Social Democratic Party of Finland
The Social Democratic Party of Finland (SDP, Finnish: Suomen sosialidemokraattinen puolue; Swedish: Finlands socialdemokratiska parti), founded as the Finnish Labour Party (Finnish: Suomen työväenpuolue; Swedish: Finska arbetarpartiet), shortened to the Social Democrats (Finnish: Sosiaalidemokraatit; Swedish: Socialdemokrater) and commonly known in Finnish as Demarit (Swedish: Socialdemokraterna),[7] is a social-democratic political party in Finland.[3] The party is currently the largest party in Finland's parliament with 40 seats.
Social Democratic Party of Finland Suomen sosialidemokraattinen puolue[nb 1] Finlands socialdemokratiska parti | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Abbreviation | SDP |
| Leader | Antti Rinne |
| Founded | 1899 |
| Headquarters | Saariniemenkatu 6, Helsinki |
| Newspaper | Demokraatti |
| Student wing | Social Democratic Students |
| Youth wing | Demarinuoret |
| Women's wing | Social Democratic Women in Finland[1] |
| Membership (2019) | 39,450[2] |
| Ideology | Social democracy[3] |
| Political position | Centre-left |
| European affiliation | Party of European Socialists |
| International affiliation | Progressive Alliance[4] Socialist International[5] |
| European Parliament group | Progressive Alliance of Socialists and Democrats[6] |
| Nordic affiliation | SAMAK The Social Democratic Group |
| Colours | Red |
| Parliament | 40 / 200 |
| European Parliament | 2 / 14 |
| Municipality councils | 1,696 / 8,999 |
| Website | |
| sdp | |
Founded in 1899, the SDP is Finland's oldest active political party. The SDP has a close relationship with SAK, the largest trade union confederation. It is also a member of the Progressive Alliance, the Socialist International, the Party of European Socialists and SAMAK.
Following the resignation of Antti Rinne in December 2019, Sanna Marin became the country's 67th Prime Minister. SDP formed a new coalition government on the basis of its predecessor, in effect continuing cooperation with the Centre Party, the Green League, the Left Alliance and the Swedish People's Party. Seven of the government's nineteen ministers are Social Democrats.[8]
History

The SDP was founded as the Finnish Labour Party in 1899. The name was changed to the present form in 1903. The SDP was closely associated with the Finnish Trade Union Federation (SAJ), established in 1907, with all of its members also being members of the party.[9] The party remained a chiefly extra-parliamentary movement until universal suffrage was introduced in 1906, after which the SDP's share of the votes reached 47% in the 1916 Finnish parliamentary election, when the party secured a majority in the parliament, the only time in the history of Finland when one party has had such a majority. The party lost its majority in the 1917 Finnish parliamentary election after independence from Russia and started a rebellion that escalated into the Finnish Civil War in 1918.
SDP members declared Finland a socialist republic, but they were defeated by the forces of the White Guard. The war resulted in most of the party leaders being killed, imprisoned or left to seek refuge in Soviet Russia. In addition, the process leading to the civil war and the war itself had stripped the party of its political legitimacy and respectability in the eyes of the right-wing majority. However, the political support for the party remained strong. In the 1919 Finnish parliamentary election, the party, reorganised by Väinö Tanner, received 80 of the 200 seats of the parliament. In 1918, former exiled SDP members founded the Communist Party of Finland (SKP) in Moscow. Although the SKP was banned in Finland until 1944, it was represented by front organizations, leading to the support of the Finnish working class being divided between the SDP and the SKP.
