Sodium perchlorate
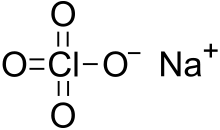
Sodium perchlorate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaClO4. It is a white crystalline, hygroscopic solid that is highly soluble in water and in alcohol. It is usually encountered as the monohydrate. The compound is noteworthy as the most water-soluble of the common perchlorate salts.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Sodium chlorate(VII) Sodium hyperchlorate Perchloric acid, sodium salt | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.647 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1502 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| NaClO4 NaClO4.H2O (monohydrate) | |
| Molar mass | 122.44 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Density | 2.4994 g/cm3 2.02 g/cm3 (monohydrate) |
| Melting point | 468 °C (874 °F; 741 K) (decomposes, anhydrous) 130 °C (monohydrate) |
| Boiling point | 482 °C (900 °F; 755 K) (decomposes, monohydrate) |
| 209.6 g/100 mL (25 °C, anhydrous) 209 g/100 mL (15 °C, monohydrate) | |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.4617 |
| Structure | |
| orthorhombic | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | ICSC 0715 |
| GHS pictograms |    |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H271, H302, H319, H373 |
| P102, P220, P305+351+338, P338 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 400 °C (752 °F; 673 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
Sodium chloride Sodium hypochlorite Sodium chlorite Sodium chlorate |
Other cations |
Lithium perchlorate Potassium perchlorate Ammonium perchlorate Caesium perchlorate |
Related compounds |
Perchloric acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Sodium perchlorate is present on the planet Mars.[1]
Selected properties
Its heat of formation is −382.75 kJ/mol, i.e. it is favorable for it to decompose into sodium chloride and dioxygen.[2] It crystallizes in the rhombic crystal system.[3]
Uses
Sodium perchlorate is the precursor to many other perchlorate salts, often taking advantage of their low solubility relative to NaClO4 (209 g/100 mL at 25 °C). Perchloric acid is made by treating NaClO4 with HCl.
Ammonium and potassium perchlorate, of interest in pyrotechnics, are prepared by double decomposition from a solution of sodium perchlorate and potassium or ammonium chlorides.
Laboratory applications
Solutions of NaClO4 are often used as an unreactive electrolyte. It is used in standard DNA extraction and hybridization reactions in molecular biology.
In medicine
Sodium perchlorate can be used to block iodine uptake before administration of iodinated contrast agents in patients with subclinical hyperthyroidism (suppressed TSH).[4]
In animal training
Sodium perchlorate may also be used as a material to train canines to detect bomb materials.[5]
Production
Sodium perchlorate is produced by anodic oxidation of sodium chlorate at an inert electrode, such as platinum.[6]
ClO3− + H2O → ClO4− + 2H+ + 2 e− (acidic medium)
ClO3− + 2 OH− → ClO4− + H2O + 2 e− (alkaline medium)
Safety
LD50 is 2 – 4 g/kg (rabbits, oral).[6]
See also
References
- https://www.letemps.ch/sciences/2015/09/28/eau-liquide-reperee-pentes-martiennes
- WebBook page for NaClO4
- Eagleson, Mary (1994). Concise Encyclopedia Chemistry. revised, illustrated. Walter de Gruyter. p. 1000. ISBN 9783110114515. Retrieved March 7, 2013.
- Becker C. [Prophylaxis and treatment of side effects due to iodinated contrast media relevant to radiological practice]. Radiologe. 2007 Sep;47(9):768-73.
- "Explosives Detection Dogs". www.special-dogs.de (in German). Retrieved 2017-07-24.
- Helmut Vogt, Jan Balej, John E. Bennett, Peter Wintzer, Saeed Akbar Sheikh, Patrizio Gallone (2002). "Chlorine Oxides and Chlorine Oxygen Acids". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a06_483.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
External links
| HClO4 | He | ||||||||||||||||
| LiClO4 | Be(ClO4)2 | B(ClO 4)− 4 B(ClO4)3 |
ROClO3 | N(ClO4)3 NH4ClO4 NOClO4 |
O | FClO4 | Ne | ||||||||||
| NaClO4 | Mg(ClO4)2 | Al(ClO4)3 | Si | P | S | ClO− 4 ClOClO3 Cl2O7 |
Ar | ||||||||||
| KClO4 | Ca(ClO4)2 | Sc(ClO4)3 | Ti(ClO4)4 | VO(ClO4)3 VO2(ClO4) |
Cr(ClO4)3 | Mn(ClO4)2 | Fe(ClO4)3 | Co(ClO4)2, Co(ClO4)3 |
Ni(ClO4)2 | Cu(ClO4)2 | Zn(ClO4)2 | Ga(ClO4)3 | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| RbClO4 | Sr(ClO4)2 | Y(ClO4)3 | Zr(ClO4)4 | Nb(ClO4)5 | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh(ClO4)3 | Pd(ClO4)2 | AgClO4 | Cd(ClO4)2 | In(ClO4)3 | Sn(ClO4)4 | Sb | TeO(ClO4)2 | I | Xe |
| CsClO4 | Ba(ClO4)2 | Hf(ClO4)4 | Ta(ClO4)5 | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg2(ClO4)2, Hg(ClO4)2 |
Tl(ClO4), Tl(ClO4)3 |
Pb(ClO4)2 | Bi(ClO4)3 | Po | At | Rn | |
| FrClO4 | Ra | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La | Ce(ClO4)x | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm(ClO4)3 | Eu(ClO4)3 | Gd(ClO4)3 | Tb(ClO4)3 | Dy(ClO4)3 | Ho(ClO4)3 | Er(ClO4)3 | Tm(ClO4)3 | Yb(ClO4)3 | Lu(ClO4)3 | |||
| Ac | Th(ClO4)4 | Pa | UO2(ClO4)2 | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
