Andrés de Urdaneta
Friar Andrés de Urdaneta, OSA (Spanish pronunciation: [anˈdɾes] : Ordizia, November 30, 1498 or 1508 [1] – Mexico City, June 3, 1568) was a maritime explorer for the Spanish Empire, an Augustinian friar of Basque heritage. As a navigator, he achieved, in 1536, the second world circumnavigation (after the first one led by Ferdinand Magellan and Juan Sebastián Elcano and their crew in 1522). In 1565, Urdaneta discovered and plotted an easterly route across the Pacific Ocean, from the Philippines to Acapulco in the Viceroyalty of New Spain (present day Mexico), which was used by the Manila galleons and came to be known as "Urdaneta's route". He was considered as "protector of the Indians" for his treatment of the Philippine natives; also the first prelate of Cebu and the Philippines in general.[2][3][4]
Andrés de Urdaneta y Cerain | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | Andrés de Urdaneta y Cerain November 30, 1498 or 1508 |
| Died | June 3, 1568 Mexico City, Viceroyalty of New Spain |
| Nationality | Crown of Castile |
| Occupation | Explorer, friar |
| Signature | |
 | |

Exploration
Urdaneta was one of the few survivors of the Loaísa expedition to reach the Spice Islands late in the year 1526, only to be taken prisoner by the Portuguese. Urdaneta spent the next eight and a half years in and around the Spice Islands, but eventually he managed to return to Europe in the Portuguese India Armada and under Portuguese guard. Upon his arrival in Lisbon on June 26, 1536, he achieved the second world circumnavigation.[5] Urdaneta accomplished his trip around the world through a journey which lasted just shy of eleven years.[6]
In Lisbon, the Portuguese authorities confiscated his charts and letters. Urdaneta then escaped to Spain, where he recreated much of the confiscated material, and presented it to the Spanish Court. King Charles I of Spain did not give him a very favouable reception either, and, wearied by his many adventures, Urdaneta returned to New Spain and there entered the Order of Hermits of St. Augustine.
At the death of the viceroy, Don Luís de Velasco, in 1564, New Spain had passed under the government of the Real Audiencia, one of whose first cares was to equip an expedition for the conquest and colonization of the Philippines. This had been ordered by Philip II in 1559. Friar Andrés de Urdaneta having been designated as the Commander, the Viceroy had the matter under consideration at the time of his death. Urdaneta was considered a great navigator and especially fitted for cruising in Indian waters. Philip II wrote urging him to join the expedition and offering him the command. Urdaneta agreed to accompany the expedition but refused to take command; the adelantado, Don Miguel López de Legazpi, was appointed as Commander. The expedition, composed of the Capitana, which carried on board Legazpi and Urdaneta, the galleons San Pablo and San Pedro, and the tenders San Juan and San Lucas, set sail on November 21, 1564.
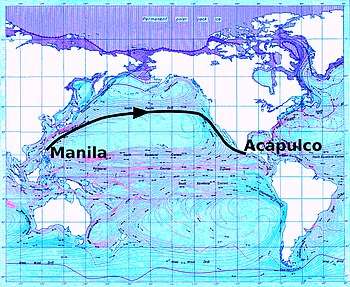
Urdaneta founded the first churches in the Philippines, the St. Vitales Church and the Basilica del Santo Niño; he served as the first prelate of the Church in Cebu. After spending some time in the islands, Legazpi determined to remain and sent Urdaneta back for the purpose of finding a better return route and to obtain help from New Spain for the Philippine colony. (For the problem of sailing east across the Pacific, which Urdaneta solved, see Manila galleon and Volta do mar.) Urdaneta set sail from San Miguel (the island of Cebu), on June 1, 1565 and was obliged to sail as far as 38 degrees north latitude to obtain favourable winds. With the voyage in trouble, Urdaneta had to assume command himself. The ship reached the port of Acapulco, on October 8, 1565, having traveled 12,000 miles (20,000 km) in 130 days. Fourteen of the crew had died; only Urdaneta and Felipe de Salcedo, nephew of López de Legazpi, had strength enough to cast the anchors.
Upon arriving, Urdaneta discovered that a member of the crew of his expedition, Alonso de Arellano—who had abandoned them just after leaving the port—had actually beaten them across the ocean, arriving at Barra de Navidad in Jalisco in August of the same year. However, Arellano was in disgrace for his rebellion against the authority of Legazpi, and his notes were far less precise and professional than Urdaneta's, and so the latter's route became the famous and trusted one.
Legacy
From Mexico, Urdaneta went to Europe to make a report on the expedition and then returned to New Spain, intending to continue on to the Philippines. However, he was dissuaded by his friends. He wrote two accounts of his voyages: one giving the account of the Loaisa expedition was published; the other, which gives the account of his return voyage, is preserved in manuscript in the archives of the Council of the Indies.
For the remainder of the 16th and 17th centuries, Spanish ships, particularly the annual Manila-Acapulco trading Galleon, used "Urdaneta's route."
In the Philippines, the city of Urdaneta in Pangasinan was named after him. The same city is the seat of one of the biggest dioceses on the country.
Urdaneta died in Mexico City in 1568.
References
- McDougall, Walter (1993). Let the Sea Make a Noise: Four Hundred Years of Cataclysm, Conquest, War and Folly in the North Pacific. New York: Avon Books.
- "Expedition of García de Loaisa 1525-26." In The Philippine Islands, 1493-1898. Cleveland, Ohio: A.H. Clark Company, 1903-9. Vol. 2, 1529-1561. Pp. 33.
- "Andrés de Urdaneta y Ceraín". Diccionario Biográfico Español. Real Academia de la Historia. Retrieved 1 November 2019.
- The Philippine Islands, 1493-1803, vol. 2, eds. Emma Helen Blair, James Alexander Robertson (Cleveland: The Arthur H. Clark Company, 1903), 33, note 5.
- Bartolomé de Letona, OSF, "Description of the Filipinas Islands" in The Philippine Islands, 1493-1803, vol. 34, eds. Emma H. Blair and James A. Robertson (Cleveland: The Arthur H. Clark Company, 1906), 208. "The Order of St. Augustine entered the islands in the year [1]565; its first superior, and first prelate of all the islands was Fray Andres de Urdaneta - a Vascongado,40 and a son of the convent and province of Mexico; he was the apostle who unfurled the gospel banner, and he planted the faith in the island of Zebu and others."
- Pangan 2016, p. 93-95
- The expedition could also be considered as the third or even the fourth circumnavigation in history, considering that Magellan and some of his men had been in the regions of Malaysia and Indonesia a decade before reaching the Philippines, or the route taken by other crew members of Magellan's expedition and later returned to Europe after Elcano`s ship, who were also brought by the Portuguese from Moluccas and then released in Lisbon.
- Mitchell, Mairin. 1964. Friar Andrés de Urdaneta, O.S.A. Macdonald and Evans, London, p. 101