Chromosome 10
Chromosome 10 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 10 spans about 133 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 4 and 4.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.
| Chromosome 10 | |
|---|---|
 Human chromosome 10 pair after G-banding. One is from mother, one is from father. | |
 Chromosome 10 pair in human male karyogram. | |
| Features | |
| Length (bp) | 133,797,422 bp (GRCh38)[1] |
| No. of genes | 706 (CCDS)[2] |
| Type | Autosome |
| Centromere position | Submetacentric[3] (39.8 Mbp[4]) |
| Complete gene lists | |
| CCDS | Gene list |
| HGNC | Gene list |
| UniProt | Gene list |
| NCBI | Gene list |
| External map viewers | |
| Ensembl | Chromosome 10 |
| Entrez | Chromosome 10 |
| NCBI | Chromosome 10 |
| UCSC | Chromosome 10 |
| Full DNA sequences | |
| RefSeq | NC_000010 (FASTA) |
| GenBank | CM000672 (FASTA) |
Genes
Number of genes
The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 10. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project (CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes.[5]
| Estimated by | Protein-coding genes | Non-coding RNA genes | Pseudogenes | Source | Release date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCDS | 706 | — | — | [2] | 2016-09-08 |
| HGNC | 708 | 244 | 614 | [6] | 2017-05-12 |
| Ensembl | 728 | 881 | 568 | [7] | 2017-03-29 |
| UniProt | 750 | — | — | [8] | 2018-02-28 |
| NCBI | 754 | 842 | 654 | [9][10][11] | 2017-05-19 |
Gene list
The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 10. For complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right.
- AFAP1L2: actin filament associated protein 1 like 2
- ALL1 encoding protein Leukemia, acute lymphocytic, susceptibility to, 1
- ALOX5: Arachidonate 5-Lipoxygenase (processes essential fatty acids to leukotrienes, which are important agents in the inflammatory response; also facilitates development and maintenance of cancer stem cells, slow-dividing cells thought to give rise to a variety of cancers, including leukemia)
- ARHGAP21: rho GTPase activating protein 21
- ARID5B: encoding protein AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 5B
- ARMH3: Armadillo Like Helical Domain Containing 3
- AS3MT: encoding enzyme Arsenite methyltransferase
- AVPI1: encoding protein Arginine vasopressin-induced protein 1
- C10orf67: chromosome 10 open reading frame 67
- C10orf99: encoding protein Chromosome 10 open reading frame 99
- CAMK1D: calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase ID
- CCAR1: Cell division cycle and apoptosis regulator 1
- CCDC3: Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 3
- CCDC186: encoding protein CCDC186
- CCNY: Cyclin-Y
- CDC123: Cell division cycle protein 123 homolog
- CDH23: cadherin-like 23
- CDNF: cerebral dopamine neurotrophic factor
- COMMD3-BMI1: COMMD3-BMI1 readthrough
- CUTC: Copper homeostasis protein cutC homolog
- CXCL12: chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 12, SDF-1, scyb12
- DDX50: DExD-box helicase 50
- DEPP: decidual protein induced by progesterone
- DHX32: DEAH-box helicase 32
- DNAJC12: DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily c, member 12
- DNAJC9: DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily c, member 9
- DPYSL4: Dihydropyrimidinase-related protein 4
- EBLN1: encoding protein Endogenous Bornavirus-like nucleoprotein 1
- ECD: ecdysoneless cell cycle regulator
- EGR2: early growth response 2 (Krox-20 homolog, Drosophila)
- EIF5AP1: eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A-like 1
- EPC1: Enhancer of polycomb homolog 1
- ERCC6: excision repair cross-complementing rodent repair deficiency, complementation group 6
- FAM107B: family with sequence similarity 107, member B
- FAM13C: family with sequence similarity 13, member C
- FAM170B: encoding protein Family with sequence similarity 170 member B
- FAM188A: family with sequence similarity 188, member A
- FAM213A: family with sequence similarity 213, member A
- FAM25BP encoding protein Protein FAM25
- FAS-AS1, long non-coding RNA
- FGFR2: fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (bacteria-expressed kinase, keratinocyte growth factor receptor, craniofacial dysostosis 1, Crouzon syndrome, Pfeiffer syndrome, Jackson–Weiss syndrome)
