Reservation in India
Reservation in India is a system of affirmative action that provides representation for historically and currently disadvantaged groups in Indian society in education, employment and politics. Enshrined in Articles 15 and 16 of the Indian Constitution, it allows the Indian government to set quotas to ensure any "socially and educationally backward classes of citizens" is properly represented in public life. It is intended to realize the promise of equality enshrined in the Constitution of India.
Reservation is primarily given to 3 groups: Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and Other Backward Classes, abbreviated as SC, ST, and OBC respectively. These are groups that have faced social and economic discrimination in the past and/or the present and were severely underrepresented in public life. Originally reservation was only given to SCs and STs but was later extended to OBCs in 1987 after the implementation of the Mandal Commission report. There are income caps on EWS (Economically weaker sections) and OBCs (Other backward classes) and no income limits exist for members of the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
Terms
There are several groups who get reservations in India.
- The first are the Scheduled Castes These communities were variously seen as at the bottom or "underneath" the caste system in South Asia, below even the Sudra varna. These castes have hereditary professions considered impure by South Asian society, such as sewage cleaning, tannery, or washing clothes, and were thus considered polluted by other castes. They are subject to the practice of untouchability, which takes the form of various social restrictions ranging from inability to touch other castes to inability to use the same water source or even live in the same area. Historically, and even now, they were barred from entering temples and other places of worship, and sometimes were not allowed to use the same roads. Today many of these castes, as well as following their traditional occupations, are also landless agricultural labourers. They are much more behind than all other castes on economic indicators like poverty or literacy. They make up around 220 million people, 17% of India's population .
- The next group are the Scheduled Tribes. The definition of this group varies, but the criteria for a Scheduled Tribe "indications of primitive traits, distinctive culture, geographical isolation, shyness of contact with the community at large, and backwardness." Most of these groups are considered Adivasis, and the original inhabitants while others are nomadic tribes who were notified as "criminal tribes" under British rule. They range in modes of existence from subsistence agriculturalists who have had interaction between the outside world to hunter-gatherer groups still in the jungles. They have suffered from exploitation of their land by the British. However, in the Northeast, many of the tribes are relatively better-off and interact much more with the outside world. They are around 100 million people, around 8% of the population . Examples include the Bodo, Gondi, Banjara, and Santal.
- The third main group are the Other Backward Classes. They were not originally in the reservation scheme, but during the premiership of Moraji Desai, the Mandal Commission studied all the communities in India to find what castes were "backward" compared to the general population. Based on 1931 census data, they estimated 52% of India's population belonged to castes that were "backward" due to various socio-economic factors like wealth or jobs performed. The possibility for providing reservation to these people was allowed for in Article 15(4) and Article 16(4), which states the government can provide reservation to "backward classes." Although the Center maintains its own list of OBC's, comprising over 5,000 castes and subcastes, each state can create their own backward caste list for in-state reservations. Most OBCs are lower castes, were classified originally in the shudra varna, and have low ritual status. However, there are other castes in the OBC list who, although ritually low, are economically dominant and in many cases are the enforcers of the caste hierarchy, including some Brahmin groups. In some states there is a divide between backward castes, who face some socio-economic disadvantage and most backward or extremely backward castes, who face a high amount of social discrimination barely above Dalits in their status. In fact, unlike Scheduled Castes, OBCs do not have to be Hindu and many states give benefits to some Muslim and Christian communities. This list is most subject to change since the criteria is not as stringent, making it a list added to often by politicians to please certain sections of their voters.
Those who are not a member of these groups are lumped together in the General category, sometimes called the Open category. These are made up of mostly high castes who do not qualify for reservations: most communities in the Brahmin, Kshatriya and Vaishya varnas. However, seats listed for general category can be taken by anyone irrespective of reservation status.
History
Before independence
Quota systems favouring certain castes and other communities existed before independence in several areas of British India. Demands for various forms of positive discrimination had been made, for example, in 1882 and 1891.[1] Shahu, the Maharaja of the princely state of Kolhapur, introduced reservation in favor of non-Brahmin and backward classes, much of which came into force in 1902. He provided free education to everyone and opened several hostels to make it easier for them to receive it. He also tried to ensure that people thus educated were suitably employed, and he appealed both for a class-free India and the abolition of untouchability. His 1902 measures created 50 percent reservation for backward communities. On 16 September 1921, the first Justice Party government passed the first Communal Government Order (G. O. # 613), thereby becoming the first elected body in the Indian legislative history to legislate reservations, which have since become standard across the country.
