Chaoyangopterus
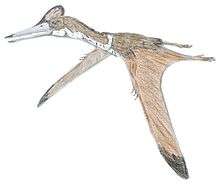
Chaoyangopterus is a genus of azhdarchoid pterodactyloid pterosaur known from a partial skeleton found in Liaoning, China. It was found in rocks of the Aptian-age Lower Cretaceous Jiufotang Formation of Dapingfang, Chaoyang.
| Chaoyangopterus | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Order: | †Pterosauria |
| Suborder: | †Pterodactyloidea |
| Family: | †Chaoyangopteridae |
| Genus: | †Chaoyangopterus Wang & Zhou, 2003 |
| Species: | †C. zhangi |
| Binomial name | |
| †Chaoyangopterus zhangi Wang & Zhou, 2003 | |
The genus was named and described in 2003 by Wang Xiaolin and Zhou Zhonghe. The type species is Chaoyangopterus zhangi. The genus name is derived from Chaoyang and a Latinised Greek pteron, "wing". The specific name honours journalist Zhang Wanlian for his efforts in protecting fossil sites.
The genus is based on holotype IVPP V13397, which includes the front of the skull, the lower jaws, the neck vertebrae, the shoulder and pelvic girdles, and the limbs. The skull is about 270 millimeters long (10.6 inches) and toothless, and its wingspan is estimated to have been around 1.85 meters (6.07 feet). Wang and Zhou concluded that it compared most closely to Nyctosaurus and classified it as a nyctosaurid, although they found that its shin was proportionally longer compared to the femur and humerus in Chaoyangopterus, that their animal had relatively shorter wings and longer legs than Nyctosaurus, and that it still had four fingers.[1]
The classification of Chaoyangopterus has since become unsettled, with subsequent reviewers disagreeing with the nyctosaurid assessment. David Unwin, in a popular work, included it without comment with the tapejarid family of azhdarchoid pterosaurs,[2] known for their large head crests. A detailed phylogenetic analysis of Liaoning pterosaurs published by Lü Junchang and Ji Qiang in 2006 found it instead to be a basal azhdarchoid of no particular familial affiliation.[3] However, subsequent analysis by Lu and Unwin found that within the Azhdarchoidea it formed a clade with several other forms such as Jidapterus and Shenzhoupterus, which they named Chaoyangopteridae.[4]
Wang and Zhou, however, stated in 2006 that Chaoyangopterus was a member of the Pteranodontidae and that Jidapterus, Eoazhdarcho and Eopteranodon are subjective junior synonyms of the former.[5] This interpretation was not supported by a 2017 redescription of Jidapterus, which was able to reliably distinguish all of these genera.[6]
Classification
Below is a cladogram showing the phylogenetic placement of Chaoyangopterus within Neoazhdarchia from Andres and Myers (2013).[7]
| Neoazhdarchia |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Paleobiology
Chaoyangopterus is known to have been a toothless pterosaur and was assumed by Wang to have been a piscivore or fish-eater, but other relevant details of its paleobiology will have to await a more detailed description. Chaoyangopterids in general are now thought to have been similar to azhdarchid pterosaurs, implying that they were probably crane-like terrestrial omnivores and opportunistic carnivores.[8]
References
- Wang Xiao-Lin; Zhou Zhong-He (2003). "Two new pterodactyloid pterosaurs from the Early Cretaceous Jiufotang Formation of Western Liaoning, China". Vertebrata PalAsiatica. 41 (1): 34–41.
- Unwin, David M. (2006). The Pterosaurs: From Deep Time. New York: Pi Press. p. 273. ISBN 0-13-146308-X.
- Lü, Junchang; Qiang Ji (2006). "Preliminary results of a phylogenetic analysis of the pterosaurs from western Liaoning and surrounding area" (PDF). Journal of the Paleontological Society of Korea. 22 (1): 239–261. Retrieved 2007-03-10.
- Lü, J.; Unwin, D.M.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X. (2008). "A new azhdarchoid pterosaur from the Lower Cretaceous of China and its implications for pterosaur phylogeny and evolution". Naturwissenschaften. 95: 891–897. doi:10.1007/s00114-008-0397-5. PMID 18509616.
- Wang, X.; Zhou, Z. (2006). "Pterosaur assemblages of the Jehol Biota and their implication for the Early Cretaceous pterosaur radiation". Geological Journal. 41: 405–418.
- Wu, W.-H.; Zhou, C.-F.; Andres, B. (2017). "The toothless pterosaur Jidapterus edentus (Pterodactyloidea: Azhdarchoidea) from the Early Cretaceous Jehol Biota and its paleoecological implications". PLoS ONE. 12 (9): e0185486. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0185486. PMC 5614613. PMID 28950013.
- Andres, B.; Myers, T. S. (2013). "Lone Star Pterosaurs". Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: 1. doi:10.1017/S1755691013000303.
- http://pterosaur.net/species.php