Eopteranodon
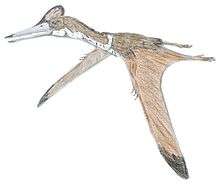
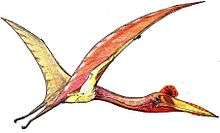
Eopteranodon (meaning "dawn Pteranodon (toothless wing)") is a genus of tapejarid pterosaur from the Aptian-age Lower Cretaceous Yixian Formation of Beipaio City, Liaoning, China. The genus was named in 2005 by Lü Junchang and Zhang Xingliao. The type species is Eopteranodon lii.
| Eopteranodon | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Order: | †Pterosauria |
| Suborder: | †Pterodactyloidea |
| Family: | †Tapejaridae |
| Subfamily: | †Sinopterinae |
| Genus: | †Eopteranodon Lü & Zhang, 2005 |
| Type species | |
| †Eopteranodon lii Lü & Zhang, 2005 | |
It is based on the type specimen or holotype BPV-078, an incomplete skeleton and skull. Its skull, including a large crest, was toothless and similar to that of Pteranodon. The skull lacks the point of the snout but it was in life less than 200 millimeters long (7.9 inches), and the animal had a wingspan of about 1.1 meters (3.6 feet). A second specimen, D2526, described in 2006, had a larger wingspan. Despite its similarities to Pteranodon, Eopteranodon was not placed into a family by its describers, who put it into the clade Pteranodontia as incertae sedis (uncertain position).[1]
Shortly thereafter, a phylogenetic study of all known Yixian pterosaurs by the same scientists found it to be close to the azhdarchoids, noted for the crested genera Tapejara and Tupuxuara, and the giant, long-necked Quetzalcoatlus.[2] A further analysis of other recently discovered forms, in 2006 still considered basal to (having split off earlier than) azhdarchoids, helped the original authors, along with David Unwin, to place these species together with Eopteranodon in a new clade Chaoyangopteridae, the possible sister group of the Azhdarchidae.[3] However, in 2017, it was considered a member of the Tapejaridae based on proportions of the crest on the lower jaw and the limbs.[4]
Classification
The cladogram below follows the 2014 analysis Andres and colleagues.[5]
| Azhdarchoidea |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- Lü, J.C.; B.K. Zhang (2005). "New pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Yixian Formation of western Liaoning". Geological Review. 51 (4): 458–462.
- Lü, Junchang; Qiang Ji (2006). "Preliminary results of a phylogenetic analysis of the pterosaurs from western Liaoning and surrounding area" (PDF). Journal of the Paleontological Society of Korea. 22 (1): 239–261. Retrieved 2007-03-10.
- Lü, J., Unwin, D.M., Xu, L., and Zhang, X. (2008). "A new azhdarchoid pterosaur from the Lower Cretaceous of China and its implications for pterosaur phylogeny and evolution." Naturwissenschaften
- Wu, W.-H.; Zhou, C.-F.; Andres, B. (2017). "The toothless pterosaur Jidapterus edentus (Pterodactyloidea: Azhdarchoidea) from the Early Cretaceous Jehol Biota and its paleoecological implications". PLoS ONE. 12 (9): e0185486. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0185486. PMC 5614613. PMID 28950013.
- Andres, B.; Clark, J.; Xu, X. (2014). "The earliest pterodactyloid and the origin of the group". Current Biology. 24 (9): 1011–6. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2014.03.030. PMID 24768054.