Kiwi
Kiwi (/ˈkiwi/ KEE-wee)[4] or kiwis are flightless birds endemic to New Zealand, in the genus Apteryx and family Apterygidae. Approximately the size of a domestic chicken, kiwi are by far the smallest living ratites (which also consist of ostriches, emus, rheas, and cassowaries).
| Kiwi | |
|---|---|
 | |
| North Island brown kiwi (Apteryx mantelli) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Clade: | Novaeratitae |
| Order: | Apterygiformes Haeckel, 1866 |
| Family: | Apterygidae Gray, 1840[1] |
| Genus: | Apteryx Shaw, 1813[1] |
| Type species | |
| Apteryx australis | |
| Species | |
|
Apteryx haastii Great spotted kiwi | |
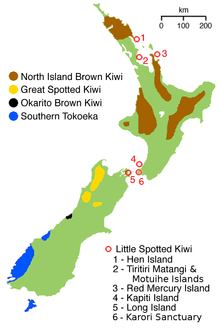 | |
| The distribution of each species of kiwi | |
| Synonyms[3] | |
|
Stictapteryx Iredale & Mathews, 1926 | |
DNA sequence comparisons have yielded the surprising conclusion that kiwi are much more closely related to the extinct Malagasy elephant birds than to the moa with which they shared New Zealand.[5] There are five recognised species, four of which are currently listed as vulnerable, and one of which is near-threatened. All species have been negatively affected by historic deforestation but currently the remaining large areas of their forest habitat are well protected in reserves and national parks. At present, the greatest threat to their survival is predation by invasive mammalian predators.
The kiwi's egg is one of the largest in proportion to body size (up to 20% of the female's weight) of any species of bird in the world.[6] Other unique adaptations of kiwi, such as their hairlike feathers, short and stout legs, and using their nostrils at the end of their long beak to detect prey before they ever see it, have helped the bird to become internationally well-known.
The kiwi is recognised as an icon of New Zealand, and the association is so strong that the term Kiwi is used internationally as the colloquial demonym for New Zealanders.[7]
Etymology
The Māori language word kiwi is generally accepted to be "of imitative origin" from the call.[8] However, some linguists derive the word from Proto-Nuclear Polynesian *kiwi, which refers to Numenius tahitiensis, the bristle-thighed curlew, a migratory bird that winters in the tropical Pacific islands.[9] With its long decurved bill and brown body, the curlew resembles the kiwi. So when the first Polynesian settlers arrived, they may have applied the word kiwi to the new-found bird.[10] The genus name Apteryx is derived from Ancient Greek "without wing": a-, "without" or "not"; pterux, "wing".[11]
The name is usually uncapitalised, with the plural either the anglicised "kiwis"[12] or, consistent with the Māori language, appearing as "kiwi" without an "‑s".[13]
Taxonomy and systematics
Although it was long presumed that the kiwi was closely related to the other New Zealand ratites, the moa, recent DNA studies have identified its closest relative as the extinct elephant bird of Madagascar,[5][14] and among extant ratites, the kiwi is more closely related to the emu and the cassowaries than to the moa.[5][15]
Research published in 2013 on an extinct genus, Proapteryx, known from the Miocene deposits of the Saint Bathans Fauna, found that it was smaller and probably capable of flight, supporting the hypothesis that the ancestor of the kiwi reached New Zealand independently from moas, which were already large and flightless by the time kiwi appeared.[16]
Species
There are five known species of kiwi, as well as a number of subspecies.
| ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
Relationships in the genus Apteryx[17]
| Image | Scientific name | Common Name | Distribution | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Apteryx haastii | great spotted kiwi or Roroa | New Zealand | The largest species, which stands about 45 cm (18 in) high and weighs about 3.3 kg (7.3 lb) (males about 2.4 kg (5.3 lb)). It has grey-brown plumage with lighter bands. The female lays just one egg, which both parents then incubate. The population is estimated to be over 20,000, distributed through the more mountainous parts of northwest Nelson, the northern West Coast, and the Southern Alps.[18] |
 | Apteryx owenii | little spotted kiwi | Kapiti Island | The small little spotted kiwi is unable to withstand predation by introduced pigs, stoats and cats, which have led to its extinction on the mainland. About 1350 remain on Kapiti Island. It has been introduced to other predator-free islands and appears to be becoming established with about 50 'Little Spots' on each island. A docile bird the size of a bantam, it stands 25 cm (9.8 in) high and the female weighs 1.3 kg (2.9 lb). She lays one egg, which is incubated by the male.[19] |
 | Apteryx rowi | Okarito kiwi, the rowi, or Okarito brown kiwi | South Island | The Okarito kiwi, first identified as a new species in 1994,[20] is slightly smaller, with a greyish tinge to the plumage and sometimes white facial feathers. Females lay as many as three eggs in a season, each one in a different nest. Male and female both incubate. The distribution of these kiwi is limited to a small area on the west coast of the South Island of New Zealand. However, studies of ancient DNA have revealed that, in prehuman times, it was far more widespread up the west coast of the South Island and was present in the lower half of the North Island, where it was the only kiwi species detected.[21] |
 | Apteryx australis | southern brown kiwi, Tokoeka, or Common kiwi | South Island | The southern brown kiwi is a relatively common species of kiwi. It is approximately the size of the great spotted kiwi and is similar in appearance to the brown kiwi, but its plumage is lighter in colour. Ancient DNA studies have shown that, in prehuman times, the distribution of this species included the east coast of South Island.[21] There are several subspecies of the Tokoeka recognised:
|
 | Apteryx mantelli or Apteryx australis | North Island brown kiwi | North Island | The North Island brown kiwi, Apteryx mantelli or Apteryx australis before 2000 (and still in some sources), is widespread in the northern two-thirds of the North Island and, with about 35,000 remaining,[23] is the most common kiwi. Females stand about 40 cm (16 in) high and weigh about 2.8 kg (6.2 lb), the males about 2.2 kg (4.9 lb). The North Island brown has demonstrated a remarkable resilience: it adapts to a wide range of habitats, even non-native forests and some farmland. The plumage is streaky red-brown and spiky. The female usually lays two eggs, which are incubated by the male.[24] |
Description

_(14728011026).jpg)
Their adaptation to a terrestrial life is extensive: like all the other ratites (ostrich, emu, rhea and cassowary), they have no keel on the sternum to anchor wing muscles. The vestigial wings are so small that they are invisible under the bristly, hair-like, two-branched feathers. While most adult birds have bones with hollow insides to minimise weight and make flight practicable, kiwi have marrow, like mammals and the young of other birds. With no constraints on weight due to flight requirements, brown kiwi females carry and lay a single egg that may weigh as much as 450 g (16 oz). Like most other ratites, they have no uropygial gland (preen gland). Their bill is long, pliable and sensitive to touch, and their eyes have a reduced pecten. Their feathers lack barbules and aftershafts, and they have large vibrissae around the gape. They have 13 flight feathers, no tail and a small pygostyle. Their gizzard is weak and their caecum is long and narrow.[25]
The eye of the kiwi is the smallest relative to body mass in all avian species resulting in the smallest visual field as well. The eye has small specialisations for a nocturnal lifestyle, but kiwi rely more heavily on their other senses (auditory, olfactory, and somatosensory system). The sight of the kiwi is so underdeveloped that blind specimens have been observed in nature, showing how little they rely on sight for survival and foraging. In an experiment, it was observed that one-third of a population of A. rowi in New Zealand under no environmental stress had ocular lesions in one or both eyes. The same experiment examined three specific specimens that showed complete blindness and found them to be in good physical standing outside of ocular abnormalities.[26] A 2018 study revealed that the kiwi's closest relatives, the extinct elephant birds, also shared this trait despite their great size.[27]
Unlike virtually every other palaeognath, which are generally small-brained by bird standards, kiwi have proportionally large encephalisation quotients. Hemisphere proportions are even similar to those of parrots and songbirds, though there is no evidence of similarly complex behaviour.[28]
Behaviour and ecology
