Roscosmos
The Roscosmos State Corporation for Space Activities (Russian: Государственная корпорация по космической деятельности «Роскосмос», Gosudarstvennaya korporatsiya po kosmicheskoy deyatyelnosti "Roskosmos"), commonly known as Roscosmos (Russian: Роскосмос), is a state corporation responsible for the wide range and types of space flights and cosmonautics programs for the Russian Federation.
Государственная Корпорация "Роскосмос" | |
 | |
 Roscosmos headquarters building in Moscow | |
| Agency overview | |
|---|---|
| Abbreviation | ROSCOSMOS |
| Formed | 25 February 1992 (as the Russian Space Agency) |
| Type | Space agency |
| Headquarters | 42 Shchepkina Street, Moscow, Russia |
| Administrator | Dmitry Rogozin |
| Primary spaceport | Baikonur Cosmodrome Vostochny Cosmodrome |
| Owner | Russian government |
| Annual budget | |
| Website | www.roscosmos.ru |
It had several precursors:
- Russian Space Agency (Russian: Российское космическое агентство, Rossiyskoye kosmicheskoye agentstvo), or RKA (Russian: РКА), established on February 25, 1992;[2]
- Russian Aviation and Space Agency (Russian: Российское авиационно-космическое агентство, Rossiyskoye aviatsionno-kosmicheskoye agentstvo), commonly known as Rosaviakosmos (Russian: Росавиакосмос), established on May 25, 1999;[2] and
- Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) (Russian: Федеральное космическое агентство (Роскосмос), Federalnoye kosmicheskoye agentstvo (Roskosmos)), established on March 9, 2004.[2]
On December 28, 2015, the Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) was abolished and the Roscosmos State Corporation for Space Activities was established by a presidential decree.[3][4][5]
The headquarters of Roscosmos are located in Moscow, while the main Mission Control Center site is in the nearby city of Korolyov as well as the Yuri Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center located in Star City of Moscow Oblast. The launch facilities used are Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan (with most launches taking place there, both crewed and uncrewed), and Vostochny Cosmodrome being built in the Russian Far East in Amur Oblast.
The current director since May 2018 is Dmitry Rogozin. In 2015 the Russian government merged Roscosmos with the United Rocket and Space Corporation, the re-nationalized Russian space industry, to create the Roscosmos State Corporation.[6]
On February 22, 2019, the Roscosmos Director, Dmitry Rogozin, has announced the construction start of new headquarters in Moscow, Zavodskaya Street 18: The National Space Centre.
History

the first satellite, Sputnik 1 (a ball under the ceiling);
the first spacesuits (lower-left corner);
the first human spaceflight module, the Vostok 3KA (center);
the first Molniya-type satellite (upper right corner);
the first space rover, Lunokhod 1 (lower right);
the first space station, Salyut 1 (left);
the first modular space station, Mir (upper left).
The Soviet space program did not have central executive agencies. Instead, its organizational architecture was multi-centered; it was the design bureaus and the council of designers that had the most say, not the political leadership. The creation of a central agency after the separation of Russia from the Soviet Union was therefore a new development. The Russian Space Agency was formed on February 25, 1992, by a decree of President Yeltsin. Yuri Koptev, who had previously worked with designing Mars landers at NPO Lavochkin, became the agency's first director.[7]
In the early years, the agency suffered from lack of authority as the powerful design bureaus fought to protect their own spheres of operation and to survive. For example, the decision to keep Mir in operation beyond 1999 was not taken by the agency; instead, it was made by the private shareholder board of the Energia design bureau. Another example is that the decision to develop the new Angara rocket was rather a function of Khrunichev's ability to attract resources than a conscious long-term decision by the agency.[7]
Crisis years
The 1990s saw serious financial problems due to the decreased cash flow, which encouraged the space agency to improvise and seek other ways to keep space programs running. This resulted in the agency's leading role in commercial satellite launches and space tourism. Scientific missions, such as interplanetary probes or astronomy missions during these years played a very small role, and although the agency had connections with the Russian aerospace forces, its budget was not part of Russia's defense budget; nevertheless, the agency managed to operate the Mir space station well past its planned lifespan, contributed to the International Space Station, and continued to fly Soyuz and Progress missions.