- FRA10AC1: Fragile site, folic acid type
- FRAT1: WNT signaling pathway regulator
- FRAT2: WNT signaling pathway regulator
- FRMPD2 encoding protein FERM and PDZ domain containing 2
- GATA3: encoding the GATA3 transcription factor. GATA3 is critical for the embryonic development of the parathyroid gland, neural component of hearing, and kidney. Haploinsufficiency of the gene underlies a rare disorder, the hypoparathyrodism, deafness, and renal dysplasia syndrome
- GHITM: growth hormone-inducible transmembrane protein
- GPRIN2: G protein-regulated inducer of neurite outgrowth 2
- GTPBP4: Nucleolar GTP-binding protein 4
- HELLS: Lymphoid-specific helicase
- HKDC1: hexokinase domain containing 1
- KIN: DNA/RNA-binding protein KIN17
- MTG1: mitochondrial GTPase 1
- NPM3: nucleoplasmin-3
- NRBF2: nuclear receptor-binding factor 2
- NSMCE4A: non-SMC element 4 homolog A
- OTUD1: encoding protein OTU deubiquitinase 1
- PCBD1: 6-pyruvoyl-tetrahydropterin synthase/dimerization cofactor of hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha (TCF1)
- PCDH15: protocadherin 15
- PI4K2A: phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase 2-alpha
- PIP4K2A: phosphatidylinositol 5 phosphate 4-kinase type-2 alpha
- PITRM1: pitrilysin metallopeptidase 1
- PLEKHS1 encoding protein Pleckstrin homology domain containing S1
- PLXDC2: plexin domain-containing protein 2
- PROSER2: proline and serine rich 2 or c10orf47
- PTEN gene: phosphatase and tensin homolog (mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1)
- RET: ret proto-oncogene (multiple endocrine neoplasia and medullary thyroid carcinoma 1, Hirschsprung disease)
- RPP30: ribonuclease P protein subunit p30
- RRP12: ribosomal RNA processing 12 homolog
- RSU1: ras suppressor protein 1
- SGPL1: sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase 1
- SMNDC1: survival motor neuron domain containing 1
- SPG9 encoding protein Spastic paraplegia 9 (autosomal dominant)
- SRGN: serglycin
- STAMBPL1: STAM binding protein like 1
- STOX1: encoding protein Storkhead box 1
- SUPV3L1: Suv3 like RNA helicase
- TACC2 encoding protein Transforming acidic coiled-coil-containing protein 2
- TBC1D12: TBC1 domain family, member 12
- TCTN3: tectonic family member 3
- TMEM10: opalin
- TMEM26: encoding protein Transmembrane protein 26
- UCN3: urocortin-3
- UROS: uroporphyrinogen III synthase (congenital erythropoietic porphyria)
- USMG5: Up-regulated during skeletal muscle growth protein 5
- USP6NL: USP6 N-terminal like protein
- UTF1: undifferentiated embryonic cell transcription factor 1
- WASHC2C: WASH complex subunit 2C
- WBP1L: WW domain binding protein 1-like
- ZNF37A: zinc finger protein 37A
- ZNF438: zinc finger protein 438
Diseases and disorders
The following diseases are related to genes on chromosome 10:
- Apert syndrome
- Barakat syndrome
- Beare–Stevenson cutis gyrata syndrome
- Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease
- Cockayne syndrome
- Congenital erythropoietic porphyria
- Cowden syndrome
- Crouzon syndrome
- Genitopatellar syndrome
- Glioblastoma multiforme
- Hermansky–Pudlak syndrome
- Hirschprung disease
- Jackson–Weiss syndrome
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2
- Nonsyndromic deafness
- Pfeiffer syndrome
- Porphyria
- Tetrahydrobiopterin deficiency
- Thiel–Behnke corneal dystrophy
- Usher syndrome
- Wolman syndrome
- Young-Simpson syndrome
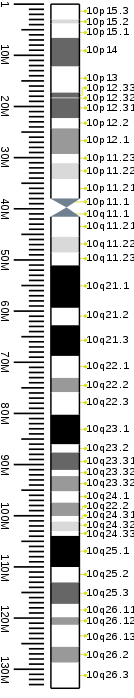
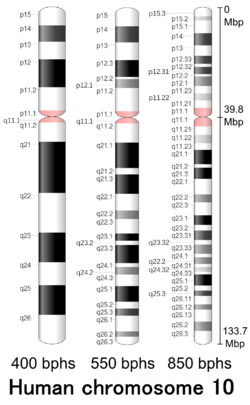
Cytogenetic band
| Chr. | Arm[17] | Band[18] | ISCN start[19] |
ISCN stop[19] |
Basepair start |
Basepair stop |
Stain[20] | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | p | 15.3 | 0 | 229 | 1 | 3,000,000 | gneg | |
| 10 | p | 15.2 | 229 | 329 | 3,000,001 | 3,800,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 10 | p | 15.1 | 329 | 630 | 3,800,001 | 6,600,000 | gneg | |
| 10 | p | 14 | 630 | 917 | 6,600,001 | 12,200,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 10 | p | 13 | 917 | 1175 | 12,200,001 | 17,300,000 | gneg | |
| 10 | p | 12.33 | 1175 | 1361 | 17,300,001 | 18,300,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 10 | p | 12.32 | 1361 | 1432 | 18,300,001 | 18,400,000 | gneg | |
