Little spotted kiwi
The little spotted kiwi, or little grey kiwi,[2] Apteryx owenii, is a small flightless bird in the kiwi family Apterygidae. It is the smallest species of all 5 kiwis, at about 0.9 to 1.9 kg (2.0–4.2 lb), about the size of a bantam. It is endemic to New Zealand, and in pre-European times occurred in both main islands, but is now restricted to a number of small offshore islands and mainland reserves protected by pest-exclusion fences.
| Little spotted kiwi | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Foraging at Zealandia EcoSanctuary, Wellington | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Apterygiformes |
| Family: | Apterygidae |
| Genus: | Apteryx |
| Species: | A. owenii |
| Binomial name | |
| Apteryx owenii | |
| Subspecies | |
|
A. o. owenii | |
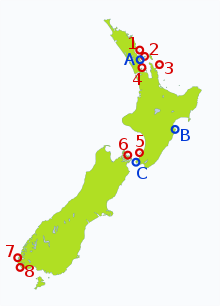 | |
| The distribution of little spotted kiwi.
Predator-free islands:
Mainland:
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
List
| |
Taxonomy

The little spotted kiwi is a ratite and belongs to the Apterygiormes Order, and the Apterygidae Family. Their binomial name Apteryx owenii breaks down to without wings and owenii which is named after Sir Richard Owen.[5] Today, only the nominate subspecies A. o. owenii exists. A subspecies, A. o. iredalei, from the North Island has been described. It became extinct in the late 19th century,[6] but the subspecies isn't universally accepted as valid.[7]
The little spotted kiwi was first described in 1847 by John Gould from a specimen obtained by F. Strang. The locality is not recorded but it probably came from Nelson or Marlborough. In 1873, Henry Potts published an account of its habits and about this time specimens were collected in South Westland and sent to England.[2]
Description
The little spotted kiwi has a length of 35 to 45 cm (14–18 in) and the weight of the male is 0.88 to 1.36 kg (1.9–3.0 lb) and the female weighs 1 to 1.95 kg (2.2–4.3 lb), making it the smallest species of kiwi.[7] Their feathers are pale-mottled grey, with fine white mottling, and are shaggy looking.[8] They lack aftershafts and barbules. They have large vibrissae feathers around the gape. They lack a tail, but have a small pygostyle.[2] Their bill is ivory and long and their legs are pale.[8]
Range and habitat
Studies on Kapiti Island show that they prefer flax, seral, and older forest habitats. Lower numbers are found in rough grassland and scrub, indicating that either they prefer other habitats or they simply need a larger territory to support themselves in these areas.[8]
Behaviour
Little spotted kiwis eat grubs and other small insects that are found underground, and occasionally eat berries. Using its sharp talons and long beak, it digs into the ground and then shoves its long beak down the softened ground. Since they can't fly to get to insects or food on trees and their eyesight is very poor, they depend on a keen sense of smell, long beak and talons.[2]They are also nocturnal. Little spotted kiwi call occasionally each night to advertise territory and to maintain contact with partners. Often pairs will duet. They are very territorial, and fight conspecifics with their sharp claws, resulting in many feathers on the ground.
Reproduction

They nest in an excavated burrow, dug by both birds and sometimes line the nest with plant material. Eggs are laid from July to January. The clutch size is one to two eggs (15% have 2), and are incubated by the male for a period of 63–76 days. After hatching they stay in the nest for 2–3 weeks and require feeding for 4 weeks.[2] The largest egg in comparison with the size of the bird is laid by the little spotted kiwi. Its egg accounts for 26 percent of its own weight—the equivalent of a human woman giving birth to a six-year-old child.
Conservation
| Location | Population | Date | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hen Island | 50 | 2012 | Increasing |
| Kapiti Island | c.1200 | 2012 | Stable |
| Red Mercury Island | 70 | 2012 | Increasing |
| Long Island | 50 | 2012 | Increasing |
| Tiritiri Matangi | 80 | 2012 | Increasing |
| Zealandia Wildlife Sanctuary | 120 | 2012 | Increasing[9] |
| Motuihe Island | 30 | 2012 | Stable |
| Anchor Island | 20 | 2015 | Increasing |
| Chalky Island | 50 | 2012 | Stable |
| Total (New Zealand) | 1670 | 2012 | Increasing |