Start of the ISS Cooperation in 2000
On Oct. 31, 2000, a Soyuz spacecraft lifted off from the Baikonur Cosmodrome at 10:53 a.m. Kazakhstan time. Onboard were Expedition One Commander William M. (Bill) Shepherd of NASA and cosmonauts Sergei Krikalev and Yuri Gidzenko of Roscosmos. The trio arrived at the International Space Station on Nov. 2, marking the start of an uninterrupted human presence on the orbiting laboratory.[8]
2004: New director
In March 2004, the agency's director Yuri Koptev was replaced by Anatoly Perminov, who had previously served as the first commander of the Space Forces.[7][9]
Improved situation in 2005–2006
The Russian economy boomed throughout 2005 from high prices for exports, such as oil and gas, the outlook for future funding in 2006 appeared more favorable. This resulted in the Russian Duma approving a budget of 305 billion rubles (about US$11 billion) for the Space Agency from 2006 January to 2015, with overall space expenditures in Russia total about 425 billion rubles for the same time period.[10] The budget for 2006 was as high as 25 billion rubles (about US$900 million), which is a 33% increase from the 2005 budget. Under the current 10-year budget approved, the budget of the Space Agency shall increase 5–10% per year, providing the space agency with a constant influx of money. In addition to the budget, Roscosmos plans to have over 130 billion rubles flowing into its budget by other means, such as industry investments and commercial space launches. It is around the time US-based The Planetary Society entered a partnership with Roscosmos.
- New science missions: Koronas Foton (launched in January 2009), Spektr R (RadioAstron, launched in July 2011), Intergelizond (2011), Spektr RG (Roentgen Gamma, 2015), Spektr UV (Ultra Violet, 2016), Spektr M (2018),[11] Celsta (2018) and Terion (2018)
- Resumption of Bion missions with Bion-M (2013)
- New weather satellites Elektro L (launched in January, 2011) and Elektro P (2015)[7]
2006–2012

The federal space budget for the year 2009 was left unchanged despite the global economic crisis, standing at about 82 billion rubles ($2.4 billion).[12] In 2011, the government spent 115 billion rubles ($3.8 bln) in the national space programs.[13]
The proposed project core budget for 2013 to be around 128.3 billion rubles. The budget for the whole space program is 169.8 billion rubles. ($5.6 bln). By 2015, the amount of the budget can be increased to 199.2 billion rubles.[9]
Priorities of the Russian space program include the new Angara rocket family and development of new communications, navigation and remote Earth sensing spacecraft.[12] The GLONASS global navigation satellite system has for many years been one of the top priorities and has been given its own budget line in the federal space budget. In 2007, GLONASS received 9.9 billion rubles ($360 million), and under the terms of a directive signed by Prime Minister Vladimir Putin in 2008, an additional $2.6 billion will be allocated for its development.[14]
Space station funding issues
Due to International Space Station involvements, up to 50% of Russia's space budget is spent on the crewed space program as of 2009. Some observers have pointed out that this has a detrimental effect on other aspects of space exploration, and that the other space powers spend much lesser proportions of their overall budgets on maintaining human presence in orbit.[15]
Despite the considerably improved budget, attention of legislative and executive authorities, positive media coverage and broad support among the population, the Russian space program continues to face several problems.[16] Wages in the space industry are low; the average age of employees is high (46 years in 2007),[16] and much of the equipment is obsolete.[17] On the positive side, many companies in the sector have been able to profit from contracts and partnerships with foreign companies; several new systems such as new rocket upper stages have been developed in recent years; investments have been made to production lines, and companies have started to pay more attention to educating a new generation of engineers and technicians.[7][17]
2011: New director
On 29 April 2011, Perminov was replaced with Vladimir Popovkin as the director of Roscosmos. The 65-year-old Perminov was over the legal age for state officials, and had received some criticism after a failed GLONASS launch in December 2010. Popovkin is a former commander of the Russian Space Forces and First Deputy Defense Minister of Russia.[18][19]
2013-2015 reorganization of the Russian space sector
As a result of a series of reliability problems, and proximate to the failure of a July 2013 Proton M launch, a major reorganization of the Russian space industry was undertaken. The United Rocket and Space Corporation was formed as a joint-stock corporation by the government in August 2013 to consolidate the Russian space sector. Deputy Prime Minister Dmitry Rogozin said "the failure-prone space sector is so troubled that it needs state supervision to overcome its problems."[20] Three days following the Proton M launch failure, the Russian government had announced that "extremely harsh measures" would be taken "and spell the end of the [Russian] space industry as we know it."[21] Information indicated then that the government intended to reorganize in such a way as to "preserve and enhance the Roscosmos space agency."[20]
