankheiten: Anzeigen, Grenzen und Methoden Einschliesslich der Rezeptur. Springer-Verlag. pp. 19–20. ISBN 978-3-7091-5694-0.