Uktenadactylus
Uktenadactylus is a genus of ornithocheirid pterodactyloid pterosaurs from the Lower Cretaceous Paw Paw Formation of Texas. Fossil remains of Uktenadactylus dated back to the Early Cretaceous period (Albian to Cenomanian stages), about 100 million years ago.
| Uktenadactylus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Illustration of the holotype snout | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Order: | †Pterosauria |
| Suborder: | †Pterodactyloidea |
| Family: | †Ornithocheiridae |
| Subfamily: | †Ornithocheirinae |
| Genus: | †Uktenadactylus Rodrigues & Kellner, 2009 |
| Type species | |
| †Coloborhynchus wadleighi Lee, 1994 | |
| Species | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Discovery and naming
In 1994, Yuong Nam-Lee named a new species within the genus Coloborhynchus: Coloborhynchus wadleighi, based on a partial snout found in 1992 in Albian layers in Tarrant County, holotype SMU 73058 (Shuler Museum of Paleontology, Southern Methodist University at Dallas). The specific name honours the collector of the fossil, Chris Wadleigh. The reference of the species to the genus Coloborhynchus was based on the fact that both C. wadleighi and the type species of Coloborhynchus, Coloborhynchus clavirostris, share the trait of having three pairs of teeth laterally placed within a broad snout tip. This would distinguish both from the species Criorhynchus simus and justify a revival of the genus Coloborhynchus that since an analysis by Reginald Walter Hooley in 1914[1] had generally been considered identical to the genus Criorhynchus or the genus the latter had again been sunk into, Ornithocheirus.[2]
As a result of the reappearance of the concept European workers referred many species discovered in South-America to Coloborhynchus, a practice rejected by most South-American researchers. In 2009 a study by the Brazilian paleontologists Taissa Rodrigues and Alexander Kellner concluded that Coloborhynchus comprised only a single species, its type species C. clavirostris. Accordingly, in the same publication they created a new genus for C. wadleighi: Uktenadactylus. The genus name is derived from Uktena, a giant horned snake from the mythology of the Cherokee and Greek daktylos, "finger", a common element in the names of pterosaurs since Pterodactylus, referring to their typical wing finger.[3]
Description
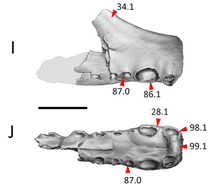
The holotype and only specimen, the partial snout, has a length of about fifteen centimetres and consists of the front end of the skull, containing the premaxilla and a small part of the maxilla. On top the base of a crest is present, gradually curving upwards and ending at a height of 7.5 centimeters (3.0 in), having attained at that point a thickness of 4 millimeters (0.16 in). The snout broadens towards the front. On the left side eight tooth sockets or alveoli are visible, on the right side six. The first pair of teeth was located in the flat tip of the snout, pointing forwards. The alveoli at first increase in size from the tip towards the back, the third pair being the largest with a diameter of either 17.6 millimeters (0.69 in) or 17.7 millimeters (0.70 in). The fourth pair is much smaller; to the back gradually the tooth sockets again increase in size. Thus a "prey grab" is formed. According to Rodrigues and Kellner the species has two unique traits: the presence of an oval depression above and in between the first pair of teeth and of a ventral medial depression between the second pair of teeth, a circular hollow positioned on the lower edge of the snout tip that Lee had interpreted as a possible pneumatic foramen.[3]
Rodrigues and Kellner base the distinction between Uktenadactylus and Coloborhynchus clavirostris on several stratigraphical, methodological and phylogenetic considerations. There is a possible age difference of perhaps over thirty million years between the Berriasian-Valanginian British and the younger Albian-Cenomanian American form. Because both taxa are based on very limited remains, that however, even within these limits are clearly distinguishable on the species level, they reject a rash assumption of generic identity. Also the uncertain affinity with the closely related form Siroccopteryx would make such an assumption problematical. Rodrigues and Kellner identify only one shared derived trait for Uktenadactylus and Coloborhynchus clavirostris: an extreme enlargement of the second and third pairs of teeth. Differences between the taxa include the more forward position of the crest with C. clavirostris, beginning at the very tip of the snout; a deeper palatal groove and shallow grooves running parallel to the ridge of the front part of the palate; a depression located below the first alveoli and a more lateral position of the second, third and fourth tooth pairs whereas the fifth and sixth pair are to the contrary much closer to the midline of the skull. Both forms share some derived traits with Siroccopteryx: the second and third teeth pairs are larger than the fourth; the tip of the snout is flat causing the "prey grab" to be rectangular in cross-section and a similar thickness of the crest. The authors conclude from this that the three taxa likely formed an, as yet unnamed, clade together within the Anhangueridae.[3]
Classification
In 2013, a topology by Andres & Myers placed Uktenadactylus within the family Ornithocheiridae, as the sister taxon of Coloborhynchus clavirostris, though in the analysis, Uktenadactylus was indentified as Coloborhynchus wadleighi.[4] In 2019 however, a different topology by Jacobs et al. also recovered Uktenadactylus within the Ornithocheiridae, but as the sister taxon of several Coloborhynchus species.[5]
|
Topology 1: Andres & Myers (2013).[4]
|
Topology 2: Jacobs et al. (2019).[5]
|
References
- Hooley, Reginald Walter (1914). "On the Ornithosaurian genus Ornithocheirus, with a review of the specimens from the Cambridge Greensand in the Sedgwick Museum, Cambridge". Annals and Magazine of Natural History. 13 (78): 529–557. doi:10.1080/00222931408693521. ISSN 0374-5481.
- Lee, Y.-N. (1994). "The Early Cretaceous Pterodactyloid Pterosaur Coloborhynchus wadleighi from North America". Palaeontology. 37 (4): 755–763.
- Rodrigues, Taissa; Kellner, Alexander W.A. (2009). "Review of the peterodactyloid pterosaur Coloborhynchus". Zitteliana B. 28: 219–228.
- Andres, B.; Myers, T. S. (2013). "Lone Star Pterosaurs". Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. 103 (3–4): 1. doi:10.1017/S1755691013000303.
- Jacobs, M.L., Martill, D.M., Ibrahim, N., Longrich, N. (2019). "A new species of Coloborhynchus (Pterosauria, Ornithocheiridae) from the mid-Cretaceous of North Africa" (PDF). Cretaceous Research. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2018.10.018.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)