Before the arrival of humans in the 13th century or earlier, New Zealand's only endemic mammals were three species of bat, and the ecological niches that in other parts of the world were filled by creatures as diverse as horses, wolves and mice were taken up by birds (and, to a lesser extent, reptiles, insects and gastropods).[29]
The kiwi's mostly nocturnal habits may be a result of habitat intrusion by predators, including humans. In areas of New Zealand where introduced predators have been removed, such as sanctuaries, kiwi are often seen in daylight. They prefer subtropical and temperate podocarp and beech forests, but they are being forced to adapt to different habitat, such as sub-alpine scrub, tussock grassland, and the mountains.[25] Kiwi have a highly developed sense of smell, unusual in a bird, and are the only birds with nostrils at the end of their long beaks. Kiwi eat small invertebrates, seeds, grubs, and many varieties of worms. They also may eat fruit, small crayfish, eels and amphibians. Because their nostrils are located at the end of their long beaks, kiwi can locate insects and worms underground using their keen sense of smell, without actually seeing or feeling them.[25] This sense of smell is due to a highly developed olfactory chamber and surrounding regions. It is a common belief that the kiwi relies solely on its sense of smell to catch prey but this has not been scientifically observed. Lab experiments have suggested that A. australis can rely on olfaction alone but is not consistent under natural conditions. Instead, the kiwi may rely on auditory and/or vibrotactile cues.[30]
Once bonded, a male and female kiwi tend to live their entire lives as a monogamous couple. During the mating season, June to March, the pair call to each other at night, and meet in the nesting burrow every three days. These relationships may last for up to 20 years.[31] They are unusual among other birds in that, along with some raptors, they have a functioning pair of ovaries. (In most birds and in platypuses, the right ovary never matures, so that only the left is functional.[25][32][33]) Kiwi eggs can weigh up to one-quarter the weight of the female. Usually, only one egg is laid per season. The kiwi lays one of the largest eggs in proportion to its size of any bird in the world,[34] so even though the kiwi is about the size of a domestic chicken, it is able to lay eggs that are about six times the size of a chicken's egg.[35] The eggs are smooth in texture, and are ivory or greenish white.[36] The male incubates the egg, except for the great spotted kiwi, A. haastii, in which both parents are involved. The incubation period is 63–92 days.[25] Producing the huge egg places significant physiological stress on the female; for the thirty days it takes to grow the fully developed egg, the female must eat three times her normal amount of food. Two to three days before the egg is laid there is little space left inside the female for her stomach and she is forced to fast.[37]
Lice in the genus Apterygon[38][39][40] and in the subgenus Rallicola (Aptericola)[41][42] are exclusively ectoparasites of kiwi species.[43]
Status and conservation
Nationwide studies show that only around 5–10% of kiwi chicks survive to adulthood without management.[44][45] However, in areas under active pest management, survival rates for North Island brown kiwi can be far higher. For example, prior to a joint 1080 poison operation undertaken by DOC and the Animal Health Board in Tongariro Forest in 2006, 32 kiwi chicks were radio-tagged. 57% of the radio-tagged chicks survived to adulthood.
Efforts to protect kiwi have had some success, and in 2017 two species were downlisted from endangered to vulnerable by the IUCN.[46]
Sanctuaries
In 2000, the Department of Conservation set up five kiwi sanctuaries focused on developing methods to protect kiwi and to increase their numbers.
- There are three kiwi sanctuaries in the North Island:
- Whangarei Kiwi Sanctuary (for Northland brown kiwi)
- Moehau Kiwi Sanctuary on the Coromandel Peninsula (Coromandel brown kiwi)
- Tongariro Kiwi Sanctuary near Taupo (western brown kiwi)
- and two in the South Island:
- Okarito Kiwi Sanctuary (Okarito kiwi)
- Haast Kiwi Sanctuary (Haast tokoeka)
A number of other mainland conservation islands and fenced sanctuaries have significant populations of kiwi, including:
- Zealandia fenced sanctuary in Wellington (little spotted kiwi)
- Maungatautari Restoration Project in Waikato (brown kiwi)
- Bushy Park Forest Reserve near Kai Iwi, Whanganui (brown kiwi)
- Otanewainuku Forest in the Bay of Plenty (brown kiwi)
- Hurunui Mainland Island, south branch, Hurunui River, North Canterbury (great spotted kiwi)
North island brown kiwi were introduced to the Cape Sanctuary in Hawke's Bay between 2008 and 2011, which in turn provided captive-raised chicks that were released back into Maungataniwha Native Forest.[47]
Operation "Nest Egg"
Operation Nest Egg is a programme run by the BNZ Save the Kiwi Trust—a partnership between the Bank of New Zealand, the Department of Conservation and the Royal Forest and Bird Protection Society. Kiwi eggs and chicks are removed from the wild and hatched and/or raised in captivity until big enough to fend for themselves—usually when they weigh around 1200 grams (42 ounces). They are then returned to the wild. An Operation Nest Egg bird has a 65% chance of surviving to adulthood—compared to just 5% for wild-hatched and raised chicks.[48] The tool is used on all kiwi species except little spotted kiwi.
