Oroquieta
Oroquieta, officially the City of Oroquieta (Cebuano: Dakbayan sa Oroquieta; Tagalog: Lungsod ng Oroquieta), is a 4th class city and capital of the province of Misamis Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 70,757 people.[3]
Oroquieta | |
|---|---|
| City of Oroquieta | |
 | |
 Seal | |
| Nickname(s): City of Good Life | |
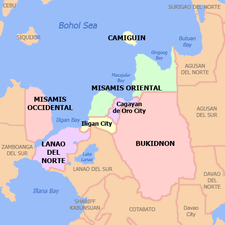
 Map of Misamis Occidental with Oroquieta highlighted | |
OpenStreetMap 
| |
.svg.png) Oroquieta Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 8°29′N 123°48′E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Northern Mindanao (Region X) |
| Province | Misamis Occidental |
| District | 1st District |
| Established | 1880 (Town) |
| Cityhood | January 1, 1970 |
| Barangays | 47 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Panlungsod |
| • Mayor | Lemuel Meyrick M. Acosta |
| • Vice Mayor | Jorge T. Almonte |
| • Congressman | Diego C. Ty |
| • Electorate | 51,487 voters (2019) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 237.88 km2 (91.85 sq mi) |
| Population (2015 census)[3] | |
| • Total | 70,757 |
| • Density | 300/km2 (770/sq mi) |
| • Households | 16,340 |
| Demonym(s) | Oroquietanon |
| Economy | |
| • Income class | 4th city income class |
| • Poverty incidence | 20.92% (2015)[4] |
| • Revenue (₱) | 462,067,940.34 (2016) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 7207 |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)88 |
| Climate type | tropical climate |
| Native languages | Subanon language Cebuano Tagalog |
| Catholic diocese | Archdiocese of Ozamiz |
| Patron saint | Our Lady of Holy Rosary |
| Website | www |
Etymology
Some sources reveal that the town got its name from the barrio in Spain where Father Toas Tomas Casado, the first parish priest, and General Domingo Moriones y Murillo, a hero in the Battle of Oroquieta, were born.
Another version is that Oroquieta had derived its name from the words oro (gold) and quita or kita (to find), in reference to the early inhabitants who had found gold along the river.
History
Layawan was the original name of Oroquieta, which was the barrio in the province of Misamis since 1861 until 1879. The early settlers then of the barrio were Boholanos. They found so many stray animals along the river, thus they named the place Layawan, which means a place of stray animals. A little later, Misamis was divided into two provinces, Misamis Occidental and Oriental. Then in 1880, Layawan changed its name to Oroquieta when it became a town.
Oroquieta became the capital (cabecera) on January 6, 1930. As capital town, people of various neighboring provinces came and inhabited in the place where they earn their living through fishing, farming, merchandising and other forms of businesses. Soon afterwards its income increased simultaneously with increase in population.
In 1942, Oroquieta was made the capital of the free Philippines by the recognized guerrillas and later the ongoing troops of the Philippine Commonwealth Army. (Personal interview with the late Atty. Vicente Blanco, Municipal Mayor during the Japanese Occupation) During this time, President Manuel L. Quezon, together with Sergio Osmeña Sr., a bodyguard and Major Manuel Nieto Sr., landed in Oroquieta after their evacuation from Corregidor to Australia.
The seat of government of the Free Philippines then was the Capitol. The Free Philippine Government was then issuing Misamis Occidental emergency notes. President Quezon, upon knowing that Oroquieta was made a capital of the Free Philippines and that the town was issuing emergency notes, authorized the Printing of the Mindanao emergency note.
Oroquieta was created a city under Republic Act 5518 and inaugurated as a chartered city on January 1, 1970. The charter converting the municipality of Oroquieta into a city were signed by President Marcos on June 25, 1969, in the presence of the then City Mayor Ciriaco C. Pastrano, with the newly elected councilors and other city officials.
Geography
Oroquieta City is bounded on the south by Aloran and the north by Lopez Jaena. On the eastern side is Iligan Bay, with Concepcion on the southwest and Sapang Dalaga on the northwest. Lowland plains and coastal lowlands are located in the city's eastern side while highlands and mountains tower over its western side.
The city occupies roughly 26,393 hectares (65,220 acres), the majority of which comprises the mountain barangays of Mialen, Toliyok, and Sebucal, averaging less than a thousand hectares per Barangay, the 47 barangays of the City outsize its urbanized counterparts.
Climate
| Climate data for Oroquieta City, Misamis Occidental | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 28 (82) |
28 (82) |
29 (84) |
31 (88) |
31 (88) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
29 (84) |
28 (82) |
30 (85) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 23 (73) |
23 (73) |
23 (73) |
23 (73) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
23 (73) |
24 (74) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 69 (2.7) |
44 (1.7) |
37 (1.5) |
29 (1.1) |
87 (3.4) |
137 (5.4) |
131 (5.2) |
141 (5.6) |
143 (5.6) |
134 (5.3) |
68 (2.7) |
53 (2.1) |
1,073 (42.3) |
| Average rainy days | 9.9 | 7.6 | 7.4 | 8.1 | 21.6 | 26.5 | 26.4 | 26.6 | 25.8 | 24.3 | 15.1 | 10.4 | 209.7 |
| Source: Meteoblue [5] | |||||||||||||
Barangays
Oroquieta City is politically subdivided into 47 barangays. Population 2015 census.