The British Raj introduced elements of reservation in the Government of India Act of 1909 and there were many other measures put in place prior to independence.[1] A significant one emerged from the Round Table Conference of June 1932, when the Prime Minister of Britain, Ramsay MacDonald, proposed the Communal Award, according to which separate representation was to be provided for Muslims, Sikhs, Indian Christians, Anglo-Indians, and Europeans. The depressed classes, roughly corresponding to the STs and SCs, were assigned a number of seats to be filled by election from constituencies in which only they could vote, although they could also vote in other seats. The proposal was controversial: Mahatma Gandhi fasted in protest against it but many among the depressed classes, including their leader, B. R. Ambedkar, favored it. After negotiations, Gandhi reached an agreement with Ambedkar to have a single Hindu electorate, with Dalits having seats reserved within it. Electorates for other religions, such as Islam and Sikhism, remained separate. This became known as the Poona Pact.[2]
After independence
After the independence of India in 1947 there were some major initiatives in favor of the STs, SCs and after the 1980s in favour of OBCs.(Other Backward Castes) and in 2019 for poor general category . The country's affirmative action program was launched in 1950 and is the oldest such programme in the world.[3]
A common form of caste discrimination in India was the practice of untouchability. SCs were the primary targets of the practice, which was outlawed by the new Constitution of India.[4]
In 1954, the Ministry of Education suggested that 20 percent of places should be reserved for the SCs and STs in educational institutions with a provision to relax minimum qualifying marks for admission by 5 percent wherever required. In 1982, it was specified that 15 percent and 7.5 percent of vacancies in public sector and government-aided educational institutes should be reserved for the SC and ST candidates, respectively.[5]
A significant change began in 1979 when the Mandal Commission or the Socially and Educationally Backward Classes Commission (SEBC) was established to assess the situation of the socially and educationally backward classes.[6] The commission did not have exact population figures for the OBCs and so used data from the 1931 census, thus estimating the group's population at 52 per cent.[7] In 1980 the commission's report recommended that a reserved quota for OBCs of 27 per cent should apply in respect of services and public sector bodies operated by the Union Government. It called for a similar change to admissions to institutes of higher education, except where states already had more generous requirements.[6] It was not until the 1990s that the recommendations were implemented in Union Government jobs.[8] In 2019 the government announces the 10% reservation in educational institutions and government jobs for economically weaker section of general category.
The Constitution of India states in article 15(4): "Nothing in [article 15] or in clause (2) of article 29 shall prevent the State from making any special provision for the advancement of any socially, and educationally backward classes of citizens of or for the Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes."[9] Article 46 of the Constitution states that "The State shall promote with special care the educational and economic interests of the weaker sections of the people, and, in particular, of the Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes, and shall protect them from social injustice and all forms of exploitation."[10]
The Supreme Court of India ruled in 1992 that reservations could not exceed 50 percent, anything above which it judged would violate equal access as guaranteed by the Constitution. It thus put a cap on reservations.[11] However, the recent amendment of the constitution exceeds 50% and also there are state laws that exceed this 50 percent limit and these are under litigation in the Supreme Court. For example, in the State of Tamil Nadu, the caste-based reservation stands at 69 percent and applies to about 87 percent of the population.
Reservation schemes
In employment
Government and public sector will heir job seekers based on reservation percentage from two different categories are 1: reservation category (SC, ST, OBC, EWC and other minorities) 2:Open category (General, SC, ST, OBC, EWC and other minorities). In hiring Major priority given to reservation category including 33% reservation for Women, priority in hiring is given by Other Minorities women, ST women, SC women, ST Men,SC Men, OBC women, OBC Men, EWC Women, EWC Men and then after Open category Will be considered. Government and public sector hiring based on Merit in open category and one more anomaly here i.e., Priority in hiring will be given by: Other Minorities women, ST women,SC women,ST Men, SC Men, OBC women, OBC Men, EWC Women,EWC Men and then General if they are equally eligibilied(for example having same marks or Rank).