More detailed plans released in October 2013 called for a re-nationalization of the "troubled space industry," with sweeping reforms including a new "unified command structure and reducing redundant capabilities, acts that could lead to tens of thousands of layoffs."[22] According to Rogozin, the Russian space sector employs about 250,000 people, while the United States needs only 70,000 to achieve similar results. He said: "Russian space productivity is eight times lower than America's, with companies duplicating one another's work and operating at about 40 percent efficiency."[22]
Under the 2013 plan, Roscosmos was to "act as a federal executive body and contracting authority for programs to be implemented by the industry."[20]
In 2016, the state agency was dissolved and the Roscosmos brand moved to the state corporation, which had been created in 2013 as the United Rocket and Space Corporation, with the specific mission to renationalize the Russian space sector.[23]
In 2018, Russian President Vladimir Putin said "it 'is necessary to drastically improve the quality and reliability of space and launch vehicles' ... to preserve Russia's increasingly threatened leadership in space."[24] In November 2018 Alexei Kudrin, head of Russian financial audit agency, named Roscosmos as the public enterprise with "the highest losses" due to "irrational spending" and outright theft and corruption.[25]
Current programs
ISS involvement

Roscosmos is one of the partners in the International Space Station (ISS) program; it contributed the core space modules Zarya and Zvezda, which were both launched by Proton rockets and later were joined by NASA's Unity Module. The Rassvet module was launched aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis[26] and will be primarily used for cargo storage and as a docking port for visiting spacecraft. The Nauka module is the last component of the ISS, due to be launched in November 2019.[27] Roscosmos is furthermore responsible for expedition crew launches by Soyuz-TMA spacecraft and resupplies the space station with Progress space transporters. After the initial ISS contract with NASA expired, Roscosmos and NASA, with the approval of the US government, entered into a space contract running until 2011, according to which Roscosmos will sell NASA spots on Soyuz spacecraft for approximately $21 million per person each way (thus $42 million to and back from the ISS per person) as well as provide Progress transport flights ($50 million per Progress as outlined in the Exploration Systems Architecture Study[28]). Roscosmos has announced that according to this arrangement, crewed Soyuz flights will be doubled to 4 per year and Progress flights also doubled to 8 per year beginning in 2008.
Roscosmos also provides space tourism for fare-paying passengers to ISS through the Space Adventures company. As of 2009, six space tourists have contracted with Roscosmos and have flown into space, each for an estimated fee of at least $20 million (USD).
Science programs
Roscosmos operates a number of programs for Earth science, communication, and scientific research. Future projects include the Soyuz successor, the Prospective Piloted Transport System, scientific robotic missions to one of the Mars moons as well as an increase in Lunar orbit research satellites.
- Luna-Glob Moon orbiter and lander, planned in 2021
- Venera-D Venus lander, planned in 2025
- Fobos-Grunt Mars mission, lost in low Earth orbit in 2012
- Mars 96 Mars mission, lost in low Earth orbit in 1996
Rockets
Roscosmos uses a family of several launch rockets, the most famous of them being the R-7, commonly known as the Soyuz rocket that is capable of launching about 7.5 tons into low Earth orbit (LEO). The Proton rocket (or UR-500K) has a lift capacity of over 20 tons to LEO. Smaller rockets include Rokot and other Stations.
Currently rocket development encompasses both a new rocket system, Angara, as well as enhancements of the Soyuz rocket, Soyuz-2 and Soyuz-2-3. Two modifications of the Soyuz, the Soyuz-2.1a and Soyuz-2.1b have already been successfully tested, enhancing the launch capacity to 8.5 tons to LEO.
New piloted spacecraft
One of Roscosmos's projects that was widely covered in the media in 2005 was Kliper, a small lifting body reusable spacecraft. While Roscosmos had reached out to ESA and JAXA as well as others to share development costs of the project, it also stated that it will go forward with the project even without the support of other space agencies. This statement was backed by the approval of its budget for 2006–2015, which includes the necessary funding of Kliper. However, the Kliper program was cancelled in July 2006,[29] and has been replaced by the new Orel project. As of 2016 no crafts were launched.
Space systems
"Resurs-P"[30] is a series of Russian commercial Earth observation satellites capable of acquiring high-resolution imagery (resolution up to 1.0 m). The spacecraft is operated by Roscosmos as a replacement of the Resurs-DK No.1 satellite.