1080 poison
In 2004, anti-1080 activist Phillip Anderton posed for the New Zealand media with a kiwi he claimed had been poisoned. An investigation revealed that Anderton lied to journalists and the public.[49] He had used a kiwi that had been caught in a possum trap. Extensive monitoring shows that kiwi are not at risk from the use of biodegradable 1080 poison.[50]
Threats
Introduced mammalian predators, namely stoats, dogs, ferrets, and cats, are the principal threats to kiwi. The biggest threat to kiwi chicks is stoats, while dogs are the biggest threat to adult kiwi.[45] Stoats are responsible for approximately half of kiwi chick deaths in many areas through New Zealand. Young kiwi chicks are vulnerable to stoat predation until they reach about 1–1.2 kg (2.2–2.6 lb) in weight, at which time they can usually defend themselves. Cats also to a lesser extent prey on kiwi chicks.[45] These predators can cause large and abrupt declines in populations. In particular, dogs find the distinctive strong scent of kiwi irresistible and easy to track, such that they can catch and kill kiwi in seconds. Motor vehicle strike is a threat to all kiwi where roads cross through their habitat. Badly set possum traps often kill or maim kiwi.[51]
Habitat destruction is another major threat to kiwi; restricted distribution and small size of some kiwi populations increases their vulnerability to inbreeding.[45] Research has shown that the combined effect of predators and other mortality (accidents etc.) results in less than 5% of kiwi chicks surviving to adulthood.[44]
Relationship to humans

The Māori traditionally believed that kiwi were under the protection of Tane Mahuta, god of the forest. They were used as food and their feathers were used for kahu kiwi—ceremonial cloaks.[52] Today, while kiwi feathers are still used, they are gathered from birds that die naturally, through road accidents, predation, or from captive birds.[53] Kiwi are no longer hunted and some Māori consider themselves the birds' guardians.[10]
Scientific documentation
In 1813, George Shaw named the genus Apteryx in his species description of the southern brown kiwi, which he called "the southern apteryx". Captain Andrew Barclay of the ship Providence provided Shaw with the specimen. Shaw's description was accompanied by two plates, engraved by Frederick Polydore Nodder; they were published in volume 24 of The Naturalist's Miscellany.[54]
Zoos
In 1851, London Zoo became the first zoo to keep kiwi. The first captive breeding took place in 1945.[55] As of 2007 only 13 zoos outside New Zealand hold kiwi.[56] The Frankfurt Zoo has 12, the Berlin Zoo has seven, Walsrode Bird Park has one, the Avifauna Bird Park in the Netherlands has three, the San Diego Zoo has five, the San Diego Zoo Safari Park has one, the National Zoo in Washington, DC has eleven, the Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute has one, and the Columbus Zoo and Aquarium has three.[57][58]
As a national symbol
The kiwi as a symbol first appeared in the late 19th century in New Zealand regimental badges. It was later featured in the badges of the South Canterbury Battalion in 1886 and the Hastings Rifle Volunteers in 1887. Soon after, the kiwi appeared in many military badges; and in 1906, when Kiwi Shoe Polish was widely sold in the UK and the US, the symbol became more widely known.[59]
During the First World War, the name "kiwi" for New Zealand soldiers came into general use, and a giant kiwi (now known as the Bulford kiwi) was carved on the chalk hill above Sling Camp in England. Usage has become so widespread that all New Zealanders overseas and at home are now commonly referred to as "Kiwis".[60]
The kiwi has since become the best-known national symbol for New Zealand, and the bird is prominent in the coat of arms, crests and badges of many New Zealand cities, clubs and organisations. At the national level, the red silhouette of a kiwi is in the centre of the roundel of the Royal New Zealand Air Force.[36][61] The kiwi is featured in the logo of the New Zealand Rugby League, and the New Zealand national rugby league team are nicknamed the Kiwis.
