Recklinghausen
Recklinghausen (German pronunciation: [ˌʁɛklɪŋˈhaʊzn̩] (![]()
Recklinghausen | |
|---|---|
 Town Hall of Recklinghausen. | |
Coat of arms | |
Location of Recklinghausen within Recklinghausen district   | |
 Recklinghausen 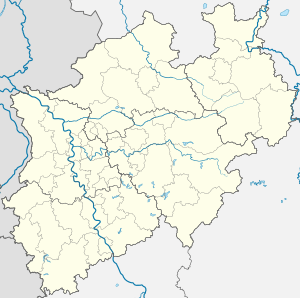 Recklinghausen | |
| Coordinates: 51°35′6″N 7°9′43″E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | North Rhine-Westphalia |
| Admin. region | Münster |
| District | Recklinghausen |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Christoph Tesche (CDU) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 66.4 km2 (25.6 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 85 m (279 ft) |
| Population (2018-12-31)[1] | |
| • Total | 112,267 |
| • Density | 1,700/km2 (4,400/sq mi) |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) |
| Postal codes | 45601–45665 |
| Dialling codes | 02361 |
| Vehicle registration | RE |
| Website | www.recklinghausen.de (in German) |
History
First mentioned in 1017 as Ricoldinchuson, in 1150 the city was the center of the surrounding Vest Recklinghausen. In 1236, the city of Recklinghausen received town privileges. There is record of Jews in the city as early as 1305.[2] As part of the County of Vest, ownership of Recklinghausen changed several times in the 15th and 16th century, and in 1576, the entire county was pawned to the Elector of Cologne. In 1582–83, again in 1586, and again in 1587, the city was plundered by partisan armies during the Cologne War, a feud over religious parity in Electorate of Cologne and electoral influence in the Holy Roman Empire.

Recklinghausen was also the site of more than 100 witchcraft trials (1514–1710). The trial activity reached a climax twice: In the time period of 1580/81 and again in 1588/89. The last person to be convicted of witchcraft was Anna Spickermann; after spending 16 months in prison, she was sentenced to death by sword and burned afterward.
Circa 1600, the administration of the Vest Recklinghausen was divided into two parts, with the eastern part administered by Recklinghausen. The town of Recklinghausen including the parish of Recklinghausen and the parishes Ahsen, Datteln, Flaesheim, Hamm-Bossendorf, Henrichenburg, Herten, Horneburg, Oer, Suderwich, Waltrop and Westerholt. Circa 1815, the Vest was made a Bürgermeisterei, with the town becoming the seat. In 1819, Herten joined the Recklinghausen Bürgermeisterei, and Erkenschwick followed in 1821.
As a target of the Oil Campaign of World War II, oil production at Recklinghausen/Forstezung[3] was bombed by the RAF on 15 January 1945; and South Recklinghausen (Recklinghausen Süd) was captured by the US 137th Infantry on 1 April 1945.[4]
Main sights

Recklinghausen is home to a museum of icons, which includes more than 1,000 Orthodox works from Russia, Greece and the Balkan countries, as well as early Coptic Christian art from Egypt. The icon museum - the largest outside the Orthodox world - was founded in 1956 and reopened after renovation in February 2006 for its 50th anniversary.
The Ruhrfestpielhaus, whose remodeling in 2001 won the German Architecture Award is home of "Die Liegende Nr 5", a famous sculpture by Henry Moore. At the Lohtor in front of a memorial for the victims of World War I, there is a large sculpture made of more than 30,000 bricks by Per Kirkeby.
Annual events
Recklinghausen hosts the annual Ruhrfestspiele, a cultural festival with an international reputation. Every year there is a cultural programme with many national and international theatrical productions starting on 1 May. In 2008 the programme included the play Speed the Plow starring Kevin Spacey and Jeff Goldblum as one of the major productions. The main theatrical stage is the Ruhrfestspielhaus but other theatres in and around Recklinghausen participate.
Transport
The two major motorways crossing the area of the city are the A2 and the A43. The city is connected to the larger waterways by the Rhein-Herne-Kanal. Recklinghausen has two railway stations. The Central Station (Recklinghausen Hauptbahnhof), which is served by Intercity and EuroCity services, and the South Station (Recklinghausen Südbahnhof).
Gallery
 central market
central market Lohtor-square with Sankt Peter's church and sculpture of Per Kirkeby
Lohtor-square with Sankt Peter's church and sculpture of Per Kirkeby former hospital in Westviertel
former hospital in Westviertel- half-timber houses in the city
- new shopping mall "PALAIS VEST"
 town-wall from the Middle Ages
town-wall from the Middle Ages
Twin towns - sister cities
Recklinghausen is twinned with:[5]
Notable people
- Frank Busemann (born 1975), decathlete
- Ursula Dirichs (born 1935), actress
- Mark Dragunski (born 1970), handball player
- Walter Giller (1927–2011), actor
- Thomas Godoj, rock singer, winner of Deutschland sucht den Superstar season 5
- Fritz Emil Irrgang (1890–1951), Nazi politician and storm trooper
- Hape Kerkeling (born 1964), comedian and author
- Rosemarie Koczy (1939–2007), ethnic Jew who survived concentration camps, artist and teacher, known for her works dealing with the Holocaust
- Renate Künast (born 1955), German politician Alliance '90/The Greens
- Martin Max (born 1968), footballer
- Moguai, DJ and producer
- Ralf Möller (born 1959), actor
- Ludger Pistor (born 1959), actor
- Karl Ridderbusch (1932–1997), opera singer
- Klaus Schulten (1947–2016), biophysicist
Mayors since 1809
- Bürgermeister
- 1809–1833: Alois Joseph Wulff
- 1833–1839: Peter Banniza
- 1840–1842: Karl Boelmann
- 1843–1850: Franz Bracht
- 1854–1890: Friedrich Hagemann
- 1890–1899: Alexander Rensing
- Oberbürgermeister
- 1899–1904: Albert von Bruchhausen
- 1904–1919: Peter Heuser
- 1919–1931: Sulpiz Hamm
- 1932–1939: Fritz Niemeyer
- 1939–1945: Fritz Emil Irrgang, NSDAP
- 1945–1946: Josef Hellermann, CDU
- 1946–1948: Wilhelm Bitter, CDU
- 1948–1952: Joseph Dünnebacke, CDU
- 1952–1972: Heinrich Auge, SPD
- 1972–1984: Erich Wolfram, SPD
- Bürgermeister
- 1984–1987: Erich Wolfram, SPD
- 1987–1998: Jochen Welt, SPD
- Hauptamtliche Bürgermeister
- 1998–1999: Peter Borggraefe, SPD
- 1999–2014: Wolfgang Pantförder, CDU
- 2014–2020: Christoph Tesche, CDU[6]
References
- "Bevölkerung der Gemeinden Nordrhein-Westfalens am 31. Dezember 2018" (in German). Landesbetrieb Information und Technik NRW. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- "The Jewish Community of Recklinghausen". Beit Hatfutsot Open Databases Project. The Museum of the Jewish People at Beit Hatfutsot.
- "Member Login - Questia School, Online Research Library for Secondary and High Schools". www.questiaschool.com. Retrieved 28 December 2017.
- "The Central Europe Campaign, Page 3 - The 35th Infantry Division in World War Two". www.35thinfdivassoc.com. Retrieved 28 December 2017.
- "Städtepartnerschaften". recklinghausen.de (in German). Recklinghausen. Retrieved 2019-11-28.
- "Bürgermeister - Stadt Recklinghausen". www.recklinghausen.de. Retrieved 28 December 2017.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Recklinghausen. |