Create HEO space system "Arctic" to address the hydrological and meteorological problems in the Arctic region and the northern areas of the Earth, with the help of two spacecraft "Arktika-M" and in the future within the system can create a communications satellite "Arktika-MS" and radar satellites "Arktika-R."[31]
The launch of two satellites "Obzor-R" (Review-R) Remote Sensing of the Earth, with the AESA radar and four spacecraft "Obzor-O" (Review-O) to capture the Earth's surface in normal and infrared light in a broad swath of 80 km with a resolution of 10 meters. The first two satellites of the projects planned for launch in 2015.
Gonets: Civilian low Earth orbit communication satellite system. On 2016, the system consists of 13 satellites (12 Gonets-M and 1 Gonets-D1).[32]
Gecko mating experiment
On 19 July 2014, Roscosmos launched the Foton-M4 satellite containing, among other animals and plants, a group of five geckos.[33][34] The five geckos, four females and one male, were used as a part of the Gecko-F4 research program aimed at measuring the effects of weightlessness on the lizards' ability to procreate and develop in the harsh environment. However, soon after the spacecraft exited the atmosphere, mission control lost contact with the vessel which led to an attempt to reestablish communication that was only achieved later in the mission. When the satellite returned to Earth after its planned two-month mission had been cut short to 44 days, the space agency researchers reported that all the geckos had perished during the flight.
The exact cause that led to the deaths of the geckos was declared unknown by the scientific team in charge of the project. Reports from the Institute of Medical and Biological Problems in Russia have indicated that the lizards had been dead for at least a week prior to their return to Earth. A number of those connected to the mission have theorized that a failure in the vessel's heating system may have caused the cold blooded reptiles to freeze to death.
Included in the mission were a number of fruit flies, plants, and mushrooms which all survived the mission.[35]
Launch control
The military counterpart of Roscosmos is the Military Space Forces (VKO). The VKO controls Russia's Plesetsk Cosmodrome launch facility. Roscosmos and the VKO share control of the Baikonur Cosmodrome, where Roscosmos reimburses the VKO for the wages of many of the flight controllers during civilian launches. Roscosmos and the VKO also share control of the Yuri Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center. It has been announced that Russia is to build another spaceport in Tsiolkovsky, Amur Oblast.[36] The Vostochny Cosmodrome is scheduled to be finished by 2018.
Subsidiaries
As of 2017, Roscosmos had the following subsidiaries:[37]
- United Rocket and Space Corporation
- Strategicheskiye Punkty Upravleniya
- Glavcosmos
- Salavat Chemical Plant
- Turbonasos
- Moscow Institute of Thermal Technology
- IPK Mashpribor
- NPO Iskra
- Makeyev Rocket Design Bureau
- All-Russian Scientific Research Institute of Electromechanics
- Information Satellite Systems Reshetnev
- Russian Space Systems
- Sistemy precizionnogo priborostroenia
- Progress Rocket Space Centre
- Chemical Automatics Design Bureau
- NPO Energomash
- Proton-PM
- Tekhnicheskiy Tsentr Novator
- AO EKHO
- NIIMP-K
- TSKB Geofizika
- Osoboye Konstruktorskoye Byuro Protivopozharnoy Tekhniki
- Tsentralnoye Konstruktorskoye Byuro Transportnogo Mashinostroyeniya
- NII komandnykh priborov
- NPO Avtomatiki
- Zlatoust Machine-Building Plant
- Krasnoyarsk Machine-Building Plant
- Miass Machine-Building Plant
- Moskovskiy zavod elektromekhanicheskoy apparatury
- Nauchno-issledovatelskiy Institut Elektromekhaniki
- NPO Novator
- PKP IRIS
- NPP Geofizika-Kosmos
- NPP Kvant
- NPP Polyus
- Ispytatelnyy tekhnicheskiy tsentr - NPO PM
- NPO PM - Maloye Konstruktorskoye Byuro
- NPO PM - Razvitiye
- Sibpromproyekt
- Scientific Research Institute of Precision Instruments
- NIIFI
- NPO Izmeritelnoy Tekhniki
- OKB MEI
- 106 Experimental Optical and Mechanical Plant
- OAO Bazalt
- Nauchno-inzhenernyy tsentr elektrotekhnicheskogo universiteta
- Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center
- NPO Tekhnomash
- Keldysh Research Center
- Arsenal Design Bureau
- MOKB Mars
- NTTS Okhrana
- NII Mashinostroyeniya
- NPO Lavochkin
- Scientific Production Association Of Automation And Instrument-Building
- OKB Fakel
- Organizatsiya Agat
- TsNIIMash
- Centre for Operation of Space Ground-based Infrastructure (TsENKI)
- NTTS Zarya
- Gagarin Research and Test Cosmonaut Training Centre (Gagarin TsPK)
- NITs RKP
Historic Russian (Soviet) space gallery
People
 Sergei Korolev, the mastermind behind the first satellite, the first craft to deliver a human into orbit, and the craft from which the first spacewalk was performed.