A kiwi has featured on the reverse side of three New Zealand coins: the one florin (two-shilling) coin from 1933 to 1966, the twenty-cent coin from 1967 to 1990, and the one-dollar coin since 1991. In currency trading the New Zealand dollar is often referred to as "the kiwi".[62]
References
Notes
- Brands, Sheila (14 August 2008). "Systema Naturae 2000 / Classification, Family Apterygidae". Project: The Taxonomicon. Retrieved 4 February 2009.
- Hemming, Francis, ed. (1958) [1916]. "Opinion 67. One hundred and two bird names placed in the Official List of Generic Names". Facsimile Edition of Opinions 1–133. Opinions and Declarations Rendered by the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature. 1B. London: International Trust for Zoological Nomenclature. p. 179.
- Gill (2010). "Checklist of the birds of New Zealand, Norfolk and Macquarie Islands, and the Ross Dependency, Antarctica" (PDF) (4th ed.). Te Papa Press. Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- "Kiwi | Definition of Kiwi at Dictionary.com". Dictionary.com. Retrieved 23 December 2019.
- Mitchell, K. J.; Llamas, B.; Soubrier, J.; Rawlence, N. J.; Worthy, T. H.; Wood, J.; Lee, M. S. Y.; Cooper, A. (23 May 2014). "Ancient DNA reveals elephant birds and kiwi are sister taxa and clarifies ratite bird evolution" (PDF). Science. 344 (6186): 898–900. doi:10.1126/science.1251981. hdl:2328/35953. PMID 24855267.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- "Birds: Kiwi". San Diego Zoo. Retrieved 19 September 2008.
- "Kiwis/Kiwi - New Zealand Immigration Service (Summary of Terms)". Glossary.immigration.govt.nz. Retrieved 13 September 2012.
- "Kiwi", The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (4th ed.), Houghton Mifflin, 2006
- "kiwi", Polynesian Lexicon Project Online, NZ
- "Kiwi a Maori", About the bird, Save the kiwi, archived from the original on 5 July 2011
- Gotch, AF (1995) [1979]. "Kiwis". Latin Names Explained. A Guide to the Scientific Classifications of Reptiles, Birds & Mammals. London: Facts on File. p. 179. ISBN 978-0-8160-3377-5.
- "the definition of kiwis". Dictionary.com. Retrieved 17 November 2016.
- "Please don't eat Kiwis". Another Spectrum. 17 August 2015. Retrieved 17 November 2016.
- "Little kiwi, huge extinct elephant bird were birds of a feather", The Times of India, IN
- News in Science, AU: ABC
- New Zealand. "Did small kiwi fly from Australia? - Canterbury Museum - New Zealand Natural and Human Heritage. Christchurch, NZ". Canterbury Museum. Archived from the original on 19 March 2014. Retrieved 30 July 2014.
- "Great Spotted Kiwi Classification". University of Wisconsin. Retrieved 9 July 2008.
- BirdLife International (2012). "Apteryx haastii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2012. Retrieved 26 November 2013.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- BirdLife International (2012). "Apteryx owenii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2012. Retrieved 26 November 2013.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- "Rowi: New Zealand native land birds". New Zealand Department of Conservation (DOC). Archived from the original on 19 February 2013. Retrieved 25 July 2009.
- Shepherd, L.D. & Lambert, D.M. (2008) Ancient DNA and conservation: lessons from the endangered kiwi of New Zealand Molecular Ecology 17, 2174–84
- "Apteryx australis (brown kiwi)". Animal Diversity Web. Retrieved 26 March 2017.
- BirdLife International (2008). "Northern Brown Kiwi". BirdLife Species Factsheet. Retrieved 6 February 2009.
- McLENNAN, J.A. (1988). "Breeding of North Island Brown Kiwi, Apteryx Australis Mantelli, in Hawke's Bay, New Zealand". New Zealand Journal of Ecology. 11: 89–97. JSTOR 24052821.
- Davies, S.J.J.F. (2003). "8 Birds I Tinamous and Ratites to Hoatzins". In Hutchins, Michael (ed.). Grzimek's Animal Life Encyclopedia (2nd ed.). Farmington Hills, MI: Gale Group. pp. 89–90. ISBN 978-0-7876-5784-0.
