Japanese archipelago
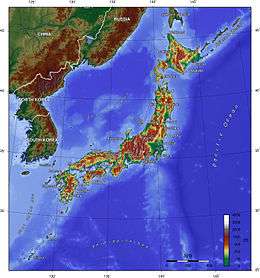
The Japanese archipelago (日本列島, Nihon Rettō) is a group of 6,852 islands that form the country of Japan. It extends over 3,000 km (1,900 mi)[1] from the Sea of Okhotsk southwest to the Philippine Sea south along the northeastern coast of the Eurasia continent. It consists of islands from the Sakhalin Island Arc, the Northeastern Japan Arc to the Ryukyu Islands and the Nanpō Islands. Japan is the largest island country in East Asia and the 4th largest island country in the world with 377,975.24 km2 (145,937.06 sq mi).[2][3] It has the 8th largest exclusive economic zone of 4,470,000 km2 (1,730,000 sq mi).[4]
.svg.png) Japanese archipelago shown in dark green | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 37°30′52″N 137°42′44″E |
| Administration | |

Terminology
The term mainland Japan is used to refer to the mainland from the remote islands. It is also used when referring to the main islands Hokkaido, Honshu, Kyushu, Shikoku and Okinawa.[5] It included Karafuto Prefecture (Sakhalin) until the end of World War II.
The term Home Islands was used at the end of World War II to define the area of Japan to which its sovereignty and the constitutional rule of the Emperor would be restricted. The term is also commonly used today to distinguish the archipelago from Japan's colonies and other territories in the first half of the 20th century.[6]
Palaeogeography
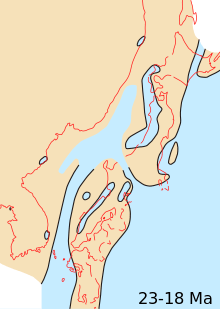 Japanese archipelago, Sea of Japan and surrounding part of continental East Asia in Early Miocene (23-18 Ma)
Japanese archipelago, Sea of Japan and surrounding part of continental East Asia in Early Miocene (23-18 Ma) Japanese archipelago, Sea of Japan and surrounding part of continental East Asia in Middle Pliocene to Late Pliocene (3.5-2 Ma)
Japanese archipelago, Sea of Japan and surrounding part of continental East Asia in Middle Pliocene to Late Pliocene (3.5-2 Ma) Japanese archipelago at the Last Glacial Maximum about 20,000 years ago, thin black line indicates present-day shorelinesVegetated landUnvegetated landOcean
Japanese archipelago at the Last Glacial Maximum about 20,000 years ago, thin black line indicates present-day shorelinesVegetated landUnvegetated landOcean
Geography
The archipelago consists of 6,852 islands[7] (here defined as land more than 100 m in circumference), of which 430 are inhabited.[8] The five main islands, from north to south, are Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa.[5] Honshu is the largest and referred to as the Japanese mainland.[9]
The current Japanese archipelago topography is:
- Sakhalin, Hokkaido, Honshu, Japan island arc composed of Shikoku and its surrounding islands;
- Kyushu, Ryukyu arc composed of Nansei Islands and other surrounding islands;
- Eastern part of Hokkaido (part of the Kuril arc);
- Nanpō Islands, Izu Peninsula (part of Izu-Bonin-Mariana Arc).
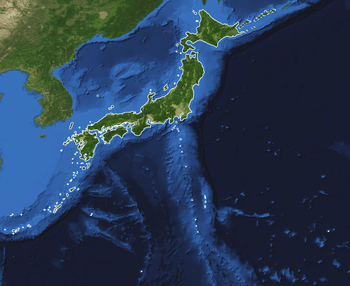

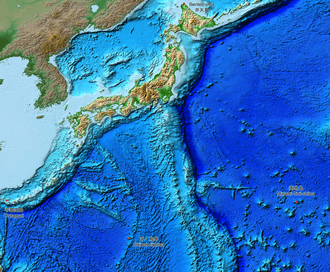
Islands and prefectures
- Hokkaido – The second largest island of Japan, and the largest and northernmost prefecture, which consists of 14 subprefectures.

- Hidaka Subprefecture
- Hiyama Subprefecture
- Iburi Subprefecture
- Ishikari Subprefecture
- Kamikawa Subprefecture
- Kushiro Subprefecture
- Nemuro Subprefecture
- Okhotsk Subprefecture
- Oshima Subprefecture
- Rumoi Subprefecture
- Shiribeshi Subprefecture
- Sorachi Subprefecture
- Sōya Subprefecture
- Tokachi Subprefecture
- Honshu – The largest and the most populated island of Japan, which consists of five regions.
- Tōhoku region consists of six prefectures.
- Kantō region consists of seven prefectures, including the capital of Japan which is the Tokyo Metropolis.
- Chūbu region consists of nine prefectures.
- Kansai region consists of seven prefectures.
- Chūgoku region consists of five prefectures.
- Shikoku – The second smallest and second least populated of the five main islands (after Okinawa), consisting of four prefectures.
- Kyushu – The third largest island of the archipelago, which consists of eight prefectures, including the Okinawa Islands in the Ryukyu island arc.
- Okinawa – The smallest and least populated of the five main islands. It is part of the Kyushu region.
- Sakhalin – Previously known and administered by the Empire of Japan as Karafuto Prefecture and a part of the Russian Federation, was sometimes considered to be geographically part of the Japanese archipelago. Japan renounced its claim to the island after World War II in the 20th century.[10]
See also
- Geography of Japan
- Japan in the Paleolithic
- List of islands of Japan
- Extreme points of Japan
- Mainland Japan
References
- "Water Supply in Japan". Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Archived from the original (website) on January 26, 2018. Retrieved 26 September 2018.
- "Island Countries Of The World". WorldAtlas.com. Archived from the original on 2017-12-07. Retrieved 2019-08-10.
- "令和元年全国都道府県市区町村別面積調(10月1日時点), Reiwa 1st year National area of each prefecture municipality (as of October 1)" (in Japanese). Geospatial Information Authority of Japan. 26 December 2019. Retrieved 2 January 2020.
- "日本の領海等概念図". 海上保安庁海洋情報部. Archived from the original on August 12, 2018. Retrieved 12 August 2018.
- 離島とは(島の基礎知識) [what is a remote island?]. MLIT (Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism) (in Japanese). Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. 22 August 2015. Archived from the original (website) on 2007-11-13. Retrieved 9 August 2019.
MILT classification 6,852 islands(main islands: 5 islands, remote islands: 6,847 islands)
- Milton W. Meyer, Japan: A Concise History, 4th ed. Lanham, Maryland: Rowman & Littlefield, 2012, ISBN 9780742541184, p. 2.
- "離島とは(島の基礎知識)". Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. Archived from the original (website) on November 13, 2007. Retrieved 3 October 2018.
- "Islands in Abundance". Look Japan. Vol. 43 no. 493–504. Limited. p. 35.
- "Japanese Archipelago", TheFreeDictionary.com, retrieved 24 June 2013.
- "The Transfer of Sakhalin". The Chautauquan. Vol. 42. p. 6.