Sergei Korolev, the mastermind behind the first satellite, the first craft to deliver a human into orbit, and the craft from which the first spacewalk was performed. Cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin, the first human to fly in space and to orbit the Earth.
Cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin, the first human to fly in space and to orbit the Earth..jpg) Cosmonaut Gherman Titov, the first man to orbit the Earth multiple times and to spend over 24 hours in space.
Cosmonaut Gherman Titov, the first man to orbit the Earth multiple times and to spend over 24 hours in space. Cosmonaut Alexei Leonov, the first person to perform a spacewalk.
Cosmonaut Alexei Leonov, the first person to perform a spacewalk. Cosmonaut Valentina Tereshkova, the first woman to fly in space.
Cosmonaut Valentina Tereshkova, the first woman to fly in space.
Spacecraft
 Vostok was the first spacecraft to carry a human being in space.
Vostok was the first spacecraft to carry a human being in space.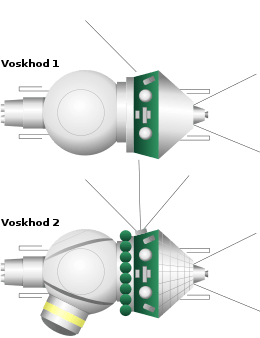 Voskhod was the first spacecraft capable of carrying more than 1 cosmonaut.
Voskhod was the first spacecraft capable of carrying more than 1 cosmonaut. Soyuz is the longest-serving crewed spacecraft design in history (1967– ), upgraded regularly.
Soyuz is the longest-serving crewed spacecraft design in history (1967– ), upgraded regularly. Progress is the longest-serving uncrewed cargo spacecraft (1978– ).
Progress is the longest-serving uncrewed cargo spacecraft (1978– ). The Soviet space program produced the canceled Space Shuttle Buran based on the discontinued Buran program.
The Soviet space program produced the canceled Space Shuttle Buran based on the discontinued Buran program.
Launch vehicles
 Soyuz rockets are responsible for launching all Soyuz and Progress spacecraft into space.
Soyuz rockets are responsible for launching all Soyuz and Progress spacecraft into space. Proton rockets are the heavylift workhorse of Russian space industry.
Proton rockets are the heavylift workhorse of Russian space industry.
Space stations
 First permanently crewed and "third-generation" space station, the Soviet/Russian Mir, which orbited the Earth from 1986 until 2001.
First permanently crewed and "third-generation" space station, the Soviet/Russian Mir, which orbited the Earth from 1986 until 2001.
See also
- American space program
- List of crewed spacecraft
- Russian space industry
- Ministry of general Machine Building of the Soviet Union
- TsNIIMash (Russian: ЦНИИмаш) is the Central Research Institute of Machine Building, an institute of the Russian aeronautics and space formed in 1946
- List of cosmonauts
- List of Russian aerospace engineers
- Timeline of Russian inventions and technology records
- International Space Olympics
- Medal "For Merit in Space Exploration"
- List of government space agencies
References
- "В Роскосмосе сравнили свой бюджет и NASA". 11 February 2020. Retrieved 17 February 2020.
- 25 февраля 1992 года образовано Российское космическое агентство, в настоящее время – Федеральное космическое агентство (Роскосмос).
- Путин подписал указ об упразднении Федерального космического агентства.
- Avaneesh Pandey (28 December 2015). "Russia's Federal Space Agency Dissolved, Responsibilities To Be Transferred To State Corporation". International Business Times.
- "Vladimir Putin abolishes Russian space agency Roscosmos". The Financial Express. 28 December 2015. Archived from the original on 1 January 2016.
- "Russia Merges United Rocket and Space Corporation with Roscosmos". Via Satellite. 23 January 2015. Retrieved 10 February 2015.