- Moore, Bret A.; Paul-Murphy, Joanne R.; Tennyson, Alan J. D.; Murphy, Christopher J. (15 September 2017). "Blind free-living kiwi offer a unique window into the ecology and evolution of vertebrate vision". BMC Biology. 15 (1): 85. doi:10.1186/s12915-017-0424-0. ISSN 1741-7007. PMC 5602912. PMID 28915882.
- "Study: Elephant Birds were Nocturnal, Possibly Blind | Paleontology | Sci-News.com". Breaking Science News | Sci-News.com. Retrieved 4 November 2018.
- Corfield, J.; Wild, J.M.; Hauber M.E. & Kubke, M.F. (2008). "Evolution of brain size in the Palaeognath lineage, with an emphasis on New Zealand ratites". Brain, Behavior and Evolution. 71 (2): 87–99. doi:10.1159/000111456. PMID 18032885.
- Kolbert, Elizabeth (22 December 2014). "The Big Kill". The New Yorker. Retrieved 16 December 2014.
- Cunningham, Susan; Castro, Isabel; Alley, Maurice (1 October 2007). "A new prey-detection mechanism for kiwi (Apteryx spp.) suggests convergent evolution between paleognathous and neognathous birds". Journal of Anatomy. 211 (4): 493–502. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2007.00786.x. ISSN 1469-7580. PMC 2375824. PMID 17711422.
- Save the Kiwi, NZ, formerly Kiwi Recovery.
- Fitzpatrick, F.L., (1934). Unilateral and bilateral ovaries in raptorial birds. The Wilson Bulletin, 46(1): 19-22
- Kinsky, F.C., (1971). The consistent presence of paired ovaries in the Kiwi (Apteryx) with some discussion of this condition in other birds. Journal of Ornithology 112(3): 334–357.
- "Wilderness New Zealand", Official Guide Book, Auckland Zoo
- Save the kiwi, archived from the original on 24 September 2011
- "The Kiwi Bird, New Zealand's Indigenous Flightless Bird". Archived from the original on 10 February 2010. Retrieved 16 January 2009.
- Piper, Ross (2007), Extraordinary Animals: An Encyclopedia of Curious and Unusual Animals, Greenwood Press
- Clay, Theresa (1960). "A new genus and species of Menoponidae (Mallophaga, Insecta) from Apteryx". Annals and Magazine of Natural History. Series 13. 3 (33): 571–576. doi:10.1080/00222936008651059.
- Tandan, B. K. (1972). "The Species of Apterygon (Insecta: Phthiraptera: Amblycera) Parasitic on Kiwis (Apteryx)" (PDF). New Zealand Journal of Science. 15 (1): 52–69.
- Palma, Ricardo L.; Price, Roger D. (2004). "Apterygon okarito a new species of chewing louse (Insecta: Phthiraptera: Menoponidae) from the Okarito brown kiwi (Aves: Apterygiformes: Apterygidae)". New Zealand Journal of Zoology. 31 (1): 67–73. doi:10.1080/03014223.2004.9518361.
- Harrison, Launcelot (1915). "Mallophaga from Apteryx, and their Significance; with a Note on the Genus Rallicola" (PDF). Parasitology. 8 (1): 88–100. doi:10.1017/S0031182000010428.
- Clay, Theresa (1972). "The Species of Rallicola (Insecta: Phthiraptera: Ischnocera) Parasitic on Kiwis (Apteryx)" (PDF). New Zealand Journal of Science. 15 (1): 70–76.
- Palma, Ricardo L. (2017). Phthiraptera (Insecta) A catalogue of parasitic lice from New Zealand. Fauna of New Zealand. 76. Lincoln, New Zealand: Landcare Research. pp. 39–41, 186–188, 245. doi:10.7931/J2/FNZ.76. ISBN 978-0-947525-19-4.
- JA McLennan; et al. (1996), Role of predation in the decline of kiwi, Apteryx spp., in New Zealand (PDF)
- "Facts and threats to kiwi". Department of Conservation. Retrieved 20 February 2018.
- "Brown kiwi and rowi no longer considered endangered". NZ Herald. 5 December 2017. Retrieved 26 May 2018.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 18 January 2015. Retrieved 11 August 2014.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Operation Nest Egg, NZ: Save the wiki, archived from the original on 3 September 2011
- Macbrayne, Rosaleen (3 September 2004). "Poison campaigner fined after using kiwi in stunt". The New Zealand Herald. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- Robertson, HA; et al. (1999). "Survival of brown kiwi exposed to 1080 poison used for control of brushtail possums in Northland, New Zealand". Archived from the original on 29 September 2011.