It became the life's work of Väinö Tanner to re-establish the SDP as a serious, governing party. The result was a much more patriotic SDP which leaned less to the left and was relatively isolated from its Nordic sister parties, namely the Danish Social Democrats, the Norwegian Labour Party and the Swedish Social Democratic Party. President Pehr Evind Svinhufvud's animosity kept the SDP out of government during his presidency from 1931 to 1937. With the exception of a brief period in 1926, when Tanner formed a minority government, the SDP was excluded from cabinet participation until Kyösti Kallio was elected President in 1937. During World War II, the party played a central role in a series of broad coalition cabinets, symbolising national unity forged in response to the threat of the Soviet Union in the Winter War of 1939–1940. The SDP was a member of the Labour and Socialist International from 1923 to 1940.[10]
During the first few months of the Continuation War (1941–1944), the country, the parliament and the cabinet were divided on the question of whether Finland's army should stop at the old border and thereby demonstratively refrain from any attempt of conquests. However, the country's dangerous position called for national unity and the SDP's leadership chose to refrain from any visible protests. This decision is sometimes indicated as one of the main reasons behind the post-war division between the main left-wing parties (the SKP and the SDP) and the high percentage of SKP voters in the first elections after the Continuation War. After the war, the SKP was allowed to continue working and the main feature of Finnish political life during the 1944–1949 period was the competition between the SDP and the SKP, both for voters and for the control of the labor unions. During this time, the political field was divided roughly equally between the SDP, the SKP and the Agrarian League, each party commanding some 25% of the vote. In the post-war era, the SDP adopted a line defending Finnish sovereignty and democracy in line with the Agrarian League and other bourgeois political parties, finally leading to the expulsion of the SKP from the cabinet in 1948. As a result, the Soviet Union remained more openly critical towards the SDP than the centre-right parties.

Because of the SDP's anti-communist activities, the United States Central Intelligence Agency supported the party by means of funds laundered through Nordic sister parties or through organizations that bought luxury goods such as coffee abroad, then imported and sold them for a high profit as post-war rationing served to inflate prices. In the 1956 Finnish presidential election, the SDP candidate Karl-August Fagerholm lost by only one electoral vote to Urho Kekkonen. Fagerholm would act as Prime Minister in the Fagerholm I Cabinet (1956–1957) and the Fagerholm II Cabinet (1958–1959). The latter cabinet was forced to resign due to Soviet pressure, leading to a series of cabinets led by the Agrarian League. In 1958, due to the election of Väinö Tanner as party chairman, a faction of the SDP resigned and formed the Social Democratic Union of Workers and Smallholders (TPSL) around the former SDP chairman Emil Skog. The dispute was over several issues, namely whether the party should function as an interest group and whether it should co-operate with the anti-communists and right-wingers or with president Kekkonen, the Agrarian League and the SKP. During the 1960s, the TPSL dwindled, its members returning one by one to the SDP or joining the SKP, with Skog himself returning to the SDP in 1965. In the 1970 Finnish parliamentary election, the TPSL failed to gain any seats in parliament. Only in 1966 was the SDP able to satisfy the Soviet Union about its friendly attitude towards it and could thus return to the cabinet. Since then, the SDP has been represented in most Finnish cabinets, often cooperating with the centrist-agrarian Centre Party (formerly the Agrarian League), but sometimes with the liberal-conservative National Coalition Party. The SDP was in opposition from 1991 to 1995, when the main parties in the cabinet were the Centre Party and the National Coalition Party (NCP).
The 1995 Finnish parliamentary election saw a landslide victory for the SDP, achieving their best results since World War II. The SDP rose to government from the opposition and leader Paavo Lipponen headed two consecutive cabinets from 1995 to 2003. During this time, the party adopted a pro-European stance and contributed actively to the Finnish membership in the European Union in 1995 in concert with the cabinet. In the 2003 Finnish parliamentary election, the SDP won 53 of the 200 seats, ending up a close second to the Centre Party. As a result, Lipponen became the Speaker of Parliament and the Centre Party leader Anneli Jäätteenmäki became the new Prime Minister, leading a coalition cabinet that included the SDP which got eight ministerial posts. After two months in office, Jäätteenmäki resigned due to a scandal relating to the Iraq leak and was replaced by Matti Vanhanen, another Centre Party representative, who commanded the Vanhanen I Cabinet.
In the 2007 Finnish parliamentary election, the SDP gained the third-most votes. The chairman of the then-largest Centre Party, Matti Vanhanen, became the Prime Minister and formed a coalition cabinet consisting of the Green League, the NCP and the Swedish People's Party of Finland (SFP), leaving the SDP to the opposition. SDP leader Eero Heinäluoma did not immediately resign as party chairman, but he did announce his withdrawal from running for party chairman in the following party conference. He was replaced by Jutta Urpilainen. The SDP suffered further losses in the 2008 Finnish municipal elections and the 2009 European Parliament election. In the 2011 Finnish parliamentary election, the SDP lost three more seats, ending up with 19.1 percent of the vote which corresponded to 42 seats, the party's worst-ever result. However, as the Centre Party lost even more voters, the SDP became the second-largest party in the country after the NCP, receiving only some 1,500 votes more than the Finns Party which came in third. After lengthy negotiations, a six-party coalition government, the Katainen Cabinet, was formed with the NCP and the SDP as the two main parties. SDP leader Jutta Urpilainen became the cabinet's Minister of Finance, with NCP chairman Jyrki Katainen serving as Prime Minister.
