Batrachognathus
Batrachognathus is an extinct genus of anurognathid pterosaur from the Late Jurassic (Oxfordian - Kimmeridgian) Karabastau Svita of the central Asian republic of Kazakhstan. The genus was named in 1948 by the Russian paleontologist Anatoly Nicolaevich Ryabinin. The type species is Batrachognathus volans. The genus name is derived from Greek batrakhos, "frog" and gnathos, "jaw", in reference to the short wide head. The specific epithet means "flying" in Latin.
| Batrachognathus Temporal range: Late Jurassic | |
|---|---|
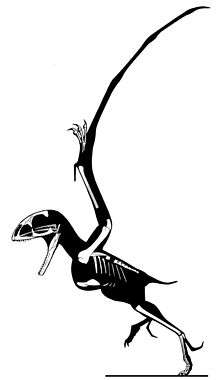 | |
| Skeletal restoration of the holotype by Jaime Headden | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Order: | †Pterosauria |
| Family: | †Anurognathidae |
| Genus: | †Batrachognathus |
| Species: | †B. volans |
| Binomial name | |
| †Batrachognathus volans Ryabinin, 1948 | |
Description
Three fossils have been found in a lacustrine sediment in the North-West Tien Shan foothills of the Karatau Mountains. In the Jurassic this area had some similarities in habitat to the Solnhofen lagoon deposits in Bavaria, Germany. The genus is based on holotype PIN 52-2, an incomplete and disarticulated skeleton consisting of skull fragments, jaws, vertebrae, ribs, legs and wing bones. The skull of 48 mm (1.9 in) long is high, short and broad. The upper jaws have in total 22 or 24 recurved conical teeth; with the lower jaws they make a short and very wide mouth. The animal is not preserved with a tail. Whether it had one is debatable; usually it is assumed a short tail was present. The wingspan has been estimated at 50 cm (20 in); David Unwin in 2000 gave a higher estimate of 75 cm (30 in). Like all anurognathids Batrachognathus is assumed to have been an insectivore, catching insects on the wing with its broad mouth.
Classification
Batrachognathus was assigned to the Anurognathidae, as a relative of Anurognathus. In 2003 Alexander Kellner named the clade Asiaticognathidae to include it and the Asian Anurognathid Dendrorhynchoides. Christopher Bennett pointed out the name Asiaticognathidae was inappropriate, as the clade lacked an Asiaticognathus, and in 2009 Kellner proposed Batrachognathinae as a replacement.[1] According to an analysis in 2006 by Lü Junchang, Batrachognathus and Jeholopterus are sister taxa.
References
- Dinosaurs and other Prehistoric Creatures, edited by Ingrid Cranfield, 2000 Salamander Books Ltd pg 280-281.
- Ryabinin A. N., 1948, "Remarks on a flying reptile from the Jurassic of the Kara-Tau", Akademia Nauk, Paleontological Institute, Trudy, 15(1): 86-93
- Alexander W. A. Kellner, Xiaolin Wang, Helmut Tischlinger, Diogenes de Almeida Campos, David W. E. Hone, and Xi Meng. (2009). "The soft tissue of Jeholopterus (Pterosauria, Anurognathidae, Batrachognathinae) and the structure of the pterosaur wing membrane", Proc. R. Soc. B doi:10.1098/rspb.2009.0846