- Apil - 723
- Binuangan - 1,103
- Bolibol - 817
- Buenavista - 1,060
- Bunga - 1,266
- Buntawan - 426
- Burgos - 663
- Canubay - 3,313
- Clarin Settlement - 600
- Dolipos Bajo - 1,059
- Dolipos Alto - 669
- Dulapo - 712
- Dullan Norte - 605
- Dullan Sur - 403
- Lower Lamac - 3,366
- Layawan - 777
- Lower Langcangan - 1,519
- Lower Loboc - 2,167
- Lower Rizal - 447
- Malindang - 323
- Mialen - 253
- Mobod - 6,108
- Ciriaco C. Pastrano (Nilabo) - 408
- Paypayan - 320
- Pines - 2,988
- Poblacion I - 2,640
- Poblacion II - 967
- Proper Langcangan - 1,884
- San Vicente Alto (Dagatan) - 1,914
- San Vicente Bajo (Baybay Dagatan) - 1,746
- Sebucal - 219
- Senote - 888
- Taboc Norte - 2,565
- Taboc Sur - 2,633
- Talairon - 4,147
- Talic - 3,531
- Toliyok - 842
- Tipan - 1,216
- Tuyabang Alto - 586
- Tuyabang Bajo - 372
- Tuyabang Proper - 354
- Upper Langcangan - 2,590
- Upper Lamac - 1,623
- Upper Loboc - 1,879
- Upper Rizal (Tipalac) - 420
- Victoria - 320
- Villaflor (Transville) - 5,290
Demographics
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[3][6][7][8] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In the 2015 census, the population of Oroquieta was 70,757 people,[3] with a density of 300 inhabitants per square kilometre or 780 inhabitants per square mile.
Health
Hospitals and healthcare facilities:
- Misamis Occidental Provincial Hospital
- St. Therese Hospital
- Dignum Foundation Hospital
- Oroquieta Community Hospital
- Tamola-Tan Medical Center
Education
Students coming from Lanao del Norte, Zamboanga del Sur, Zamboanga del Norte and Misamis Occidental come to Oroquieta to pursue their college education.
| College/University | Location |
|---|---|
| Misamis University (MU) | Ozamis St. Poblacion 1, Oroquieta City |
| University of Science and Technology of Southern Philippines (USTSP) | Rizal St. Mobod Highway, Oroquieta City |
| Dr. Solomon U. Molina College (DSUMC) | Independence St. Villaflor, Oroquieta City |
| C-Lan Institute of Technology | LM Building, Ozamis St. Lower Langcangan, Oroquieta City |
| Oroquieta Agro Industrial School (OAIS) | Villaflor, Oroquieta City |
| Southern Capital College (SCC) | Juan Luna St. Poblacion 2, Oroquieta City |
| Stella Maris College (SMC) | Rizal St. Poblacion 1, Oroquieta City |
| Misamis Occidental Technological Institute (MOTI) | Pastrano St. Poblacion 1, Oroquieta City |
| Deor 'N Dune Academe School of Technology | JC Building, Barrientos St. Poblacion 2, Oroquieta City |
| National Institute for Technical Excellence, Inc. (NITEX) | De Barras Building, Barrientos St. Poblacion 2, Oroquieta City |
Secondary Schools
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Talairon National High School
- Oroquieta City National High School
- Mobod Integrated School
- Misamis Occidental Science and Technology High School
- Senote National High School
- Rizal National High School
- Bunga National High School
- Stella Maris College
City Officials 2019-2022
- Mayor: Lemuel Meyrick M. Acosta
- Vice Mayor: Jorge T. Almonte
- Congressman (1st District): Diego C. Ty
- Councilors:
- Sol Jude Gamalinda
- Jecjec Amboang
- Joel Aclao
- Donna Iyog
- Isaias Jun Claros
- Vincent Guantero
- Arthur Enanoria
- Noel Undag
- Aileen Taladua
- Diosebel Maghinay
See also
Notes
- "City". Quezon City, Philippines: Department of the Interior and Local Government. Retrieved 30 May 2013.
- "Province: Misamis Occidental". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- Census of Population (2015). "Region X (Northern Mindanao)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- "PSA releases the 2015 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Quezon City, Philippines. Retrieved 12 October 2019.
- "Oroquieta: Average Temperatures and Rainfall". Meteoblue. Retrieved 29 April 2020.
- Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region X (Northern Mindanao)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Region X (Northern Mindanao)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. NSO.
- "Province of Misamis Occidental". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Oroquieta. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Oroquieta City. |