In the 2014 party conference, Urpilainen was narrowly defeated by her challenger Antti Rinne in a 257 to 243 vote.[11] Urpilainen subsequently stepped down as the Minister of Finance, passing the seat on to Rinne.[12] In the 2015 Finnish parliamentary election, the drop of support continued for the SDP. The party lost eight more seats compared to the 2011 parliamentary election, ending up with 34 seats and 16.5 percent of the vote. With the repeat of the worst-ever result, the SDP dropped to being the fourth largest political party in Finland, receiving 50,110 fewer votes than the NCP, yet 237,000 more votes than the Green League. The SDP was left in the opposition and provided extensive criticism on the actions of the Sipilä Cabinet on matters such as alcohol policy, cuts to education spending and the so-called active model.[13] On 22 June 2016, Maria Tolppanen, a Finns Party representative, joined the SDP. This increased the SDP's parliamentary seat number to 35.[14] In the 2019 Finnish parliamentary election, the SDP gained 6 seats in comparison to the 2015 parliamentary election and became the largest party in the parliament.[15] Based on the answers and initial talks with all parties, Rinne announced that he would negotiate forming a government with the Centre Party, the Green League, the Left Alliance and the SFP.[16] The negotiations were ultimately successful and the Rinne Cabinet was formally inaugurated on 6 June 2019.[17] On 3 December 2019, Rinne resigned as Prime Minister after the Center Party had expressed a lack of confidence in Rinne for his handling of the events surrounding a postal strike in Finland.[18] He was followed in the position by Sanna Marin, who was appointed as Prime Minister on 10 December 2019.[19]
Ideology
The SDP is a centre-left social-democratic party. The SDP is opposed to Finland joining NATO and is for Finland remaining in the Partnership for Peace. In the 2015 Finnish parliamentary election, 91% of SDP candidates were opposed to NATO membership.[20]
The SDP is in favor of LGBT adoption rights, the construction of nuclear power plants, the conservation of Swedish as one of Finland's two official languages and the increase of funding to public universities.[21] The party is advocating for Finland to become oil-independent by 2030.[22] The SDP has advocated for policies preventing foreigners from working in Finland.[23] In the 2015 Finnish parliamentary election, only the Finns Party had a higher share of candidates opposed to the easing of work-based immigration.[24]
The party opposed economic reforms both in the 2011 Finnish parliamentary election and in the subsequent government program negotiations.[25][26][27] The SDP maintains a close relationship with trade unions. The party has opposed social reforms that would reduce the role of earnings-related unemployment benefits. The government pays them to recipients through financial middlemen that are almost exclusively trade unions.[28] The SDP supports the separation of church and state.[29]
Voter base
The average age of an SDP member is 61.5 years.[30] Over one half of all SDP voters are active members of the workforce.