The 1993 Supreme Court ruling in the Indra Sawhney case said that reservations in job promotions are "unconstitutional" or not in accordance with the political constitution but allowed its continuation for five years.[12][11] In 1995, the 77th amendment to the Constitution was made to amend Article 16 before the five-year period expired to continue with reservations for SC/STs in promotions.[13] It was further modified through the 85th amendment to give the benefit of consequential seniority to SC/ST candidates promoted by reservation.[14]
The 81st amendment was made to the Constitution to permit the government to treat the backlog of reserved vacancies as a separate and distinct group, to which the ceiling of 50 per cent did not apply.[15] The 82nd amendment inserted a provision in Article 335 to enable states to give concessions to SC/ST candidates in promotion.[16]
The validity of all the above four amendments was challenged in the Supreme Court through various petitions clubbed together in M. Nagaraj & Others Vs. Union of India & Others, mainly on the ground that these altered the Basic Structure of the Constitution. In 2006, the Supreme Court upheld the amendments but stipulated that the concerned state will have to show, in each case, the existence of "compelling reasons" - which include "backwardness", "inadequacy of representation" and overall "administrative efficiency - before making provisions for reservation. The court further held that these provisions are merely enabling provisions. If a state government wishes to make provisions for reservation to SC/STs in the promotion, the state has to collect quantifiable data showing backwardness of the class and inadequacy of representation of that class.[17]
In 2007, the Government of Uttar Pradesh introduced reservation in job promotions. However, citing the Supreme Court decision, the policy was ruled to be unconstitutional by the Allahabad High Court in 2011.[18] The decision was challenged in the Supreme Court, which upheld it in 2012 by rejecting the government's argument because it failed to furnish sufficient valid data to justify the move to promote employees on a caste basis.[19]
In education
Government Universities will allot seats based on reservation percentage from two different categories are 1: reservation category (SC,ST,OBC,EWC and other minorities) 2:Open category (General,SC,ST,OBC,EWC and other minorities). In allotment, Major priority given to reservation category including 33% reservation for Women, priority in allotting is given by Other Minorities women,ST women,SC women,ST Men,SC Men, OBC women, OBC Men, EWC Women, EWC Men and then after Open category Will be considered. Government Universities will be allotted based on Merit in open category and one more exemption here i.e., priority in alloting will be given by: Other Minorities women,ST women,SC women,ST Men,SC Men, OBC women,OBC Men, EWC Women,EWC Men and then General if they are equally eligible (for example having same marks or Rank) and reservation percentage under consideration for entrance exams fees,for cut off marks,for allotment of seats and also applicable to other government schemes.
In India scholarships or student aid is available for—SCs, STs, BCs, OBCs, women, Muslims, and other minorities. Only about 0.7% of scholarships or student aid in India is based on merit, given the grossly inadequate representation of above-mentioned categories in employment and education due to historic, societal and cultural reasons.[20]
New rules implementation of UPA Government do not provide scholarship scheme and reservation quota of students and employees of colleges under central University and State University approved by the UGC.
States
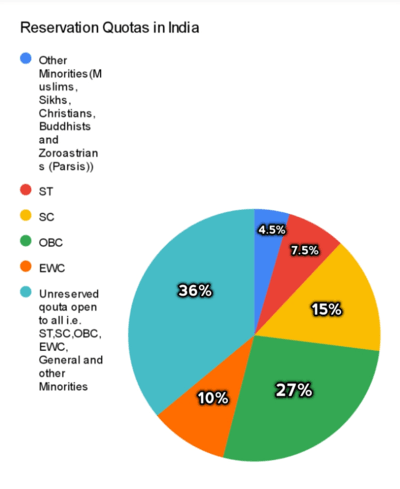
In central-government funded higher education institutions, 22.5% of available seats are reserved for Scheduled Caste (SC) and Scheduled Tribe (ST) students (7.5% for STs, 15% for SCs).[21] This reservation percentage has been raised to 49.5%[21] by including an additional 27% reservation for OBCs. This ratio is followed even in Parliament and all elections where a few constituencies are earmarked for those from certain communities (which will next rotate in 2026 per the Delimitation Commission).