- Harvey, Brian (2007). "The design bureaus". The Rebirth of the Russian Space Program (1st ed.). Germany: Springer. ISBN 978-0-387-71354-0.
- Loff, Sarah (2015-10-28). "Oct. 31, 2000, Launch of First Crew to International Space Station". NASA. Retrieved 2020-01-24.
- Бюджет на 2013 год предполагает рекордное финансирование космонавтики. Spacecorp.ru. Retrieved on 2013-08-02.
- "Russian govt agrees 12.5 bln eur 10-yr space programme". Forbes. July 15, 2005. Archived from the original on 2007-05-01.
- ВЗГЛЯД / Российские ученые создали новую технологию для космических телескопов. Vz.ru. Retrieved on 2013-08-02.
- "No cut in Russian 2009 space spending, $2.4 bln on 3 programs". RIA Novosti. 2009-03-18. Retrieved 2009-08-23.
- "Russia allocates $3.8 billion for space programs in 2011". RIA Novosti. 2011-01-11.
- "Russia increases number of operational Glonass satellites to 17". RIA Novosti. 2009-06-04. Retrieved 2009-08-23.
- Afanasyev, Igor; Dmitri Vorontsov (2009-11-01). "Building on sand?The Russian ISS segment is to be completed by 2016". Russia & CIS Observer. Retrieved 2010-01-03.
- "Russia's Space Program in 2006: Some Progress but No Clear Direction". Moscow Defense Brief. 2006. Retrieved 2009-08-23.
- Kislyakov, Andrei (2008-05-15). "Russian space program bedeviled by problems". Retrieved 2009-08-23.
- Popovkin replaces Perminov at Russian space agency RIA Novosti 2011-04-29
- "Space Agency Chief Replaced". The Moscow Times. 2011-05-03.
- Messier, Doug (2013-08-30). "Rogozin: Russia to Consolidate Space Sector into Open Joint Stock Company". Parabolic Arc. Retrieved 2013-09-01.
- Nilolaev, Ivan (2013-07-03). "Rocket failure to lead to space industry reform". Russia Behind The Headlines. Retrieved 2013-09-01.
- Messier, Doug (2013-10-09). "Rogozin Outlines Plans for Consolidating Russia's Space Industry". Parabolic Arc. Retrieved 2013-10-11.
- Kelly Dickerson (28 December 2015). "Vladimir Putin just signed a decree to replace Russia's space agency". Tech Insider. Retrieved 2015-12-29.
- Putin challenges Roscosmos to "drastically improve" on space and launch, SpaceNews, 20 July 2018, accessed 21 July 2018.
- "Алексей Кудрин назвал "Роскосмос" рекордсменом по финансовым нарушениям — Meduza". Meduza (in Russian). Retrieved 2018-11-26.
- Chris Gebhardt (9 April 2009). "STS-132: PRCB baselines Atlantis' mission to deliver Russia's MRM-1". NASAspaceflight.com. Retrieved 12 November 2009.
- "Russian Launch Manifest". sworld.com.au. 2015. Retrieved June 15, 2014.
- www.flightglobal.com
- Zak, Anatoly. "Resurs-P remote-sensing satellite". RussianSpaceWeb. Retrieved 29 June 2013.
- ВЗГЛЯД / Роскосмос начал создание космической системы «Арктика». Vz.ru (2012-10-16). Retrieved on 2013-08-02.
- "Russia completes its Gonets orbital group". Retrieved 2015-03-31.
- Brumfiel, Geoff (Sep 2, 2014). "Russian Space Experiment On Gecko Sex Goes Awry". KPBS.
- Nichols, Mary (Sep 2, 2014). "Russia's Orbiting Sex Experiment Geckos Die In Space". Design & Trend. Archived from the original on 2014-10-06.
- "Sex geckos die in orbit on Russian space project". BBC News. Sep 2, 2014.
- Solovyov, Dmitry (April 28, 2016). "Russia launches first rocket from new spaceport at second attempt". Reuters. Retrieved July 15, 2016.
- "О мерах по созданию Государственной корпорации по космической деятельности "Роскосмос"". Pravo.gov.ru. Retrieved 1 August 2017.
External links
- (in Russian) Roscosmos home page in Russian
- Roscosmos home page in English
- Russian Space Program
- The future of the Russian space program. Infographics from RIA Novosti.