| 10 | p | 12.31 | 1432 | 1604 | 18,400,001 | 22,300,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 10 | p | 12.2 | 1604 | 1662 | 22,300,001 | 24,300,000 | gneg | |
| 10 | p | 12.1 | 1662 | 1891 | 24,300,001 | 29,300,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 10 | p | 11.23 | 1891 | 2063 | 29,300,001 | 31,100,000 | gneg | |
| 10 | p | 11.22 | 2063 | 2235 | 31,100,001 | 34,200,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 10 | p | 11.21 | 2235 | 2406 | 34,200,001 | 38,000,000 | gneg | |
| 10 | p | 11.1 | 2406 | 2621 | 38,000,001 | 39,800,000 | acen | |
| 10 | q | 11.1 | 2621 | 2850 | 39,800,001 | 41,600,000 | acen | |
| 10 | q | 11.21 | 2850 | 3051 | 41,600,001 | 45,500,000 | gneg | |
| 10 | q | 11.22 | 3051 | 3252 | 45,500,001 | 48,600,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 10 | q | 11.23 | 3252 | 3409 | 48,600,001 | 51,100,000 | gneg | |
| 10 | q | 21.1 | 3409 | 3753 | 51,100,001 | 59,400,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 10 | q | 21.2 | 3753 | 3839 | 59,400,001 | 62,800,000 | gneg | |
| 10 | q | 21.3 | 3839 | 4097 | 62,800,001 | 68,800,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 10 | q | 22.1 | 4097 | 4469 | 68,800,001 | 73,100,000 | gneg | |
| 10 | q | 22.2 | 4469 | 4655 | 73,100,001 | 75,900,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 10 | q | 22.3 | 4655 | 4970 | 75,900,001 | 80,300,000 | gneg | |
| 10 | q | 23.1 | 4970 | 5200 | 80,300,001 | 86,100,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 10 | q | 23.2 | 5200 | 5331 | 86,100,001 | 87,700,000 | gneg | |
| 10 | q | 23.31 | 5331 | 5558 | 87,700,001 | 91,100,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 10 | q | 23.32 | 5558 | 5672 | 91,100,001 | 92,300,000 | gneg | |
| 10 | q | 23.33 | 5672 | 5887 | 92,300,001 | 95,300,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 10 | q | 24.1 | 5887 | 5973 | 95,300,001 | 97,500,000 | gneg | |
| 10 | q | 24.2 | 5973 | 6131 | 97,500,001 | 100,100,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 10 | q | 24.31 | 6131 | 6202 | 100,100,001 | 101,200,000 | gneg | |
| 10 | q | 24.32 | 6202 | 6317 | 101,200,001 | 103,100,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 10 | q | 24.33 | 6317 | 6374 | 103,100,001 | 104,000,000 | gneg | |
| 10 | q | 25.1 | 6374 | 6646 | 104,000,001 | 110,100,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 10 | q | 25.2 | 6646 | 6761 | 110,100,001 | 113,100,000 | gneg | |
| 10 | q | 25.3 | 6761 | 6890 | 113,100,001 | 117,300,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 10 | q | 26.11 | 6890 | 7090 | 117,300,001 | 119,900,000 | gneg | |
| 10 | q | 26.12 | 7090 | 7219 | 119,900,001 | 121,400,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 10 | q | 26.13 | 7219 | 7506 | 121,400,001 | 125,700,000 | gneg | |
| 10 | q | 26.2 | 7506 | 7721 | 125,700,001 | 128,800,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 10 | q | 26.3 | 7721 | 8050 | 128,800,001 | 133,797,422 | gneg |
References
- "Human Genome Assembly GRCh38 - Genome Reference Consortium". National Center for Biotechnology Information. 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2017-03-04.
- "Search results - 10[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("has ccds"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". NCBI. CCDS Release 20 for Homo sapiens. 2016-09-08. Retrieved 2017-05-28.
- Tom Strachan; Andrew Read (2 April 2010). Human Molecular Genetics. Garland Science. p. 45. ISBN 978-1-136-84407-2.
- Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (850 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-06-03. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- Pertea M, Salzberg SL (2010). "Between a chicken and a grape: estimating the number of human genes". Genome Biol. 11 (5): 206. doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-5-206. PMC 2898077. PMID 20441615.
- "Statistics & Downloads for chromosome 10". HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee. 2017-05-12. Retrieved 2017-05-19.
- "Chromosome 10: Chromosome summary - Homo sapiens". Ensembl Release 88. 2017-03-29. Retrieved 2017-05-19.
