1978 Tour de France
The 1978 Tour de France was the 65th edition of the Tour de France, one of cycling's Grand Tours. It took place between 29 June and 23 July, with 22 stages covering a distance of 3,908 km (2,428 mi).
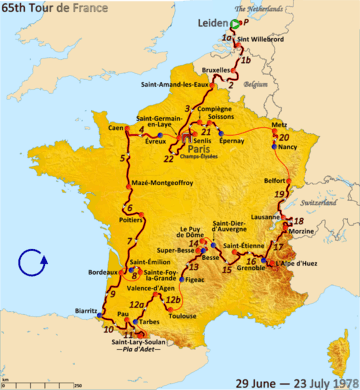 Route of the 1978 Tour de France | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Race details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dates | 29 June – 23 July | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stages | 22 + Prologue, including two split stages | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance | 3,908 km (2,428 mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Winning time | 112h 03' 02" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Results | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1978 Tour had a high-profile doping case when Michel Pollentier was caught in an attempt to cheat the doping test, after he had won the 16th stage to Alpe d'Huez, and had taken the lead in the general classification. Pollentier left the race, and the overall victory became a battle between Joop Zoetemelk and Bernard Hinault. In the end, it was won by debutant Bernard Hinault, for the first of his five victories. The points classification was won by Freddy Maertens, and the mountains classification by Mariano Martínez.
Teams
The 1978 Tour started with 11 teams, each sent 10 cyclists, a total of 110.[1][2]
The teams entering the race were:
Pre-race favourites
Since the 1977 Tour de France, dominant riders as Eddy Merckx, Felice Gimondi, Raymond Poulidor and Luis Ocaña had retired.[3] Lucien Van Impe, the winner of 1976, had broken his collarbone and was still recovering.[4]
The main contenders were debutant Hinault, who had won the 1978 Vuelta a España, and Joop Zoetemelk, who had already finished in second place for three times. Pre-race analysis judged Hinault better in the time trials, and Zoetemelk better in the mountains.[4] Bernard Thévenet, the winner of the 1977 Tour de France, was out of form, and not considered a favourite.[1]
Route and stages
The 1978 Tour de France started on 29 June, and had two rest days, in Biarritz and Alpe d'Huez.[5] The highest point of elevation in the race was 2,115 m (6,939 ft) at the summit of the Col du Tourmalet mountain pass on stage 11.[6][7]
The twenty-first stage from Epernay to Senlis was split in three parts: 78.5 km from Epernay to Soissons, directly followed by 59 km from Soissons to Compiègne, directly followed by 70.5 km from Compiègne to Senlis; the sprints in Soissons and Compiegne counted as flying stages, which were won by Freddy Maertens and Wilfried Wesemael.[8] Although they technically had the same status as all other stages, these flying stages are not shown in most overviews.