| State/UT | SC | ST | OBC | Other reserved | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andhra Pradesh | 15 | 6 | 29 | 50 | |
| A&N Islands | 38 | ||||
| Arunachal Pradesh | 80 | ||||
| Assam | 7 | 15 | 27 | 50 | |
| Bihar | 15 | 1 | 34 | 50 | |
| Chandigarh | 27 | ||||
| Chhattisgarh | 13 | 32 | 27 | ||
| D&D&D&NH | 3 | 9 | 27 | ||
| Delhi | 15 | 7 | 27 | 50 | |
| Goa | 2 | 12 | 27 | ||
| Gujarat | 7 | 14 | 27 | 10 | 59 |
| Haryana | 20 | 30 | 50 | ||
| Himachal Pradesh | 25 | 4 | 20 | 10 | |
| Jharkhand | 11 | 27 | 22 | ||
| Karnataka | 15 | 3 | 32 | 50 | |
| Kerala | 8 | 2 | 40 | ||
| Lakshadweep | 100 | ||||
| Madhya Pradesh | 16 | 20 | 14 | 50 | |
| Maharashtra | 13 | 7 | 19 | 36 | 75 |
| Manipur | 3 | 34 | 17 | ||
| Meghalaya | 80 | ||||
| Mizoram | 80 | ||||
| Nagaland | 80 | ||||
| Odisha | 16 | 22 | 27 | ||
| Puducherry | 16 | 34 | |||
| Punjab | 29 | 12 | |||
| Rajasthan | 16 | 12 | 26 | 54 | |
| Sikkim | 5 | 21 | 24 | ||
| Tamil Nadu | 18 | 1 | 50 | 69 | |
| Telangana | 10 | 62 | |||
| Tripura | 17 | 31 | 2 | ||
| Uttar Pradesh | 21 | 2 | 27 | 50 | |
| Uttarakhand | 18 | 3 | 13 | ||
| West Bengal | 22 | 6 | 7 | 35 |
The exact percentages vary from state to state:
- In Tamil Nadu, OBC reservation is divided into 30% Backward Caste and 20% Most Backward Caste[22]
- In Maharashtra in addition to the reservation for SC/ST/OBC, there is 16% for SEBCs, 2% for SBCs, Nomadic tribes - NT-A (Vimukta jati) - 3%, NT-B -2.5%, NT-C (Dhangar)-3.5% ,NT-D (Banjari)-2%
- In Northeast India, especially in Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Nagaland and Mizoram, reservation for ST in State Govt. jobs is 80% with only 20% unreserved. In the Central Universities of NEHU(shillong) and Rajiv Gandhi University, 60% of seats are reserved for ST students.
- In West Bengal, the OBC community is divided into OBC A & B.[23] In West Bengal there is no reservation on religious basis but some economically and educationally backward Muslim castes (basis surnames pertaining to different profession e.g. cobbler, weaver etc.) have been included along with their Hindu counterparts in the OBC list namely OBC A and OBC B, in both lists caste from both communities are there. But in higher educational institutes, till now there is no reservation for the OBC community but there is reservation in regard to admission in primary, secondary and higher secondary studies.[24][23]
Gender
The Women's Reservation Bill was passed by the Rajya Sabha on 9 March 2010 by a majority vote of 186 members in favour and 1 against. As of March 2013, the Lok Sabha has not voted on the bill. Critics say gender cannot be held as a basis for reservation alone other factors should also be considered e.g. economic, social conditions of woman candidate especially when applying reservation for educated women.
In Gujarat and Andhra Pradesh, 33% of posts are reserved for females in all government departments and services, such as police, health, education and general administration.[25][26][27]
Religion
There is no reservation granted on the basis of religion in the Central educational institutions at the national level, although reservation has been extended to religious minorities in some states. The Tamil Nadu government has allotted 3.5% of seats each to Muslims and Christians, thereby altering the OBC reservation to 23% from 30% (since it excludes persons belonging to Other Backward Castes who are either Muslims or Christians).[28]
The Government of Andhra Pradesh introduced a law enabling 4 percent reservations for Muslims in 2004. This law was upheld by the Supreme Court in an interim order in 2010 but it constituted a Constitution bench to look further into the issue.[29][30] The referral was to examine the constitutional validity of quotas based on religion.[31] Kerala Public Service Commission has a quota of 6% for Muslims. Religious minority (Muslim or Christian) educational institutes also have 50% reservation for Muslim or Christian religions. The Central government has listed a number of Muslim communities as backward Muslims, making them eligible for reservation.[32]
Controversy
The Union Government on 22 December 2011 announced the establishment of a sub-quota of 4.5% for religious minorities within the existing 27% reservation for Other Backward Classes. The reasoning given was that Muslim communities that have been granted OBC status are unable to compete with Hindu OBC communities.[33] It was alleged that the decision was announced as the Election Commission announced Assembly elections in five states on 24 December 2011. The government would not have been able to announce this due to the model code of conduct. On 12 January 2012, the Election Commission stayed implementation of this decision for violation of the model code of conduct.[34] Later, Justice Sachar, head of the Sachar Committee that was commissioned to prepare a report on the latest social, economic and educational condition of the Muslim community of India, criticised the government decision, saying "Such promises will not help the backward section of minorities. It is like befooling them. These people are making tall claims just to win elections". He suggested that instead of promising to give reservations, the government should focus on basic issues of improving administration and governance.[35]
On 28 May 2012, the Andhra Pradesh High Court quashed the sub-quota. The court said that the sub-quota has been carved out only on religious lines and not on any other intelligible basis. The court criticized the decision: "In fact, we must express our anguish at the rather casual manner in which the entire issue has been taken up by the central government.".[36]
Agitations
In 2008 and 2010, the Gurjar community in Rajasthan demanded reclassification from OBC to ST for increased reservation benefits. They began violently protesting on the streets of Rajasthan and blocked several rail lines. Police firing on Gurjars began a tit-for-tat cycle of violence between Police and Gurjars. The violence ended with 37 people dead. Their move was opposed by the Meenas, the main ST community in Rajasthan. In 2019, the agitation restarted as Gurjars demanded 5% reservation instead of 1%, and began blocking trains to this effect.[37]
