Cenomanian
The Cenomanian is, in the ICS' geological timescale, the oldest or earliest age of the Late Cretaceous epoch or the lowest stage of the Upper Cretaceous series.[2] An age is a unit of geochronology; it is a unit of time; the stage is a unit in the stratigraphic column deposited during the corresponding age. Both age and stage bear the same name.
| System/ Period |
Series/ Epoch |
Stage/ Age |
Age (Ma) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paleogene | Paleocene | Danian | younger | |
| Cretaceous | Upper/ Late |
Maastrichtian | 66.0 | 72.1 |
| Campanian | 72.1 | 83.6 | ||
| Santonian | 83.6 | 86.3 | ||
| Coniacian | 86.3 | 89.8 | ||
| Turonian | 89.8 | 93.9 | ||
| Cenomanian | 93.9 | 100.5 | ||
| Lower/ Early |
Albian | 100.5 | ~113.0 | |
| Aptian | ~113.0 | ~125.0 | ||
| Barremian | ~125.0 | ~129.4 | ||
| Hauterivian | ~129.4 | ~132.9 | ||
| Valanginian | ~132.9 | ~139.8 | ||
| Berriasian | ~139.8 | ~145.0 | ||
| Jurassic | Upper/ Late |
Tithonian | older | |
| Subdivision of the Cretaceous system according to the ICS, as of 2017.[1] | ||||
As a unit of geologic time measure, the Cenomanian age spans the time between[3] 100.5 ± 0.9 and 93.9 ± 0.8 million years ago (Mya). In the geologic timescale, it is preceded by the Albian and is followed by the Turonian. The Upper Cenomanian starts around at 95 Mya.
The Cenomanian is coeval with the Woodbinian of the regional timescale of the Gulf of Mexico and the early part of the Eaglefordian of the regional timescale of the East Coast of the United States.
At the end of the Cenomanian, an anoxic event took place, called the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary event or the "Bonarelli event", that is associated with a minor extinction event for marine species.
Stratigraphic definitions
The Cenomanian was introduced in scientific literature by French palaeontologist Alcide d'Orbigny in 1847. Its name comes from the New Latin name of the French city of Le Mans (département Sarthe), Cenomanum.
The base of the Cenomanian stage (which is also the base of the Upper Cretaceous series) is placed at the first appearance of foram species Rotalipora globotruncanoides in the stratigraphic record. An official reference profile for the base of the Cenomanian (a GSSP) is located in an outcrop at the western flank of Mont Risou, near the village of Rosans in the French Alps (département Hautes-Alpes, coordinates: 44°23'33"N, 5°30'43"E). The base is, in the reference profile, located 36 meters below the top of the Marnes Bleues Formation.[4]
The top of the Cenomanian (the base of the Turonian) is at the first appearance of ammonite species Watinoceras devonense.
Important index fossils for the Cenomanian are the ammonites Calycoceras naviculare, Acanthoceras rhotomagense, and Mantelliceras mantelli.
Sequence stratigraphy and palaeoclimatology
The late Cenomanian represents the highest mean sea level observed in the Phanerozoic eon, the past 600 million years (about 150 meters above present-day sea levels). A corollary is that the highlands were at all time lows, so the landscape on Earth was one of warm broad shallow seas inundating low-lying land areas on the precursors to today's continents. What few lands rose above the waves were made of old mountains and hills, upland plateaus, all much weathered. Tectonic mountain building was minimal and most continents were isolated by large stretches of water. Without highlands to break winds, the climate would have been windy and waves large, adding to the weathering and fast rate of sediment deposition.