| Stage | Date | Course | Distance | Type | Winner | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | 29 June | Leiden (Netherlands) | 5 km (3.1 mi) | Individual time trial | ||
| 1a | 30 June | Leiden to Sint Willebrord (Netherlands) | 135 km (84 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 1b | Sint Willebrord (Netherlands) to Brussels (Belgium) | 100 km (62 mi) | Plain stage | |||
| 2 | 1 July | Brussels (Belgium) to Saint-Amand-les-Eaux | 199 km (124 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 3 | 2 July | Saint-Amand-les-Eaux to Saint-Germain-en-Laye | 244 km (152 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 4 | 3 July | Évreux to Caen | 153 km (95 mi) | Team time trial | TI–Raleigh–McGregor | |
| 5 | 4 July | Caen to Mazé-Montgeoffroy | 244 km (152 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 6 | 5 July | Mazé-Montgeoffroy to Poitiers | 162 km (101 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 7 | 6 July | Poitiers to Bordeaux | 242 km (150 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 8 | 7 July | Saint-Émilion to Sainte-Foy-la-Grande | 59 km (37 mi) | Individual time trial | ||
| 9 | 8 July | Bordeaux to Biarritz | 233 km (145 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 9 July | Biarritz | Rest day | ||||
| 10 | 10 July | Biarritz to Pau | 192 km (119 mi) | Hilly stage | ||
| 11 | 11 July | Pau to Saint-Lary-Soulan Pla d'Adet | 161 km (100 mi) | Stage with mountain(s) | ||
| 12a | 12 July | Tarbes to Valence d'Agen | 158 km (98 mi) | Plain stage | Cancelled | |
| 12b | Valence d'Agen to Toulouse | 96 km (60 mi) | Plain stage | |||
| 13 | 13 July | Figeac to Super Besse | 221 km (137 mi) | Hilly stage | ||
| 14 | 14 July | Besse-en-Chandesse to Puy de Dôme | 52 km (32 mi) | Individual time trial | ||
| 15 | 15 July | Saint-Dier-d'Auvergne to Saint-Étienne | 196 km (122 mi) | Hilly stage | ||
| 16 | 16 July | St-Étienne to Alpe d'Huez | 241 km (150 mi) | Stage with mountain(s) | ||
| 17 July | Alpe d'Huez | Rest day | ||||
| 17 | 18 July | Grenoble to Morzine | 225 km (140 mi) | Stage with mountain(s) | ||
| 18 | 19 July | Morzine to Lausanne (Switzerland) | 137 km (85 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 19 | 20 July | Lausanne (Switzerland) to Belfort | 182 km (113 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 20 | 21 July | Metz to Nancy | 72 km (45 mi) | Individual time trial | ||
| 21 | 22 July | Epernay to Senlis | 207 km (129 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 22 | 23 July | Saint Germain en Laye to Paris (Champs-Élysées) | 162 km (101 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| Total | 3,908 km (2,428 mi)[10] | |||||
Race overview

During the prologue, held in the Netherlands, the weather was bad. The four top places were taken by Dutch cyclists, with Jan Raas the winner. The team directors then had a meeting, and all but the manager of Raas' team voted to request the Tour directors to not count the results from the prologue for the overall classification. The directors agreed, so the prologue results did not count.[11][12] Jan Raas was still given the stage win, but he was not recognized as race leader, so he was not allowed to wear the yellow jersey during the first stage. The winner of the previous year, Bernard Thévenet, was allowed to wear the yellow jersey, but he refused.[11] In that first stage, Raas and his team were full of anger. Raas escaped close to the finish, and beat everybody by a second, thus becoming the race's leader after all.[11]
Raas lost the lead in the third stage. The fourth stage was run as a time trial. The TI–Raleigh team was specialized in this, and they won the stage. Klaus-Peter Thaler of the TI–Raleigh team became the new leader, thanks to the bonification seconds.[11] Hinault beat Zoetemelk in the time trial in stage eight.[4] Joseph Bruyère, former second man of Eddy Merckx, finished in second place and became the new race leader.[11]