At the time it was described, the species was common on the western side of the South Island and in Marlborough. Then a regular trade in skins sprang up and large numbers were collected for European museums. Further, with the advance of European settlement, birds were killed by prospectors and others for food and their attendant dogs and cats took their toll. The species was extinct on the North Island by 1938 when the last four South Island birds were moved from d'Urville Island to the population that had been established on Kapiti Island.[7] After they were released on Kapiti Island, they were also moved to Red Mercury Island, Hen Island, Tiritiri Matangi Island, Chalky Island, and Long Island in the Queen Charlotte Sound. In 2000, about 20 little spotted kiwis were released into Karori Wildlife Sanctuary. This was the first time since the 19th century that little spotted kiwis could be found on the mainland of the North Island.[8]In 2015, 20 kiwis were translocated from Kapiti Island to Anchor Island.
As the smallest species of kiwi, the little spotted kiwi would be very vulnerable to the main kiwi predators like cats, dogs, and stoats, however it is now restricted to several off-shore island reserves (mainly Kapiti Island) which are mostly free of introduced predators. The little spotted kiwi's conservation status is listed as "range restricted" (by 'Save the Kiwi'), with a growing population. Formerly classified as "vulnerable" by the IUCN,[10] it was suspected to be more numerous than generally assumed. Following the evaluation of its population size, this was found to be correct, and it was consequently downlisted to "near threatened" status in 2008 as, although not rare, its small range puts it at risk. The lack of predators, apart from weka (Gallirallus australis), is important to its increasing numbers. It has an occurrence range of 31 km2 (12 sq mi), and a population of 1600 was estimated in the year 2012.[1]
Footnotes
- BirdLife International (2012). "Apteryx owenii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2012. Retrieved 26 November 2013.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Davies, S. J. J. F. (2003)
- Gould, John (1847). "On a new species of Apteryx". Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London. 15 (1): 93–94. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.1847.tb00159.x.
- Gill; et al. (2010). "Checklist of the birds of New Zealand, Norfolk and Macquarie Islands, and the Ross Dependency, Antarctica" (PDF) (4th ed.). Te Papa Press. Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- Gotch, A. F. (1995)
- Hume, J. P.; Walters, M. (2012). Extinct Birds. London: A & C Black. pp. 23–24. ISBN 1-4081-5725-X.
- Folch, A.; Jutglar, F.; Garcia, E.F.J. (2018). del Hoyo, Josep; Elliott, Andrew; Sargatal, Jordi; Christie, David A.; de Juana, Eduardo (eds.). "Little Spotted Kiwi (Apteryx owenii)". Handbook of the Birds of the World Alive. Barcelona, Spain: Lynx Edicions. Retrieved 18 August 2018.
- BirdLife International (2008a)
- Save the Kiwi.org
- BirdLife International (2008b)
References
- BirdLife International (2008a). "Little Spotted Kiwi - BirdLife Species Factsheet". Data Zone. Retrieved 6 Feb 2009.
- BirdLife International (2008b). "What's New (2008)". IUCN RedList. Archived from the original on 2007-08-28. Retrieved 4 Feb 2009.
- Davies, S.J.J.F. (2003). "Kiwis". In Hutchins, Michael (ed.). Grzimek's Animal Life Encyclopedia. 8 Birds I Tinamous and Ratites to Hoatzins (2nd ed.). Farmington Hills, MI: Gale Group. pp. 89–90, 92–93. ISBN 0-7876-5784-0.
- Gotch, A.F. (1995) [1979]. "Kiwis". Latin Names Explained. A Guide to the Scientific Classifications of Reptiles, Birds & Mammals. London: Facts on File. p. 181. ISBN 0-8160-3377-3.
- "Little Spotted Kiwi". Kiwis for Kiwi. Retrieved 9 January 2020.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Apteryx owenii. |