Jats have been demanding OBC status since the 1990s. In 2016, they began an agitation to get this status. To this effect they began protesting by blockading roads and lines, but later the protests turned violent. Riots spread to Delhi and western Uttar Pradesh, and even Rajasthan. The epicentre of the violence was in Rothak, and almost ₹34000 crores ($4.8 billion) worth of property was damaged and 30 were killed. Bowing to the pressure, the Haryana government created a special category for Jats and other upper castes called BC, and appointed 10% reservation, but the measure was blocked in court.[38]
Beginning in 2015, the Patidar community (better known as Patel) began agitating for OBC status in Gujarat. This movement consisted of massive demonstrations across the state, led by Hardik Patel. Later many of these protests turned violence, resulting in curfews across the state and crores worth of damage. Talks with the government broke down, and the violence restarted. After the Jat agitation began in 2016, the Patidars flared up again and led a march through Gujarat, but protests in several cities turned violent and the RAF was sent in.[38]
Marathas, the dominant caste of Maharashtra, have been agitating for OBC status since the 1990s. In 2016, after the rape and murder of a 15-year old Maratha girl in Kopardi, the Maratha community organized massive protests throughout Maharashtra. Their demands included death for the accused as well as reservations for the Maratha community which makes up 35% of the state's population. The protests were mainly peaceful. Some road blocks turned violent in 2017 and 2018, but overall the protests were peaceful. Their demand was met when the Maharashtra government instituted a special SEBC category for them with 16% reservation.[38]
Economic status
The Union Government tabled the Constitution (One Hundred And Twenty-Fourth Amendment) Bill, 2019 which provided 10% additional quota for the economically weaker sections amongst the erstwhile unreserved category students. The definition of 'economically weaker sections' will be defined by the State from time to time.[39] The constitutional amendment has laid down that they will be restricted to people with household income less than 8 Lakh per annum, or those who own agricultural land below five acres. Business Today has commented that these criteria cover almost 100 percent of the population.[40] Several petitions have been filed before the Supreme Court of India challenging the legality of this amendment.[41]
Exclusions
There are no exclusions for SC/ST people.
For OBC's people in the following categories are not entitled to take advantage of the reservation system:
- Children of officials in high office as per the Constitution.[lower-alpha 1]
- Children of civil servants in high positions.[lower-alpha 2]
- Children of armed force officers of high rank.[lower-alpha 3]
- Children of professionals and those engaged in trade and industry.[lower-alpha 4]
- Children of property owners.[lower-alpha 5]
- Children of people with annual income exceeding ₹8,00,000 (regarded as the "creamy layer").[42]
Institutions of Excellence, research institutions, Institutions of National and Strategic Importance such as Centre for Development of Advanced Computing, Homi Bhabha National Institute and its ten constituent units, the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (Mumbai), the North Eastern Indira Gandhi Regional Institute of Health and Medical Sciences (Shillong), Physical Research Laboratory (Ahmedabad), the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (Thiruvananthapuram) and the Indian Institute of Remote Sensing (Dehradun) do not have reservations for higher education.[lower-alpha 6] However Institutes of National Importance such as Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs),[46]Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs),[47] National Institutes of Technology (NIT) and Indian Institute of Information Technology (IIIT) have provision of reservation in admission process for undergraduate and graduate programs.[48]
On 27 October 2015, the Supreme Court directed the state and the Central governments to end the regional quota and to ensure that super-specialty medical courses are kept "unreserved, open and free" from any domicile status after the court had allowed petitions files by some MBBS doctors.[49]
Creamy layer
The term creamy layer was first coined in 1974 in the State of Kerala vs N. M. Thomas case when a judge said that the "benefits of the reservation shall be snatched away by the top creamy layer of the backward class, thus leaving the weakest among the weak and leaving the fortunate layers to consume the whole cake".[50][51] The 1992 Indra Sawhney vs Union of India judgement laid down the limits of the state's powers: it upheld the ceiling of 50 percent quotas, emphasised the concept of "social backwardness", and prescribed 11 indicators to ascertain backwardness. The judgement also established the concept of qualitative exclusion, such as "creamy layer".[52][53][54] The creamy layer applies only to OBCs.[55] The creamy layer criteria were introduced at Rs 1 lakh in 1993 and revised to Rs 2.5 lakh in 2004, ₹4.5 lakh in 2008 and ₹6 lakh in 2013, but now the ceiling has been raised to ₹8 lakh (in September 2017).[56] In October 2015, the National Commission for Backward Classes (NCBC) proposed that a person belonging to OBC with an annual family income of up to ₹15 lakh should be considered as minimum ceiling for OBC.[57] The NCBC also recommended sub-division of OBCs into "backward", "more backward" and "extremely backward" groups and to divide the 27 per cent quota amongst them in proportion to their population, to ensure that stronger OBCs do not corner the quota benefits.[58][59]
Reservation in states
Maharashtra
Maharashtra earlier had 50% reservation in educational institutions and government jobs. In June 2019, Bombay High Court allowed 12% and 13% reservation respectively education and jobs for Maratha caste (SEBC) .[60] After the Union Cabinet approved the 10% reservation for the Economically Weaker Section (EWS),[61] the reservation has been estimated to increase up to 75% making Maharashtra the state with the highest percentage of reservation in the country.