The eleventh stage included the toughest mountains in the Pyrenées. On the last mountain, the Pla d'Adet, Pollentier and Zoetemelk attacked, and Martinez and Hinault soon followed. Martinez rode away to win the stage, and Hinault won some seconds on Zoetemelk. Bruyère stayed the leader, with Hinault in second place and Zoetemelk in third place.[4] During that stage, Thevenet retired.[11] The next day, the twelfth stage was scheduled, split into two sections. This meant that after the transfer from the previous stage, the riders were not in bed before 12:00 am, and had to wake up at 5:00 am.[11] In the early stage to Valence-d'Agen, the riders held a strike against the early start. They rode at a slow pace of 20 kilometres per hour (12 mph),[4] arrived at the finish well behind schedule, and crossed the finish line walking.[13] The Tour officials canceled the stage.[4] The fourteenth stage was an individual mountain time trial. Zoetemelk won the stage, beating Bruyère by 55 seconds and Hinault by 100 seconds.[4] Hinault had lost some time because his lightweight bike, that he intended to use for the steepest part, broke when he hit a spectator while changing bikes.[11]

In the sixteenth stage, that ended on top of Alpe d'Huez, Pollentier attacked. At the foot of the Alpe d'Huez, Pollentier had a margin of two minutes. He was chased by Hinault, Zoetemelk and Kuiper, who at 4 km before the finish had closed the gap to 50 seconds. Hinault then attacked, and Kuiper could follow but Zoetemelk had to let them go. Pollentier stayed away, won the stage and became the new leader of the general classification.[4] As stage winner and general classification leader, Pollentier had to go to the doping control. Pollentier first went to his hotel, and was only found two hours later.[11] Another cyclist at the doping control, Antoine Guttierrez, was found with a fake urine sample, trying to use it to fake the doping control. This device did not work, and the race doctor discovered the fraud. He then checked the other cyclists, and Pollentier was using the same fraud.[11] Pollentier was removed from the race, and Zoetemelk became the new leader.[4] Pollentier later explained that he tried to evade the controls because he had taken amphetamines for breathing, and he did not know if it would give back a positive test.[11]
In the seventeenth stage, Kuiper, third in the general classification, crashed, broke a clavicle, and had to leave the race.[11] Hinault was only 14 seconds behind Zoetemelk at the start of the time trial in stage 20. Hinault won that time trial by more than four minutes over Zoetemelk, and became the race leader.[4]
Doping
In total, 110 doping tests were done. Three cyclists were penalised for doping offences, all tested after the sixteenth stage;[14] Antoine Guttierrez, for attempt of fraud; Michel Pollentier, for attempt of fraud; and José Nazabal. Nazabal had already anticipated the positive result, and had left the race before the eighteenth stage. Guttierrez and Pollentier were removed from the race and banned for two months; Nazabal was set back to the last place of the stage, received ten minutes penalty time in the general classification, a fine of 1000 Swiss Francs and one month provisional suspension.
Classification leadership and minor prizes
There were several classifications in the 1978 Tour de France, four of them awarding jerseys to their leaders.[15] The most important was the general classification, calculated by adding each cyclist's finishing times on each stage. The cyclist with the least accumulated time was the race leader, identified by the yellow jersey; the winner of this classification is considered the winner of the Tour.[16] Some rules were changed after the 1977 Tour de France, mainly concerning the time bonuses. In previous years, intermediate sprints were not associated with time bonuses, but in 1978, the winner of such a sprint got 20 seconds bonification time, if he was part of an escape (defined as a group with less than 20% of the total cyclists, with a margin of 20 seconds of more on the next group).[17] The penalty system was also changed. In previous years, cyclists who broke the rules on minor points (being pushed, taking drinks on places where it was not allowed) were penalised with points in the points classification. From 1978 on, time penalties were also given for the general classification.[17]