Prominent Social Democrats
| Oskari Tokoi | Chairman of the Senate in 1917 |
| Yrjö Sirola | Founder of the Communist Party of Finland |
| Väinö Tanner | Prime Minister (1926–1927) Foreign Minister (1939–1940) |
| Karl-August Fagerholm | Prime Minister (1948–1950, 1956–1957 and 1958–1959) Speaker of Parliament (1945–1948, 1950–1956, 1957–1958, 1958–1962 and 1965–1966) |
| Rafael Paasio | Prime Minister (1966–1968 and 1972) |
| Kalevi Sorsa | Prime Minister (1972–1975, 1977–1979 and 1982–1987) |
| Mauno Koivisto | Prime Minister (1968–1970 and 1979–1982) President (1982–1994) |
| Pentti Väänänen | Secretary General of the Socialist International (1983–1989) |
| Martti Ahtisaari | President (1994–2000) Nobel Peace Prize laureate (2008) |
| Erkki Tuomioja | Foreign Minister (2000–2007 and 2011–2015) |
| Paavo Lipponen | Prime Minister (1995–2003) Speaker of the Parliament (2003–2007) |
| Tarja Halonen | Foreign Minister (1995–2000) President (2000–2012) |
| Eero Heinäluoma | Speaker of the Parliament (2011–2015) |
| Jutta Urpilainen | Finance Minister and Deputy Prime Minister (2011–2014) |
| Antti Rinne | Finance Minister and Deputy Prime Minister (2014–2015) Prime Minister (2019) |
| Sanna Marin | Prime Minister (2019–present) Minister of Transport and Communications (2019) |
Leaders of the Social Democrats
| Time | Leader |
|---|---|
| 1899–1900 | Nils Robert af Ursin |
| 1900 | J. A. Salminen |
| 1900–1903 | K. F. Hellstén |
| 1903–1905 | Taavi Tainio |
| 1905–1906 | Emil Perttilä |
| 1906–1909 | Edvard Valpas-Hänninen |
| 1909–1911 | Matti Paasivuori |
| 1911–1913 | Otto Wille Kuusinen |
| 1913–1917 | Matti Paasivuori |
| 1917–1918 | Kullervo Manner |
| 1918–1926 | Väinö Tanner |
| 1926–1930 | Matti Paasivuori |
| 1930–1942 | Kaarlo Harvala |
| 1942–1944 | Väinö Salovaara |
| 1944–1946 | Onni Hiltunen |
| 1946–1957 | Emil Skog |
| 1957–1963 | Väinö Tanner |
| 1963–1975 | Rafael Paasio |
| 1975–1987 | Kalevi Sorsa |
| 1987–1991 | Pertti Paasio |
| 1991–1993 | Ulf Sundqvist |
| 1993–2005 | Paavo Lipponen |
| 2005–2008 | Eero Heinäluoma |
| 2008–2014 | Jutta Urpilainen |
| 2014–present | Antti Rinne |
Election results
Parliament of Finland
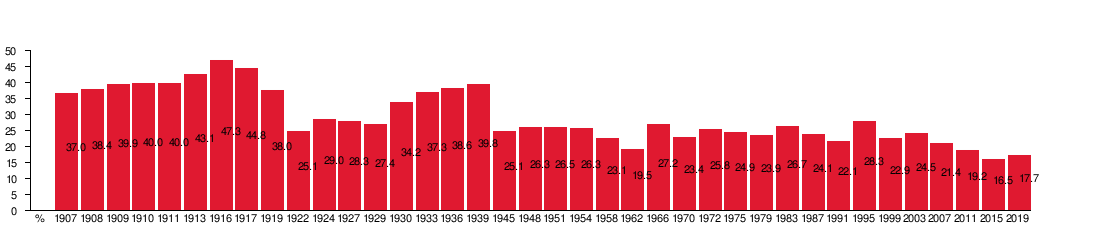
| Parliament of Finland | |||||||||
| Year | Popular vote | Number of seats | Status | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | ± pp | Rank | Seats | +/– | Rank | |||
| 1907 | 329,946 | 37.03% | 80 / 200 |
Opposition | |||||
| 1908 | 310,826 | 38.40% | 83 / 200 |
Opposition | |||||
| 1909 | 337,685 | 39.89% | 84 / 200 |
Opposition | |||||
| 1910 | 316,951 | 40.04% | 86 / 200 |
Opposition | |||||
| 1911 | 321,201 | 40.03% | 86 / 200 |
Opposition | |||||
| 1913 | 312,214 | 43.11% | 90 / 200 |
Opposition | |||||
| 1916 | 376,030 | 47.29% | 103 / 200 |
Opposition | |||||
| 1917 | 444,670 | 44.79% | 92 / 200 |
Opposition | |||||
| 1919 | 365,046 | 37.98% | 80 / 200 |
Opposition | |||||
| 1922 | 216,861 | 25.06% | 53 / 200 |
Opposition | |||||
| 1924 | 255,068 | 29.02% | 60 / 200 |
Opposition (1924–1926) | |||||
| Leading government (1926–1927) | |||||||||
| 1927 | 257,572 | 28.30% | 60 / 200 |
Opposition | |||||
