List of regions of Japan
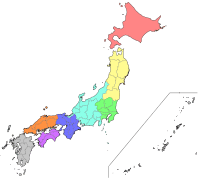
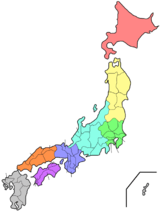
Japan is traditionally divided into eight regions. They are not official administrative units, but are used for regional division of Japan in a number of contexts. For instance, maps and geography textbooks divide Japan into the eight regions, weather reports usually give the weather by region, and many businesses and institutions use their home region as part of their name (Kinki Nippon Railway, Chūgoku Bank, Tōhoku University, etc.).
| Administrative divisions of Japan |
|---|
| Prefectural |
| Prefectures |
| Sub-prefectural |
| Municipal |
| Sub-municipal |
Each region groups several of the country's 47 prefectures, except for the region of Hokkaidō which corresponds to Hokkaidō Prefecture. Of the four main islands of Japan, three make up a region each while the largest island of Honshū is divided into five regions. Okinawa Prefecture is usually included in Kyūshū, but is sometimes treated as its own ninth Okinawa region.
While Japan has eight High Courts, their jurisdictions do not correspond to the eight traditional regions below. (See Judicial system of Japan for details).
Table
| Region | Population | Area in km2[1] | Prefectures contained |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hokkaidō | 5.4 million[2] | 83,000 | Hokkaidō |
| Tōhoku | 8.91 million[3] | 67,000 | Akita, Aomori, Fukushima, Iwate, Miyagi, Yamagata |
| Kantō | 43.3 million[4] | 32,000 | Chiba, Gunma, Ibaraki, Kanagawa, Saitama, Tochigi, Tōkyō |
| Chūbu | 21.4 million[5] | 67,000 | Aichi, Fukui, Gifu, Ishikawa, Nagano, Niigata, Shizuoka, Toyama, Yamanashi |
| Kansai (also known as Kinki) | 22.5 million[6] | 33,000 | Hyōgo, Kyōto, Mie, Nara, Ōsaka, Shiga, Wakayama |
| Chūgoku | 7.3 million[7] | 32,000 | Hiroshima, Okayama, Shimane, Tottori, Yamaguchi |
| Shikoku | 3.8 million[8] | 19,000 | Ehime, Kagawa, Kōchi, Tokushima |
| Kyūshū | 14.5 million[9] | 44,000 | Fukuoka, Ōita, Kagoshima, Kumamoto, Miyazaki, Nagasaki, Okinawa, Saga |
Regions and islands
This is a list of Japan's major islands, traditional regions, and subregions, going from northeast to southwest.[10][11] The eight traditional regions are marked in bold.
- Hokkaidō (the island and its archipelago)
- Honshū
- Tōhoku region (northern part)
- Kantō region (eastern part)
- Nanpō Islands (part of Tokyo Metropolis)
- Chūbu region (central part)
- Hokuriku region (northwestern Chūbu)
- Kōshin'etsu region (northeastern Chūbu)
- Tōkai region (southern Chūbu)
- Kansai (or Kinki) region (west-central part)
- Chūgoku region (western part)
- San'in region (northern Chūgoku)
- San'yō region (southern Chūgoku)
- Shikoku
- Kyūshū
See also
- Ecoregions of Japan
- Prefectures of Japan
- Geography of Japan
References
- Japan's Regional Megamarkets - Semantic Scholar (PDF)
- What special characteristics does Hokkaido have? from Kids Web Japan
- What special characteristics does the Tohoku region have? from Kids Web Japan
- What special characteristics does the Kanto region have? from Kids Web Japan
- What special characteristics does the Chubu region have? from Kids Web Japan
- What special characteristics does the Kinki region have? from Kids Web Japan
- What special characteristics does the Chugoku region have? from Kids Web Japan
- What special characteristics does the Shikoku region have? from Kids Web Japan
- What special characteristics does the Kyushu-Okinawa region have? from Kids Web Japan
- Regions of Japan on japan-guide.com
- Regions of Japan on web-japan.org
External links
![]()