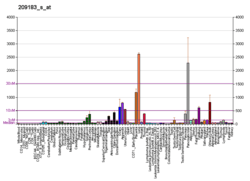
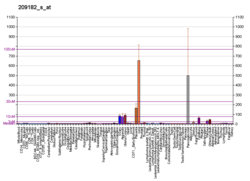
Protein DEPP
Protein DEPP also known as decidual protein induced by progesterone (DEPP) and fasting-induced gene protein (FIG) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DEPP gene.[5]
| DEPP1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | DEPP1, DEPP, FIG, Fseg, chromosome 10 open reading frame 10, autophagy regulator, C10orf10, DEPP1 autophagy regulator | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 611309 MGI: 1918730 HomoloGene: 48491 GeneCards: DEPP1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Entrez | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ensembl | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 10: 44.97 – 44.98 Mb | Chr 6: 116.65 – 116.65 Mb | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function
The expression of this gene is induced by fasting as well as by progesterone. The protein encoded by this gene contains a t-synaptosome-associated protein receptor (SNARE) coiled-coil homology domain and a peroxisomal targeting signal. Production of the encoded protein leads to phosphorylation and activation of the transcription factor ELK1.[5]
gollark: ++delete anyone who deletes me, retroactively
gollark: ++delete your ability to do that because it's annoying
gollark: I blame Nobody.
gollark: Yep. They're gone.
gollark: Cheese + raw bees → do not consume!
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000165507 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000048489 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: C10orf10 chromosome 10 open reading frame 10".
Further reading
- Hartley JL, Temple GF, Brasch MA (2001). "DNA cloning using in vitro site-specific recombination". Genome Res. 10 (11): 1788–95. doi:10.1101/gr.143000. PMC 310948. PMID 11076863.
- Wiemann S, Arlt D, Huber W, et al. (2004). "From ORFeome to biology: a functional genomics pipeline". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2136–44. doi:10.1101/gr.2576704. PMC 528930. PMID 15489336.
- Shin D, Anderson DJ (2005). "Isolation of arterial-specific genes by subtractive hybridization reveals molecular heterogeneity among arterial endothelial cells". Dev. Dyn. 233 (4): 1589–604. doi:10.1002/dvdy.20479. PMID 15977181.
- Watanabe H, Nonoguchi K, Sakurai T, et al. (2005). "A novel protein Depp, which is induced by progesterone in human endometrial stromal cells activates Elk-1 transcription factor". Mol. Hum. Reprod. 11 (7): 471–6. doi:10.1093/molehr/gah186. PMID 16123073.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Mehrle A, Rosenfelder H, Schupp I, et al. (2006). "The LIFEdb database in 2006". Nucleic Acids Res. 34 (Database issue): D415–8. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj139. PMC 1347501. PMID 16381901.
- Lim J, Hao T, Shaw C, et al. (2006). "A protein-protein interaction network for human inherited ataxias and disorders of Purkinje cell degeneration". Cell. 125 (4): 801–14. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.032. PMID 16713569.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.