Additionally, there was a points classification, where cyclists got points for finishing among the best in a stage finish, or in intermediate sprints. The cyclist with the most points lead the classification, and was identified with a green jersey.[18]
There was also a mountains classification. The organisation had categorised some climbs as either first, second, third, or fourth-category; points for this classification were won by the first cyclists that reached the top of these climbs first, with more points available for the higher-categorised climbs. The cyclist with the most points lead the classification, and wore a white jersey with red polka dots.[19]
Another classification was the young rider classification.[20] This was decided the same way as the general classification, but restricted to riders who were born after 1 July 1978, and were in their first or second year as professional cyclist. There were 34 riders that qualified for the classification on the start list.[21] The leader wore a white jersey.[20]
The fifth individual classification was the intermediate sprints classification. This classification had similar rules as the points classification, but only points were awarded on intermediate sprints. In 1978, this classification had no associated jersey.[22]
The team classification in 1977 was calculated with the times of the three best cyclists per team, but was in 1978 changed to the best five cyclists.[17][23] The riders in the team that led this classification were identified by yellow caps.[22] There was also a team points classification. Cyclists received points according to their finishing position on each stage, with the first rider receiving one point. The first three finishers of each team had their points combined, and the team with the fewest points led the classification. The riders of the team leading this classification wore green caps.[22] The Kas team finished with only two cyclists, so was not eligible for the team classifications.[24] The Souvenir Henri Desgrange was given in honour of Tour founder Henri Desgrange to the first rider to pass a point on stage 11 in the valley village of Sainte-Marie de Campan climb. This prize was won by Christian Seznec.[25]
In addition, there was a combativity award, in which a jury composed of journalists gave points after certain stages to the cyclist they considered most combative. The split stages each had a combined winner.[26] At the conclusion of the Tour, Paul Wellens won the overall super-combativity award, also decided by journalists.[5]
Final standings
| Legend | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Denotes the winner of the general classification | Denotes the winner of the points classification | ||
| Denotes the winner of the mountains classification | Denotes the winner of the young rider classification | ||
General classification
| Rank | Rider | Team | Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Renault–Gitane–Campagnolo | 107h 18' 00" | |
| 2 | Miko–Mercier–Vivagel | + 3' 56" | |
| 3 | Flandria–Velda–Lano | + 6' 54" | |
| 4 | C&A | + 9' 04" | |
| 5 | Miko–Mercier–Vivagel | + 12' 50" | |
| 6 | TI–Raleigh–McGregor | + 14' 38" | |
| 7 | Kas–Campagnolo | + 17' 08" | |
| 8 | TI–Raleigh–McGregor | + 17' 26" | |
| 9 | C&A | + 21' 01" | |
| 10 | Jobo–Spidel–La Roue d'Or | + 22' 58" |
Points classification
| Rank | Rider | Team | Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Flandria–Velda–Lano | 242 | |
| 2 | Peugeot–Esso–Michelin | 185 | |
| 3 | Renault–Gitane–Campagnolo | 123 | |
| 4 | TI–Raleigh–McGregor | 109 | |
| 5 | C&A | 100 | |
| 6 | TI–Raleigh–McGregor | 91 | |
| 7 | Renault–Gitane–Campagnolo | 79 | |
| 8 | Renault–Gitane–Campagnolo | 74 | |
| 9 | Miko–Mercier–Vivagel | 71 | |
| 10 | Teka | 70 |
Mountains classification
| Rank | Rider | Team | Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jobo–Spidel–La Roue d'Or | 187 | |
