Samaritan script
The Samaritan script is used by the Samaritans for religious writings, including the Samaritan Pentateuch, writings in Samaritan Hebrew, and for commentaries and translations in Samaritan Aramaic and occasionally Arabic.
|
Egyptian hieroglyphs 32 c. BCE
Hangul 1443 Thaana 18 c. CE (derived from Brahmi numerals) |
| Samaritan | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | |
| Languages | Samaritan Hebrew, Samaritan Aramaic |
Time period | 600 BCE – present |
Parent systems | |
| Direction | Right-to-left |
| ISO 15924 | Samr, 123 |
Unicode alias | Samaritan |
Unicode range | U+0800–U+083F |
Samaritan is a direct descendant of the Paleo-Hebrew alphabet, which was a variety of the Phoenician alphabet in which large parts of the Hebrew Bible were originally penned. All these scripts are believed to be descendants of the Proto-Sinaitic script. That script was used by the ancient Israelites, both Jews and Samaritans. The better-known "square script" Hebrew alphabet traditionally used by Jews is a stylized version of the Aramaic alphabet called "Assyrian writing" (כתב אשורי) which they adopted from the Persian Empire (which in turn adopted it from the Arameans). After the fall of the Persian Empire, Judaism used both scripts before settling on the Aramaic form. For a limited time thereafter, the use of paleo-Hebrew (proto-Samaritan) among Jews was retained only to write the Tetragrammaton, but soon that custom was also abandoned.
The Samaritan alphabet first became known to the Western world with the publication of a manuscript of the Samaritan Pentateuch in 1631 by Jean Morin.[2] In 1616 the traveler Pietro della Valle had purchased a copy of the text in Damascus, and this manuscript, now known as Codex B, was deposited in a Parisian library.[3]
Development
The table below shows the development of the Samaritan script. On the left are the corresponding Hebrew letters for comparison. Column I is the Paleo-Hebrew alphabet. Column X shows the modern form of the letters.
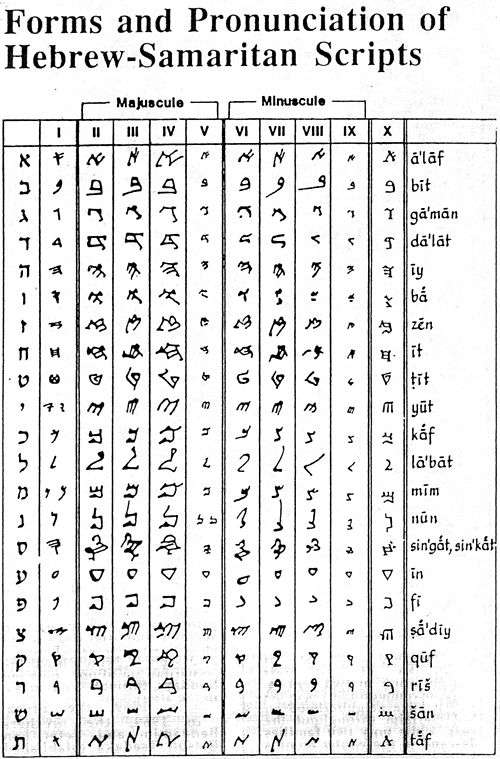
Letters

|
Consonants
|
Vowels
|
Punctuation
|
Unicode
Samaritan script was added to the Unicode Standard in October 2009 with the release of version 5.2.
The Unicode block for Samaritan is U+0800–U+083F:
| Samaritan[1][2] Official Unicode Consortium code chart (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| U+080x | ࠀ | ࠁ | ࠂ | ࠃ | ࠄ | ࠅ | ࠆ | ࠇ | ࠈ | ࠉ | ࠊ | ࠋ | ࠌ | ࠍ | ࠎ | ࠏ |
| U+081x | ࠐ | ࠑ | ࠒ | ࠓ | ࠔ | ࠕ | ࠖ | ࠗ | ࠘ | ࠙ | ࠚ | ࠛ | ࠜ | ࠝ | ࠞ | ࠟ |
| U+082x | ࠠ | ࠡ | ࠢ | ࠣ | ࠤ | ࠥ | ࠦ | ࠧ | ࠨ | ࠩ | ࠪ | ࠫ | ࠬ | ࠭ | ||
| U+083x | ࠰ | ࠱ | ࠲ | ࠳ | ࠴ | ࠵ | ࠶ | ࠷ | ࠸ | ࠹ | ࠺ | ࠻ | ࠼ | ࠽ | ࠾ | |
| Notes | ||||||||||||||||
Notes
- Himelfarb, Elizabeth J. "First Alphabet Found in Egypt", Archaeology 53, Issue 1 (Jan./Feb. 2000): 21.
- Exercitationes ecclesiasticae in utrumque Samaritanorum Pentateuchum, 1631
- Flôrenṭîn 2005, p. 1: "When the Samaritan version of the Pentateuch was revealed to the Western world early in the 17th century... [footnote: 'In 1632 the Frenchman Jean Morin published the Samaritan Pentateuch in the Parisian Biblia Polyglotta based on a manuscript that the traveler Pietro Della Valle had bought from Damascus sixteen years previously.]"
Bibliography
- Flôrenṭîn, Moše (2005). Late Samaritan Hebrew: A Linguistic Analysis of Its Different Types. Brill. ISBN 978-900413841-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
External links
- A Samaritan Bible, at the British library
- Omniglot.com - Samaritan alphabet
- Link to free Samaritan font (consonants only as of 2010)