Palaeontology
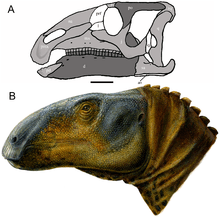
The crown group Crocodylia, the true crocodiles, first appear during the Cenomanian.[5]
Belemnites
| Belemnites of the Cenomanian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
Bony fish
| Bony fish of the Albian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
| Akfabou Formation, Morocco; Upper Plattenkalk; Italy | An ichthyodectid osteoglossomorph. | |||
| A member of Pachycormiformes. | ||||
Ankylosauria
| Ankylosaurs of the Cenomanian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
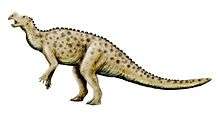
| Albian or Aptian to Cenomanian | Upper Greensand Group, Cambridgeshire, England | A nodosaurid with an armor of oval plates set almost horizontally into the skin, with spikes protruding from the neck and shoulder area, along the spine, its size has been estimated to be in the range of 3.0 to 5.5 m (10 to 18 ft) long and about 380 kg (840 lb) in weight. | ||
| Cenomanian to Turonian | Cedar Mountain Formation, Utah, USA | thought of as a nodosaurid ankylosaur, although its precise relationships within that family are uncertain | ||
| Wyoming, Kansas, USA | A nodosaurid ankylosaur about 4 to 6 m (13 to 20 ft) long with bony dermal plates covering the top of its body, it may have had spikes along its side, as well. It had four short legs, five-toed feet, a short neck, and a long, stiff, clubless tail. | |||
| Late Albian to early Cenomanian | Dakota Formation, Kansas, USA | A genus of nodosaurid known from a nearly complete skull | ||
| Late Albian to early Cenomanian | Frontier Formation, Wyoming, USA | A poorly known genus of nodosaurid | ||
| Baynshiree Svita Formation, Dzun-Bayan, Mongolia | An ankylosaurid known from the remains of its skull | |||
| Chaochuan Formation, Zhejiang, China | Ankylosaurid | |||
| Ruyang, Henan, China | Ankylosaurid | |||
Crocodylomorphs
| Crocodylomorphs of the Maastrichtian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
|
95 Ma | Kem Kem Beds, Morocco | A genus of giant, flat-headed eusuchian crocodyliform within the family Aegyptosuchidae. |
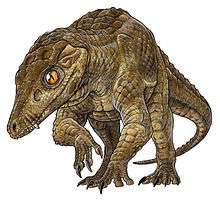 Araripesuchus patagonicus |
|
Egypt | Aegyptosuchus was once considered to be a member of Stomatosuchidae, it is now understood to be a more derived neosuchian and placed within Eusuchia in its own family, Aegyptosuchidae. | ||
|
125–66 Ma |
|
A long-lived, widespread, and diverse genus of basal notosuchians that appeared early in the Cretaceous and lasted until the end of it. Multiple species are from this genus, three of them having lived during the Cenomanian, and have been found from both South America and Africa. | |
|
Niger; Morocco | A genus of rather large neosuchian crocodyliform. It was similar to its closely related Stomatosuchus. | ||
|
Egypt | A genus of large neosuchian crocodyliform. Its flattened skull had a long, flat, lid-like snout, which was lined with small, conical teeth. The mandible may have been toothless and may have supported a pelican-like throat pouch. Aegyptosuchus | ||
Ornithopoda
| Ornithopods of the Cenomanian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
| Cerro Lisandro Formation, Neuquén, Argentina | A small bipedal herbivore, almost 2 m (7 ft) long | |||
|
Bihariosaurus |
Bihor, Romania | An iguanodont similar to Camptosaurus | ||
| Albian-Cenomanian | Utah, USA | A basal hadrosaur | ||
| Fostoria | Australia | A new iguanodont | ||
| Albian-Cenomanian | Australia | A large ornithopod that stood about 5 m high known from about 60% of its skeleton | ||
| Cenomanian-Turonian | Bajo Barreal Formation, Chubut, Argentina | A hypsilophodontid or other basal ornithopod, Notohypsilophodon would have been a bipedal herbivore. Its size has not been estimated. | ||
| Blackleaf Formation, Montana, and Wayan Formation, Idaho, USA | A burrowing hypsilophodont | |||
| Flower Mound, Texas, USA | A primitive hadrosauroid, Protohadros reached 6 m (19.5 ft) in length and had many hadrosaur-like features. | |||
| Cenomanian-Turonian | China | A poorly known iguanodont | ||
| Pari Aike Formation, Lake Viedma, Santa Cruz | A 4 metres (13 ft) long elasmarian | |||
Plesiosauria
| Plesiosaurs of the Cenomanian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
| Belle Fourche Shale, Wyoming, USA | A pliosaurid characterized by a moderately long symphysis bearing eight pairs of teeth that are nearly circular in cross-section and are smooth on the outer surface (except near the base), ribs of the neck vertebrae being singled-headed (double-headed in Jurassic pliosaurs), and a long slender interpectoral bar on the coracoid | 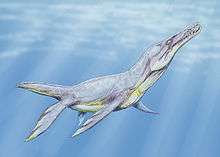 Plesiopleurodon | ||
| Graneros Shale Formation, Colorado and Belle Fourche Formation, Montana | Thalassomedon is among the largest elasmosaurids, with a total length of 10.86 metres (35.6 ft) for the holotype. | |||