- Scheduled Castes (SC) (13%)
- Scheduled Tribes (ST) (7%)
- Other Backward Classes (OBC) (19%)
- Special Backward Classes (SBC) (2%)
- Socially and economically backward class (SEBC - Maratha) (13%)
- Economically Weaker Section (EWS) (10%)
- Nomadic Tribes - A (Vimukta jati) (3%)
- Nomadic Tribes - B (Banjara) (2.5%)
- Nomadic Tribes - C (Dhangar) (3.5%)
- Nomadic Tribes - D (Vanjari) (2%)
Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh state percentage of reservation is =50% approx. 66.66% reservations including women are applicable in Andhra Pradesh in Education and Government jobs.
- Scheduled Castes – 15%
- Scheduled Tribes – 6%
- Backward Classes (A, B, C, D) – 27%
- Physically Handicapped (Blind, Deaf & Dumb and OPH) – 3% (1 per cent each)
- Ex-servicemen (APMS only) – 1% (0.5% in general)
- Women - 33.33% (in all categories, means 16.66% in general category)
Addition of disabled, ex-serviceman, women in general category 16.66% makes it 66.66%
The Andhra Pradesh Govt says economically backward children are admitted into private schools under Right To Education (RTE) Act and that caste-based reservations also apply to private schools.[62]
The reservation for women cuts across all classes and communities and is a horizontal and not vertical reservation. As such the total % of reservations has to be counted at 50% only; and that is in consonance with the Supreme Court dicta that reservations, in general, ought not to exceed 50% of the posts/seats if the right to equal opportunity to all without discrimination guaranteed under Article 16 is to be vindicated and respected.
Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh has 80% reservation for Scheduled Tribes.
See also
Notes
- Included among the high office holders are the President of India, the Vice-President of India, Judges of the Supreme Court of India, the High Courts chairman, the members of Union Public Service Commission, members of the State Public Service Commission, Chief Election Commissioner, Comptroller Auditor-General of India or any person holding positions of a constitutional nature.[42]
- Included among this category are Class I or Class II officers, unless dead or incapacitated.[43] The criteria used for Group A and B are the same as the employees of the Public sector.[42]
- High ranks include the rank of colonel and above in the army or in equivalent posts in the Navy, the Air Force, and the Paramilitary Force. But that will hold true provided that-
- "the wife of an armed forces officer is herself in the armed forces (i.e., the category under consideration) the rule of exclusion will apply only when she herself has reached the rank of Colonel."