| 1929 | 260,254 | 27.36% | 59 / 200 |
Opposition | |||||
| 1930 | 386,026 | 34.16% | 66 / 200 |
Opposition | |||||
| 1933 | 413,551 | 37.33% | 78 / 200 |
Opposition | |||||
| 1936 | 452,751 | 38.59% | 83 / 200 |
Opposition (1936–1937) | |||||
| Coalition government (1937–1939) | |||||||||
| 1939 | 515,980 | 39.77% | 85 / 200 |
Coalition government | |||||
| 1945 | 425,948 | 25.08% | 50 / 200 |
Coalition government | |||||
| 1948 | 494,719 | 26.32% | 54 / 200 |
Leading government (1948–1950) | |||||
| Opposition (1950–1951) | |||||||||
| Coalition government (1951) | |||||||||
| 1951 | 480,754 | 26.52% | 53 / 200 |
Coalition government (1951–1953) | |||||
| Opposition (1953–1954) | |||||||||
| Coalition government (1954) | |||||||||
| 1954 | 527,094 | 26.25% | 54 / 200 |
Coalition government (1954–1956) | |||||
| Leading government (1956–1957) | |||||||||
| Opposition (1957–1958) | |||||||||
| 1958 | 449,536 | 23.12% | 48 / 200 |
Leading government (1958–1959) | |||||
| Opposition (1959–1962) | |||||||||
| 1962 | 448,930 | 19.50% | 38 / 200 |
Opposition | |||||
| 1966 | 645,339 | 27.23% | 55 / 200 |
Leading government | |||||
| 1970 | 594,185 | 23.43% | 52 / 200 |
Leading government | |||||
| 1972 | 664,724 | 25.78% | 55 / 200 |
Leading government | |||||
| 1975 | 683,590 | 24.86% | 54 / 200 |
Coalition government (1975–1976) | |||||
| Opposition (1976–1977) | |||||||||
| Leading government (1977–1979) | |||||||||
| 1979 | 691,512 | 23.89% | 52 / 200 |
Leading government | |||||
| 1983 | 795,953 | 26.71% | 57 / 200 |
Leading government | |||||
| 1987 | 695,331 | 24.14% | 56 / 200 |
Coalition government | |||||
| 1991 | 603,080 | 22.12% | 48 / 200 |
Opposition | |||||
| 1995 | 785,637 | 28.25% | 63 / 200 |
Leading government | |||||
| 1999 | 612,963 | 22.86% | 51 / 200 |
Leading government | |||||
| 2003 | 683,223 | 24.47% | 53 / 200 |
Coalition government | |||||
| 2007 | 594,194 | 21.44% | 45 / 200 |
Opposition | |||||
| 2011 | 561,558 | 19.10% | 42 / 200 |
Coalition government | |||||
| 2015 | 490,102 | 16.51% | 34 / 200 |
Opposition | |||||
| 2019 | 546,471 | 17.73% | 40 / 200 |
Leading government | |||||
Municipal
| Municipal Councils | |||
| Year | Councillors | Votes | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1945 | 2,100 | 265,689 | |
| 1950 | 377,294 | 25.05% | |
| 1953 | 449,251 | 25.53% | |
| 1956 | 424,977 | 25.42% | |
| 1960 | 2,261 | 414,175 | 21.10% |
| 1964 | 2,543 | 530,878 | 24.75% |
| 1968 | 2,351 | 540,450 | 23.86% |
| 1972 | 2,533 | 676,387 | 27.05% |
| 1976 | 2,735 | 665,632 | 24.82% |
| 1980 | 2,820 | 699,280 | 25.50% |
| 1984 | 2,830 | 666,218 | 24.70% |
| 1988 | 2,866 | 663,692 | 25.23% |
| 1992 | 3,130 | 721,310 | 27.08% |
| 1996 | 2,742 | 583,623 | 24.55% |
| 2000 | 2,559 | 511,370 | 22.99% |
| 2004 | 2,585 | 575,822 | 24.11% |
| 2008 | 2,066 | 541,187 | 21.23% |
| 2012 | 1,729 | 487,924 | 19.57% |
| 2017 | 1,697 | 498,252 | 19.38% |
European Parliament
| Parliament of Finland | |||||||||
| Year | Popular vote | Number of seats | Status | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | ± pp | Rank | Seats | +/– | Rank | |||
| 1996 | 482,577 | 21.45% | 4 / 16 |