- "Threats to Kiwi" Archived 13 January 2015 at the Wayback Machine, Whakatane Kiwi Trust
- "Kiwi and people: early history", Te Ara, NZ: The Government
- New Zealand Embassy and Smithsonian National Zoo host handover ceremony to return kiwi feathers to New Zealand, New Zealand Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade
- Shaw, George; Nodder, Frederick P. (1813). "Apteryx australis. The Southern Apteryx". The Naturalist's Miscellany. 24. Plates 1057–1058.
- "Captive management plan for kiwi" (PDF). New Zealand Department of Conservation. June 2004. p. 10. Retrieved 17 August 2009.
- Fowler, Murray E; Miller, R Eric (2007), Zoo and Wild Animal Medicine Current Therapy, Elsevier Health Sciences, p. 215
- Gibson, Eloise (29 April 2010). "Shy envoys off on their OE". New Zealand Herald. p. a4.
- "Kiwi Fun Facts". Smithsonian's National Zoo. 7 October 2016. Retrieved 23 November 2016.
- Brooks, Miki. Lessons From a Land Down Under: Devotions from New Zealand. Lulu. pp. 3–4. ISBN 9780557098842.
- "A kiwi country", Te Ara
- "The Kiwi". About New Zealand. NZ Search. Archived from the original on 24 May 2010. Retrieved 16 January 2009.
- "Kiwi falls after Wheeler talks down intervention, QE". The National Business Review. NZ. 27 October 2012. Retrieved 27 October 2012.
- Kerry-Jayne, Kerry-Jayne. "Petrels, Breeding". Te Ara. Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 13 April 2019.
- Sanz-Aguilar, Ana (2012). "Is Laying a Large Egg Expensive? Female-Biased Cost of First Reproduction in a Petrel" (PDF). The Auk. BioOne Complete. 129 (3): 510–516. doi:10.1525/auk.2012.12011. hdl:10261/99097.
Further reading
- Burbidge, M.L., Colbourne, R.M., Robertson, H.A., and Baker, A.J. (2003). Molecular and other biological evidence supports the recognition of at least three species of brown kiwi. Conservation Genetics, 4(2):167–77
- Cooper, Alan et al. (2001). Complete mitochondrial genome sequences of two extinct moas clarify ratite evolution. Nature, 409: 704–07.
- SavetheKiwi.org "Producing an Egg". Archived from the original on 29 June 2007. Retrieved 13 August 2007.
- "Kiwi (Apteryx spp.) recovery plan 2008–2018. (Threatened Species Recovery Plan 60)" (PDF). Wellington, NZ: Department of Conservation. 2008. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- Le Duc, D., G. Renaud, A. Krishnan, M.S. Almen, L. Huynen, S. J. Prohaska, M. Ongyerth, B. D. Bitarello, H. B. Schioth, M. Hofreiter, et al. 2015. Kiwi genome provides insights into the evolution of a nocturnal lifestyle. Genome Biology 16:147-162.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Apteryx. |
| Look up kiwi in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1920 Encyclopedia Americana article Apteryx. |
- "Great Spotted Kiwi", Species: birds, ARKive, archived from the original on 14 June 2007, retrieved 31 October 2006.
- "Land birds: Kiwi", Native animals: birds, NZ: Department of Conservation, archived from the original on 3 October 2009, retrieved 25 July 2009.
- Kiwi recovery, NZ: BNZ Save The Kiwi Trust.
- Kiwi, TerraNature.
- How the Kiwi Lost his Wings (Maori legend), /hoopermuseum.earthsci.carleton.ca.
- "Kiwi", Te Ara – the Encyclopedia of New Zealand, NZ: The Government, archived from the original on 8 June 2008.
- "North Island Brown Kiwi feeding in the wild", YouTube (daylight video).
- Pests & threats, Taranaki Kiwi Trust, archived from the original on 2 April 2012.
- "Case studies on 1080: the facts", 1080 and kiwi, NZ: 1080 facts, archived from the original on 2 December 2011.