| 2 | Renault–Gitane–Campagnolo | 176 | |
| 3 | Miko–Mercier–Vivagel | 155 | |
| 4 | Miko–Mercier–Vivagel | 90 | |
| 5 | Flandria–Velda–Lano | 73 | |
| 6 | Miko–Mercier–Vivagel | 70 | |
| 7 | TI–Raleigh–McGregor | 68 | |
| 8 | Flandria–Velda–Lano | 63 | |
| 9 | Fiat | 54 | |
| 10 | C&A | 53 |
Young rider classification
| Rank | Rider | Team | Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | TI–Raleigh–McGregor | 107h 25' 26" | |
| 2 | Miko–Mercier–Vivagel | + 05' 34" | |
| 3 | Flandria–Velda–Lano | + 36' 21" | |
| 4 | Lejeune–BP | + 38' 09" | |
| 5 | Fiat | + 40' 14" | |
| 6 | C&A | + 45' 03" | |
| 7 | Renault–Gitane–Campagnolo | + 50' 24" | |
| 8 | Kas–Campagnolo | + 50' 54" | |
| 9 | Flandria–Velda–Lano | + 52' 52" | |
| 10 | Renault–Gitane–Campagnolo | + 58' 24" |
Intermediate sprints classification
| Rank | Rider | Team | Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Renault–Gitane–Campagnolo | 95 | |
| 2 | Fiat | 60 | |
| 3 | Renault–Gitane–Campagnolo | 52 | |
| 4 | Flandria–Velda–Lano | 44 | |
| 5 | C&A | 21 | |
| 6 | Fiat | 18 | |
| 7 | Renault–Gitane–Campagnolo | 18 | |
| 8 | Peugeot–Esso–Michelin | 16 | |
| 9 | Renault–Gitane–Campagnolo | 15 | |
| 10 | Flandria–Velda–Lano | 14 |
Team classification
| Rank | Team | Time |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Miko–Mercier–Vivagel | 562h 05' 52" |
| 2 | TI–Raleigh–McGregor | + 17' 20" |
| 3 | C&A | + 17' 22" |
| 4 | Flandria–Velda–Lano | + 1h 15' 45" |
| 5 | Renault–Gitane–Campagnolo | + 1h 47' 46" |
| 6 | Peugeot–Esso–Michelin | + 4h 25' 36" |
| 7 | Lejeune–BP | + 4h 29' 18" |
| 8 | Teka | + 4h 51' 32" |
| 9 | Jobo–Spidel–La Roue d'Or | + 5h 02' 48" |
| 10 | Fiat | + 7h 04' 37" |
Team points classification
| Rank | Team | Time |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | TI–Raleigh–McGregor | 720 |
| 2 | Renault–Gitane–Campagnolo | 909 |
| 3 | Flandria–Velda–Lano | 972 |
| 4 | Miko–Mercier–Vivagel | 1072 |
| 5 | Peugeot–Esso–Michelin | 1144 |
| 6 | C&A | 1456 |
| 7 | Jobo–Spidel–La Roue d'Or | 1656 |
| 8 | Lejeune–BP | 1729 |
| 9 | Fiat | 2347 |
| 10 | Teka | 2629 |
Super Prestige Pernod ranking
The top twelve places of the general classification awarded points that contributed towards the Super Prestige Pernod ranking,[34] an international season-long road cycling competition, with the winner seen as the best all-round rider.[35] The 110 points accrued by Bernard Hinault moved him to the top, replacing Francesco Moser, who did not ride the Tour.[36]
| Rank | Rider | Team | Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Renault–Gitane–Campagnolo | 210 | |
| 2 | Sanson–Campagnolo | 178 | |
| 3 | Miko–Mercier–Vivagel | 136 | |
| 4 | Sanson–Campagnolo | 104 | |
| 5 | Flandria–Velda–Lano | 104 | |
| 6 | C&A | 103 |
See also
References
- "65ème Tour de France 1978" [65th Tour de France 1978]. Mémoire du cyclisme (in French). Retrieved 6 April 2020.
- "Historique du Tour de France - Year 1978: The starters". Amaury Sport Organisation. Archived from the original on 13 September 2011. Retrieved 18 September 2011.
- Thompson, p.215
- Boyce, Barry (2006). "1978: The Cannibal Retires, the Badger Shines". Cycling Revealed. Archived from the original on 20 July 2010. Retrieved 16 May 2011.
- Augendre 2016, p. 69.
- Augendre 2016, p. 188.
- "Ronde van Frankrijk" [Tour de France]. De Waarheid (in Dutch). 24 June 1978. p. 7 – via Delpher.
- "Acht Nederlandse zege's". Het vrije volk (in Dutch). Koninklijke Bibliotheek. 24 July 1978. p. 16. Archived from the original on 15 December 2013. Retrieved 8 December 2013.
- Zwegers, Arian. "Tour de France GC top ten". CVCCBike.com. Archived from the original on 16 May 2008. Retrieved 15 August 2011.
- Augendre 2016, p. 109.
- McGann & McGann 2008, pp. 111–117.
- "The story of the 1978 Tour de France". ROAD Magazine. No. August 2011. Valencia, CA: H3 Publications. pp. 90–94. Archived from the original on 6 March 2019. Retrieved 6 March 2019 – via BlueToad.
- Thompson, p.102
- "Tombés au champs d'honneur" (in French). Magazine Sport & Vie. July 2003. Archived from the original on 13 December 2007. Retrieved 16 May 2011.