Pterosauria
| Pterosaurs of the Cenomanian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
| Brazil | An ornithocheirid pterosaur | 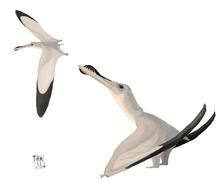 | ||
| Albian-Turonian | Chalk Formation and Cambridge Greensand, England | |||
Sauropoda
| Sauropods of the Cenomanian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
| Andesaurus | Candeleros Formation, Argentina |
| ||
| Argentinosaurus | Huincul Formation, Neuquén, Argentina | |||
| Diamantinasaurus | Winton Formation, Queensland, Australia | |||
| Paralititan | Bahariya Formation, Egypt | |||
| Puertasaurus | Pari Aike Formation, Patagonia, Argentina | Originally believed to be from Maastrichtian age. | ||
| Qiaowanlong | China | |||
| Sibirosaurus | Kiya River, Russia | |||
Theropoda
| Theropods of the Cenomanian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
| Iren Dabasu Formation, Mongolia | A medium sized tyrannosauroid closely related to later Eutyrannosauria. |
| ||
| Winton Formation, Queensland, Australia | A megaraptoran. | |||
| Bahariya Oasis, Egypt; Niger | A large theropod of dubious classification. May be synonymous with Deltadromeus. | |||
| Kem Kem Formation, Eckhar Formation, Bahariya Formation, Morocco; Niger; Egypt | A large carcharodontosaurid. Original specimens destroyed in World War II, new remains uncovered in the 1990s. Two species known; C. saharicus and C. iguidensis. Contemporaneous with Rugops, Spinosaurus and Deltadromeus/Bahariasaurus. | |||
| Morocco | A ceratosaur or possible neovenatorid carnosaur, it may be synonymous with Bahariasaurus and contemporaneous with Spinosaurus, Rugops, and Carcharodontosaurus. | |||
| Mongolia | ||||
| Mongolia | A therizinosaurid | |||
| Mongolia | A therizinosaurid | |||
| Candeleros Formation, Argentina | A carcharodontosaurid, it is one of the largest theropods currently known. | |||
| Huincul Formation, Argentina | A carcharodontosaurid known from multiple specimens in a single bone bed | |||
| Utah | A tyrannosauroid. | |||
| Moreno Hill Formation, Zuni Basin, New Mexico; Tropic Shale, Utah, USA | A therizinosaur, two species are known: N. mckinleyi and N. graffmani. | |||
| Brasil | A spinosaurid, the largest theropod thus far recovered from Brazil | |||
| Pari Aike Formation, Patagonia, Argentina; South America | A megaraptoran originally thought to have been from Maastrichtian deposits | |||
| Niger | An abelisaurid, contemporaneous with Spinosaurus, Carcharodontosaurus, and Deltadromeus/Bahariasaurus. | |||
| Mongolia | A theropod belonging to the Therizinosauridae family. | |||
| Thailand | ||||
|
Siats |
Cenomanian | Mussentuchit Member, Cedar Mountain Formation, Utah, USA | An 11- to 12-m neovenatorid carcharodontosaur known from juvenile remains, it is the youngest allosauroid known from North America. | |
| Tafilalt, Morocco | A spinosaurid known from fragmentary remains | |||
| Bahariya Oasis, Egypt; Tunisia; Morocco | A spinosaurid, it is currently considered one of the largest known theropods at an estimated 15 m (49 ft). | |||
| Comahue, Argentina | A unenlagiine dromaeosaurid | |||
|
unnamed enantiornithine bird[6] |
Nammoura, Ouadi al Gabour, Lebanon | |||
| Bajo Barreal Formation, Chubut Province, Argentina | An abelisaurid | |||
References
- Super User. "ICS - Chart/Time Scale". www.stratigraphy.org.
- See for a detailed geologic timescale Gradstein et al. (2004)
- International Commission on Stratigraphy. "International Stratigraphic Chart" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-05-29. Retrieved 2008-06-17.
- The GSSP for the Cenomanian was established by Kennedy et al. (2004)
- Mateus, O., Callapez P. M., & Puértolas-Pascual E. (2017). The oldest Crocodylia? a new eusuchian from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian) of Portugal. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology, Program and Abstracts. 2017, 160.
- Vecchia, F. M. D.; Chiappe, L. M. (2002). "First avian skeleton from the Mesozoic of northern Gondwana". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 22 (4): 856. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2002)022[0856:FASFTM]2.0.CO;2.
Further reading
- Gradstein, F.M.; Ogg, J.G. & Smith, A.G.; 2004: A Geologic Time Scale 2004, Cambridge University Press.
- Kennedy, W.J.; Gale, A.S.; Lees, J.A. & Caron, M.; 2004: The Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) for the base of the Cenomanian Stage, Mont Risou, Hautes-Alpes, France, Episodes 27, pp. 21–32.
External links
- GeoWhen Database - Cenomanian
- Late Cretaceous timescale, at the website of the subcommission for stratigraphic information of the ICS
- Stratigraphic chart of the Lower Cretaceous (including the Cenomanian), at the website of Norges Network of offshore records of geology and stratigraphy
- Cenomanian Microfossils: 20+ images of Foraminifera