- "Human chromosome 10: entries, gene names and cross-references to MIM". UniProt. 2018-02-28. Retrieved 2018-03-16.
- "Search results - 10[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("genetype protein coding"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". NCBI. 2017-05-19. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- "Search results - 10[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ( ("genetype miscrna"[Properties] OR "genetype ncrna"[Properties] OR "genetype rrna"[Properties] OR "genetype trna"[Properties] OR "genetype scrna"[Properties] OR "genetype snrna"[Properties] OR "genetype snorna"[Properties]) NOT "genetype protein coding"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". NCBI. 2017-05-19. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- "Search results - 10[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("genetype pseudo"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". NCBI. 2017-05-19. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (400 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-03-04. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (550 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2015-08-11. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- International Standing Committee on Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). ISCN 2013: An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Karger Medical and Scientific Publishers. ISBN 978-3-318-02253-7.
- Sethakulvichai, W.; Manitpornsut, S.; Wiboonrat, M.; Lilakiatsakun, W.; Assawamakin, A.; Tongsima, S. (2012). "Estimation of band level resolutions of human chromosome images" (PDF). In Computer Science and Software Engineering (JCSSE), 2012 International Joint Conference on: 276–282. doi:10.1109/JCSSE.2012.6261965.
- Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (850 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-06-03. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- "p": Short arm; "q": Long arm.
- For cytogenetic banding nomenclature, see article locus.
- These values (ISCN start/stop) are based on the length of bands/ideograms from the ISCN book, An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Arbitrary unit.
- gpos: Region which is positively stained by G banding, generally AT-rich and gene poor; gneg: Region which is negatively stained by G banding, generally CG-rich and gene rich; acen Centromere. var: Variable region; stalk: Stalk.
- Deloukas P, Earthrowl ME, Grafham DV, Rubenfield M, French L, Steward CA, Sims SK, Jones MC, Searle S, Scott C, Howe K, Hunt SE, Andrews TD, Gilbert JG, Swarbreck D, Ashurst JL, Taylor A, Battles J, Bird CP, Ainscough R, Almeida JP, Ashwell RI, Ambrose KD, Babbage AK, Bagguley CL, Bailey J, Banerjee R, Bates K, Beasley H, Bray-Allen S, Brown AJ, Brown JY, Burford DC, Burrill W, Burton J, Cahill P, Camire D, Carter NP, Chapman JC, Clark SY, Clarke G, Clee CM, Clegg S, Corby N, Coulson A, Dhami P, Dutta I, Dunn M, Faulkner L, Frankish A, Frankland JA, Garner P, Garnett J, Gribble S, Griffiths C, Grocock R, Gustafson E, Hammond S, Harley JL, Hart E, Heath PD, Ho TP, Hopkins B, Horne J, Howden PJ, Huckle E, Hynds C, Johnson C, Johnson D, Kana A, Kay M, Kimberley AM, Kershaw JK, Kokkinaki M, Laird GK, Lawlor S, Lee HM, Leongamornlert DA, Laird G, Lloyd C, Lloyd DM, Loveland J, Lovell J, McLaren S, McLay KE, McMurray A, Mashreghi-Mohammadi M, Matthews L, Milne S, Nickerson T, Nguyen M, Overton-Larty E, Palmer SA, Pearce AV, Peck AI, Pelan S, Phillimore B, Porter K, Rice CM, Rogosin A, Ross MT, Sarafidou T, Sehra HK, Shownkeen R, Skuce CD, Smith M, Standring L, Sycamore N, Tester J, Thorpe A, Torcasso W, Tracey A, Tromans A, Tsolas J, Wall M, Walsh J, Wang H, Weinstock K, West AP, Willey DL, Whitehead SL, Wilming L, Wray PW, Young L, Chen Y, Lovering RC, Moschonas NK, Siebert R, Fechtel K, Bentley D, Durbin R, Hubbard T, Doucette-Stamm L, Beck S, Smith DR, Rogers J (2004). "The DNA sequence and comparative analysis of human chromosome 10". Nature. 429 (6990): 375–81. doi:10.1038/nature02462. PMID 15164054.
- Deloukas P, French L, Meitinger T, Moschonas NK (2000). "Report of the third international workshop on human chromosome 10 mapping and sequencing 1999". Cytogenet Cell Genet. 90 (1–2): 1–12. doi:10.1159/000015653. PMID 11060438.
- Gilbert F (2001). "Chromosome 10". Genet Test. 5 (1): 69–82. doi:10.1089/109065701750168824. PMID 11336406.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Human chromosome 10. |
- National Institutes of Health. "Chromosome 10". Genetics Home Reference. Retrieved 2017-05-06.
- "Chromosome 10". Human Genome Project Information Archive 1990–2003. Retrieved 2017-05-06.