||||||
| 1999 | 221,836 | 17.86% | 3 / 16 |
||||||
| 2004 | 350,525 | 21.16% | 3 / 14 |
||||||
| 2009 | 292,051 | 17.54% | 2 / 13 |
||||||
| 2014 | 212,211 | 12.31% | 2 / 13 |
||||||
| 2019 | 267,342 | 14.62% | 2 / 13 |
||||||
Presidential elections
Indirect
| Year | Candidate | Popular vote | First ballot | Second ballot | Third ballot | Results | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | Seats | Rank | Votes | % | Rank | Votes | % | Rank | Votes | % | Rank | |||||
| 1919 | Väinö Tanner | 1 / 300 |
0.5 | 4th | Lost | ||||||||||||
| 1925 | Väinö Tanner | 165,091 | 26.55 | 79 / 300 |
1st | 78 / 300 |
26.0 | 1st | 2 / 300 |
0.7 | 5th | Lost | |||||
| 1931 | Väinö Tanner | 252,550 | 30.2 | 90 / 300 |
1st | 90 / 300 |
30.0 | 1st | 0 / 300 |
0.0 | 4th | Lost | |||||
| 1937 | 341,408 | 30.68 | 95 / 300 |
1st | Lost | ||||||||||||
| 1940 | Johan Helo | 4 / 300 |
1.30 | 2nd | Lost | ||||||||||||
| 1943 | |||||||||||||||||
| 1946 | |||||||||||||||||
| 1950 | 343,828 | 21.80 | 64 / 300 |
2nd | |||||||||||||
| 1956 | Karl-August Fagerholm | 442,408 | 23.33 | 72 / 300 |
2nd | 72 / 300 |
24.0 | 2nd | 114 / 300 |
38.0 | 1st | 149 / 300 |
49.7 | 2nd | Lost | ||
| 1962 | Rafael Paasio | 289,366 | 13.08 | 36 / 300 |
3rd | 37 / 300 |
12.3 | 3rd | Lost | ||||||||
| 1968 | Urho Kekkonen | 315,068 | 15.46 | 55 / 300 |
4th | 201 / 300 |
67.0 | 1st | Won | ||||||||
| 1978 | Urho Kekkonen | 569,154 | 23.25 | 74 / 300 |
1st | 259 / 300 |
86.3 | 1st | Won | ||||||||
| 1982 | Mauno Koivisto | 1,370,314 | 43.10 | 144 / 300 |
1st | 145 / 300 |
48.3 | 1st | 167 / 300 |
55.7 | 1st | Won | |||||
| 1988[nb 2] | Mauno Koivisto | 1,513,234 | 48.90 | 128 / 301 |
1st | 144 / 301 |
48.0 | 1st | 189 / 301 |
63.0 | 1st | Won | |||||
Direct
| Year | Candidate | 1st round | 2nd round | Results | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | ± pp | Rank | Votes | % | ± pp | Rank | |||
| 1994 | Martti Ahtisaari | 828,038 | 25.91 | 1,723,485 | 53.85 | Won | ||||
| 2000 | Tarja Halonen | 1,224,431 | 40.03 | 1,644,532 | 51.63 | Won | ||||
| 2006 | Tarja Halonen | 1,397,030 | 46.31 | 1,630,980 | 51.79 | Won | ||||
| 2012 | Paavo Lipponen | 205,020 | 6.70 | Lost | ||||||
| 2018 | Tuula Haatainen | 97,294 | 3.25 | Lost | ||||||
Notes
- For historical reasons, the party's name is spelled in the old-fashioned way, with a short a.
- The 1988 presidential election was partially indirect. After Koivisto had failed to get a majority of the popular vote, he was elected president in the electoral college which the voters voted for alongside the direct vote.
References
- "Member Organisations". Socialist International Women. Retrieved 14 February 2019.
- "About the SDP". Suomen sosialidemokraattinen puolue (in Finnish). 2019. Retrieved 9 May 2020.
- Nordsieck, Wolfram (2019). "Finland". Parties and Elections in Europe.
- "Parties & Organisations". Progressive Alliance. Retrieved 22 July 2019.
- "Full list of member parties and organisations". Socialist International. Retrieved 22 July 2019.
- Terry, Chris (3 March 2014). "Social Democratic Party of Finland (SDP)". The Democratic Society. Retrieved 16 March 2019.