- "the service ranks below Colonel of husband and wife shall not be clubbed together"
- "if the wife of an officer in the armed forces is in civil employment, this will not be taken into account for applying the rule of exclusion unless she falls in the service category under item No.II in which case the criteria and conditions"[42]
- If a person has a high paying job such as physician, lawyer, chartered accountant, income tax consultant, financial or management consultant, dental surgeon, engineer, architect, computer specialist, film artist or other film professionals, author, playwright, sports person, sports professional, media professional or any other vocations of like status. If the husband holds one of the above jobs and the wife doesn't then the husband's income will be taken into consideration and if the wife holds one of the above jobs then the wife's income will be taken into consideration. The income of the family as a whole will be taken into account because the whole point of the reservation system is to raise the social status of the people that belong to the SC's, ST's and OBCs and if a family's income is high already it is considered that it raises their social status as well.[42]
- Included in this category are those who have irrigated land area which is equal to or more than 85% of the statutory ceiling area will be excluded from the reservation. They would only be under reservation if the land is exclusively unirrigated. Those with vacant buildings can use them for residential, industrial or commercial purposes, hence they are not covered under reservations.[42]
- Such institutions include the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing, Homi Bhabha National Institute and its ten constituent units, the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (Mumbai), the North Eastern Indira Gandhi Regional Institute of Health and Medical Sciences (Shillong), Physical Research Laboratory (Ahmedabad), the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (Thiruvananthapuram) and the Indian Institute of Remote Sensing (Dehradun).[44][45]
References
- Laskar, Mehbubul Hassan. "Rethinking Reservation in Higher Education in India" (PDF). ILI Law Review. pp. 29–30. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 April 2012.
- Menon, V. P. (1957). Transfer of Power in India (Reprinted ed.). Orient Blackswan. pp. 49–50. ISBN 978-81-250-0884-2.
- "Human Development Report 2016" (PDF). UNDP. p. 119. Retrieved 21 March 2017.
- Passin, Herbert (October 1955). "Untouchability in the Far East". Monumenta Nipponica. 11 (3): 247–267. doi:10.2307/2382914. JSTOR 2382914.
- "Educational Safeguards". Department of Education. Government of India. Archived from the original on 19 June 2009. Retrieved 27 November 2011.
- Bhattacharya, Amit (8 April 2006). "Who are the OBCs?". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 27 June 2006. Retrieved 19 April 2006.
- Ramaiah, A. (6 June 1992). "Identifying Other Backward Classes" (PDF). Economic and Political Weekly. pp. 1203–1207. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 December 2005. Retrieved 27 May 2006.
- "Implementation of Recommendations of Mandal Commission". Parliament of India. Retrieved 4 November 2011.
- Article 15, Section 4 of the Constitution of India (1950)
- Article 46, Section 0 of the Constitution of India (1950)
- "Indra Sawhney Etc. vs Union of India And Others, Etc. on 16 November, 1992". IndianKanoon.org. Retrieved 22 August 2012.
(4) Reservation being an extreme form of protective measure or affirmative action it should be confined to minority of seats. Even though the Constitution does not lay down any specific bar but the constitutional philosophy being against proportional equality the principle of balancing equality ordains reservation, of any manner, not to exceed 50%." , "Reservation in promotion is constitutionally impermissible as once the advantaged and disadvantaged are made equal and are brought in one class or group then any further benefit extended for promotion on the inequality existing prior to being brought in the group would be treating equals unequally. It would not be eradicating the effects of past discrimination but perpetuating it.
- "BJP's OBC pitch: How stronger new backward classes panel will function". The Indian Express.
- "Seventy Seventh Amendment". Indiacode.nic.in. Retrieved 19 November 2011.
- "Eighty Fifth Amendment". Indiacode.nic.in. 4 January 2002. Retrieved 19 November 2011.
- "Eighty First Amendment". Indiacode.nic.in. 29 August 1997. Retrieved 19 November 2011.
- "Eighty Second Amendment". Indiacode.nic.in. Retrieved 19 November 2011.
- Kapadia, S. H. "M.Nagaraj & Others vs Union of India & Others on 19 October 2006". Retrieved 22 August 2012.
We reiterate that the ceiling-limit of 50%, the concept of creamy layer and the compelling reasons, namely, backwardness, inadequacy of representation and overall administrative efficiency are all constitutional requirements without which the structure of equality of opportunity in Article 16 would collapse.", "As stated above, the impugned provision is an enabling provision. The State is not bound to make reservation for SC/ST in matter of promotions.
- "Promotion quota not legally sustainable: HC". The Times of India. 5 January 2011. Retrieved 10 August 2012.
- "Supreme Court upholds High court's decision to quash quota in promotion". The Times of India. 28 April 2012. Retrieved 10 August 2012.
- "Guess how many Indians get merit-based scholarship". Rediff. 1 September 2014. Retrieved 8 May 2016.
- "Affirmative Action and Peer Effects: Evidence from Caste Based Reservation in General Education Colleges in India" (PDF). Virginia University,Virginia. Retrieved 5 November 2011.
- "Status of Reservation of OBC in Various States". pib.nic.in. Retrieved 24 February 2019.
- ":: Backward Classes Welfare Department, Government of West Bengal ::". Retrieved 2 February 2015.
- ":: BCW Department-Govt of West Bengal, Reservation ::". Retrieved 2 February 2015.