- Nauright & Parrish 2012, pp. 452–455.
- Nauright & Parrish 2012, pp. 452–453.
- "Bonificaties, truien, punten en klassementen". Het Vrije Volk (in Dutch). De Arbeiderspers. 29 June 1978. Retrieved 13 July 2013.
- Nauright & Parrish 2012, pp. 453–454.
- Nauright & Parrish 2012, p. 454.
- Nauright & Parrish 2012, pp. 454–455.
- "Henk Lubberding rijdt een geweldige Tour, ook al valt dat nauwelijks op" [Henk Lubberding is driving a great Tour, even though that is hardly noticeable]. Leeuwarder Courant (in Dutch). 14 July 1978. p. 9. Archived from the original on 6 March 2019 – via De Krant van Toen.
- Nauright & Parrish 2012, p. 455.
- "Tour de France '78 bijna 4000 km lang" [Tour de France '78 almost 4000 km long]. Leeuwarder Courant (in Dutch). 10 November 1977. p. 13. Archived from the original on 6 March 2019 – via De Krant van Toen.
- "Clasificaciones oficiales" (PDF). Mundo Deportivo (in Spanish). 24 July 1978. p. 25. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 October 2019.
- "Tour-Varia" [Tour-Miscellaneous]. De Stem (in Dutch). 12 July 1978. p. 8 – via Krantenbank Zeeland.
- van den Akker 2018, pp. 211–216.
- "Tour panorama". Gazet van Antwerpen (in Dutch). 24 July 1978. p. 11. Archived from the original on 14 February 2019.
- van den Akker, Pieter. "Informatie over de Tour de France van 1978" [Information about the Tour de France from 1978]. TourDeFranceStatistieken.nl (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 2 March 2019. Retrieved 2 March 2019.
- Magowan 1979, p. 198.
- Duker 1978, "Final general classification".
- Magowan 1979, p. 199.
- van den Akker, Pieter. "Stand in het jongerenklassement – Etappe 22" [Standings in the youth classification – Stage 22]. TourDeFranceStatistieken.nl (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 24 April 2019. Retrieved 6 March 2019.
- Duker 1978, "Hot spot sprints classification".
- "Gedupeerd comité dreigt met rechter Leiden lijdt door Peter Heerkens" [The injured committee is in danger of being led by judge Peter Heerkens]. Limburgs Dagblad (in Dutch). 30 June 1978. p. 29 – via Delpher.
- Moore, Richard (13 June 2017). "Remembering Super Prestige Pernod, the season-long battle for title of best rider in the world". CyclingTips. Wade Wallace. Archived from the original on 4 February 2019. Retrieved 3 February 2019.
- "Tour-puntig" [Tour-pointed]. Limburgs Dagblad (in Dutch). 30 June 1978. p. 9 – via Delpher.
Bibliography
- Augendre, Jacques (2016). Guide historique [Historical guide] (PDF). Tour de France (in French). Paris: Amaury Sport Organisation. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 August 2016. Retrieved 27 October 2016.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Duker, Peter (1978). Tour de France 1978. Keighley, UK: Kennedy Brothers Publishing. OCLC 67121801.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Magowan, Robin (1979). Tour de France: The 75th anniversary cycle race. London: Stanley Paul. ISBN 978-0-09-138730-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- McGann, Bill; McGann, Carol (2008). The Story of the Tour de France: 1965–2007. 2. Indianapolis, IN: Dog Ear Publishing. ISBN 978-1-59858-608-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Nauright, John; Parrish, Charles (2012). Sports Around the World: History, Culture, and Practice. 2. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-59884-300-2.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Thompson, Christopher S. (2008). The Tour de France: A Cultural History. Oakland, CA: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-25630-9.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- van den Akker, Pieter (2018). Tour de France Rules and Statistics: 1903–2018. Self-published. ISBN 978-1-79398-080-9.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
External links
![]()