- Icoronato, Katja (June 25, 2019). "Ministerivastuun alla ei voi enää puhua pötyä - Demarit selittelevät tätä fuulausta vielä pitkään". Uusi Suomi (in Finnish). Retrieved June 28, 2018.
- "Ministers". Valtioneuvosto. Retrieved 20 June 2019.
- Roselius, Aapo; Tepora, Tuomas (2014). The Finnish Civil War 1918: History, Memory, Legacy. Brill Academic Publishers. p. 32. ISBN 9789004243668.
- Kowalski, Werner (1985). Geschichte der sozialistischen arbeiter-internationale: 1923–1919. Berlin: Dt. Verl. d. Wissenschaften (in German).
- "Antti Rinne on SDP:n uusi puheenjohtaja". Yle. 9 May 2014. Retrieved 5 December 2019.
- "Antti Rinteestä uusi valtiovarainministeri". Helsingin Sanomat. 28 May 2014. Retrieved 5 December 2019.
- "Eduskunta hyväksyi työttömyysturvalain aktiivimalleineen – Teollisuusliitto tuomitsee ja väläyttää lakkoa". Yle Uutiset (in Finnish). Retrieved 2018-01-02.
- "Perussuomalaisten kansanedustaja loikkaa Sdp:n riveihin". Helsingin Sanomat. 22 June 2016. Retrieved 22 June 2016.
- "Parliamentary Elections 2019: Party Results". Ministry of Justice. 15 April 2019. Retrieved 16 April 2019.
- "Näin syntyi hallitusohjelmasta neuvotteleva uusi punamulta". Yle. 8 May 2019. Retrieved 5 December 2019.
- "Finland's new government: SDP, Centre dominate ministerial portfolios". yle. 3 June 2019. Retrieved 5 December 2019.
- "Finnish PM Rinne resigns". Yle. 3 December 2019. Retrieved 6 December 2019.
- "Finland's record-young PM appointed, faces confidence vote next week". Yle. 10 December 2019. Retrieved 11 December 2019.
- "Enemmistö eduskuntavaaliehdokkaista vastustaa Natoa" [A majority of parliamentary candidates oppose NATO]. Iltasanomat (in Finnish). 14 March 2015. Retrieved 9 May 2020.
- "Values A-Z". Social Democratic Party of Finland. Retrieved 3 February 2018.
- Sims, Alexandra (14 March 2020). "Finland plans to completely phase out coal by 2030". The Independent. Retrieved 9 May 2020.
- Bucken-Knapp, Gregg; Hinnfors, Jonas; Levin, Pia; Spehar, Andrea (23 June 2014). "No nordic model: Understanding differences in the labour migration policy preferences of mainstream Finnish and Swedish political parties". Comparative European Politics. 12 (6): 584–602. Retrieved 9 May 2020.
- "Centre Party split over immigration". Yle. 7 March 2015. Retrieved 9 May 2020.
- Elonen, Piia (3 April 2011). "Puolueiden mielestä talouskasvu ratkoo ongelmat" [The parties believe that economic growth will solve the problems]. Helsingin Sanomat (in Finnish). Retrieved 9 May 2020.
- Elonen, Piia (3 April 2011). "Ekonomistit teilaavat puolueiden talouspolitiikan" [Economists are asking for economic policy]. Helsingin Sanomat (in Finnish). Retrieved 9 May 2020.
- Sutinen, Teija (2 February 2013). "Sdp:n eläkelinja syntyi puolivahingossa" [The SDP's pension line was born in a semi-accident]. Helsingin Sanomat (in Finnish). Retrieved 9 May 2020.
- Soininvaara, Osmo (2010). SATA-komitea. Miksi asioista päättäminen on niin vaikeaa (in Finnish).
- "Aloite 149 kirkon ja valtion suhde harkintaan" [Initiative 149 Church-State Relationship Consideration] (in Finnish). Social Democratic Party of Finland. 2017. Retrieved 9 May 2020.
- "Tutkimus: Tällaisia puolueiden jäsenet ovat – keskusta ja SDP eläkeikäisten puolueita ja perussuomalaiset miesten". Yle Uutiset (in Finnish). Retrieved 24 November 2017.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Social Democratic Party of Finland. |

_(cropped).jpg)