- "33% reservation for women in all Gujarat state government jobs". Deccan Herald. 13 October 2014. Retrieved 3 September 2015.
- "Gujarat increases women's reservation to 33% in government jobs". dna. 14 October 2014. Retrieved 3 September 2015.
- Arora, N.D. (2010). Political Science for Civil Services Main Examination. Tata McGraw-Hill Education. p. 19. ISBN 9780070090941.
- Viswanathan, S. (16 November 2007). "A step forward". Frontline. 24 (22). Archived from the original on 20 November 2010.
- PTI. "Interim relief to AP on Muslim reservation". The Hindu. Retrieved 14 June 2015.
- "Supreme Court to hear govt on Muslim quota". The Times of India. Retrieved 14 June 2015.
- "Centre Seeks SCs approval on Muslim Reservation". timesofindia-economictimes. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
- A, Roshan (2 February 2010). "State Government Provides Reservation to Muslims". Economic TImes. Retrieved 6 February 2010.
- "4.5% quota fails to impress Muslims in Uttar Pradesh". The Times of India. 23 December 2011.
- "Election Commission stalls 4.5% sub-quota in poll states". The Times of India. 12 January 2012. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
- "Govt trying to befool minorities with quota: Sachar". 19 February 2012. Retrieved 20 February 2012.
- "HC Quashes Centre's 4.5% Sub-Quota for Minorities". 28 May 2012. Archived from the original on 29 May 2012. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
- DelhiFebruary 10, India Today Web Desk New; February 10, 2019UPDATED:; Ist, 2019 13:39. "10 trains affected as Gujjar quota agitation enters Day 3". India Today. Retrieved 24 March 2020.CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
- "Jats, Marathas, and Patels Want Quotas, But Do They Need Them?". Economic and Political Weekly: 7–8. 5 June 2015.
- ET Explains: What is Constitution (One Hundred And third Amendment) Bill, 2019?, The Economic Times, 9 January 2019.
- In-depth: Who is eligible for the new reservation quota for general category?, Business Today, 8 January 2019.
- "Challenge to reservation for economically poor". 1, Law Street. 11 February 2019. Retrieved 20 February 2019.
- "Judgement Writ Petition (Civil) No.930 of 1990 – Indira Sawhney Versus Union of India And others (16.11.1992)" (PDF). National Commission for Backward Classes. Retrieved 5 November 2011.
- Office Memorandum, ncbc.nic.in, pp. 7–8
- "Press Information Bureau English Releases". Retrieved 2 February 2015.
- "Extraordinary Part II - Section I" (PDF). The Gazette of India. Retrieved 24 February 2019.
- "Two-Year Post Graduate Programme in Management". Indian Institute of Management Ahmedabad.
- "Reservation of Seats". UCEED.
- "Concessions Provided for Students". National Institute of Technology Patna.
- "No quota in higher medicine: SC". The Telegraph. 27 October 2015.
- "Supreme Court Of India JUDGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM".
- "Scourge of reservation: The invisible creamy layer". The Pioneer.
- "Explained: Order reserved". The Indian Express.
- "For an equitable society, reservations must be extended to private sector". The Indian Express. 23 October 2015. Retrieved 8 May 2016.
- "Plea to reconsider judgement in Indra Sawhney case of 1992".
- "'Can't keep SC/ST creamy layer out of quota benefits' - Times of India". The Times of India. Retrieved 24 February 2019.
- "Raise 'creamy layer' to Rs 10.5 lakh: OBC panel".
- "OBC panel backs off, won't make 'creamy layer' reservation criteria stringent".
- "OBC sub-division, relaxing creamy layer is a must: NCBC tells govt".
- "Raise 'creamy layer' to Rs 10.5 lakh: OBC panel". The Times of India. Retrieved 8 May 2016.
- "Bill for 16% Maratha quota for PG Medical admission passes Maharashtra legislature test - Key points to know". Zee Business. 21 June 2019. Retrieved 23 June 2019.
- Bureau, Our. "Cabinet approves 10% quota for EWS in general category". @businessline. Retrieved 23 June 2019.
- School Education – The Andhra Pradesh Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Rules 2010, Government of Andhra Pradesh, 22 February 2011. p. 9, Point 4. Archived 27 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine
Further reading
- Shourie, Arun (2012). Falling over backwards: An essay on reservations and judicial populism. New Delhi: HarperCollins Publishers. ISBN 978-9350293553
- Joseph, Manu (23 August 2004). "What If Reservations Had Come To An End In 1960?". Outlook. Retrieved 10 April 2018.