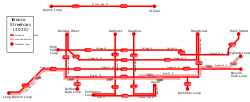
Toronto streetcar system
The Toronto streetcar system is a network of ten streetcar routes in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, operated by the Toronto Transit Commission (TTC). It is the third busiest light-rail system in North America. The network is concentrated primarily in Downtown Toronto and in proximity to the city's waterfront. Much of the streetcar route network dates from the 19th century. Most of Toronto's streetcar routes operate on street trackage shared with vehicular traffic, and streetcars stop on demand at frequent stops like buses.
 | |||
_(26689006592).jpg) Flexity Outlook streetcars | |||
| Overview | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Locale | Toronto, Ontario, Canada | ||
| Transit type | Streetcar | ||
| Number of lines | 10[1] | ||
| Number of stations | 685 stops[2] | ||
| Daily ridership | 530,600 (avg. weekday, Q4 2019)[3] | ||
| Annual ridership | 165,690,600 (2019)[3] | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | 1861 (catenary electrification since 1892)[4] | ||
| Operator(s) | Toronto Transit Commission | ||
| Character | Street running | ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 83 km (52 mi)[5] | ||
| Track gauge | 4 ft 10 7⁄8 in (1,495 mm) | ||
| Minimum radius of curvature | 36 ft 0 in (10,973 mm)[6] | ||
| Electrification | Trolley wire, 600 V DC | ||
| |||
Toronto's streetcars provide most of the downtown core's surface transit service. Four of the TTC's five most heavily used surface routes are streetcar routes. In 2019, ridership on the streetcar system totalled over 165 million.[3]
History
Pre-TTC history (1861–1921)

The main predecessors of the TTC were:
- Toronto Street Railway (1861–1891)
- Toronto Railway Company (1891–1921)
- Toronto Civic Railways (1911–1921)
In 1861, the City of Toronto issued a thirty-year transit franchise (Resolution 14, By-law 353) for a horse-drawn street railway, after the Williams Omnibus Bus Line had become heavily loaded. Alexander Easton's Toronto Street Railway (TSR) opened the first street railway line in Canada on September 11, 1861, operating from Yorkville Town Hall to the St. Lawrence Market. At the end of the TSR franchise, the City government ran the railway for eight months but ended up granting a new thirty-year franchise to the Toronto Railway Company (TRC) in 1891. The TRC was the first operator of horseless streetcars in Toronto. The first electric car ran on August 15, 1892, and the last horse car ran on August 31, 1894, to meet franchise requirements.
There came to be problems with interpretation of the franchise terms for the City. By 1912, the city limits had extended significantly, with the annexation of communities to the north (1912: North Toronto) and the east (1908: Town of East Toronto) and the west (1909: the City of West Toronto—The Junction). After many attempts to force the TRC to serve these areas, the City created its own street railway operation, the Toronto Civic Railways (TCR) to do so, and built several routes. Repeated court battles forced the TRC to build new cars, but they were of old design. When the TRC franchise ended in 1921, the Toronto Transportation Commission was created, combining the city-operated Toronto Civic Railways lines into its new network.
Early TTC history (1921–1945)
The TTC began in 1921 as solely a streetcar operation, with the bulk of the routes acquired from the private TRC and merged with the publicly operated Toronto Civic Railways. In 1923, the TTC took over the Lambton, Davenport and Weston routes of the Toronto Suburban Railway (TSR) and integrated them into the streetcar system.

In 1925, routes were operated on behalf of the Township of York (as Township of York Railway), but the TTC was contracted to operate them. One of these routes was the former TSR Weston route.
In 1927, the TTC became the operator of three radial lines of the former Toronto and York Radial Railway. The TTC connected these lines to the streetcar system in order to share equipment and facilities, such as carhouses, but the radials had their own separate management within the TTC's Radial Department. The last TTC-operated radial (North Yonge Railways) closed in 1948.
Plans for abandonment (1945–1989)
After the Second World War, many cities across North America and Europe[7] began to eliminate their streetcar systems in favour of buses. During the 1950s, the TTC continued to invest in streetcars and the TTC took advantage of other cities' streetcar removals by purchasing extra PCC cars from Cleveland, Birmingham, Kansas City, and Cincinnati.
In 1966, the TTC announced plans to eliminate all streetcar routes by 1980. Streetcars were considered out of date, and their elimination in almost all other cities made it hard to buy new vehicles and maintain the existing ones. Metro Toronto chair William Allen claimed in 1966 that "streetcars are as obsolete as the horse and buggy".[8] Many streetcars were removed from service when Line 2 Bloor–Danforth opened in February 1966.
The plan to abolish the streetcar system was strongly opposed by many people in the city, and a group named "Streetcars for Toronto" was formed to work against the plan. The group was led by Professor Andrew Biemiller and transit advocate Steve Munro. It had the support of city councillors William Kilbourn and Paul Pickett, and urban advocate Jane Jacobs. Streetcars for Toronto presented the TTC board with a report that found retaining the streetcar fleet would, in the long run, be cheaper than converting to buses. This combined with a strong public preference for streetcars over buses changed the decision of the TTC board.[9][10]
The busiest north–south and east–west routes were replaced respectively by the Yonge–University and the Bloor–Danforth subway line, and the northernmost streetcar lines, including the North Yonge and Oakwood routes, were replaced by trolley buses (and later by diesel buses). Two lines that operated north of St. Clair Avenue were abandoned for other reasons. The Rogers Road route was abandoned to free up streetcars for expanded service on other routes.[11] The Mount Pleasant route was removed because of complaints that streetcars slowed automobile traffic. Earlier, the TTC had contemplated abandonment because replacement by trolleybuses was cheaper than replacing the aging tracks.[12]

However, the TTC maintained most of its existing network, purchasing new custom-designed Canadian Light Rail Vehicles (CLRV) and Articulated Light Rail Vehicles (ALRV), with the first CLRV entering service in 1979. It also continued to rebuild and maintain the existing fleet of PCC (Presidents' Conference Committee) streetcars until they were no longer roadworthy.
When Kipling station opened in 1980 as the new western terminus of Line 2 Bloor–Danforth, it had provision for a future streetcar or LRT platform opposite the bus platforms. However, there was no further development for a surface rail connection there.[13]
In the early 1980s, a streetcar line was planned to connect Kennedy station to Scarborough Town Centre. However, as that line was being built, the Province of Ontario persuaded the TTC to switch to using a new technology called the Intermediate Capacity Transit System (now Bombardier Innovia Metro) by promising to pay for any cost overruns (which eventually amounted to over $100 million). Thus, the Scarborough RT (now Line 3 Scarborough) was born, and streetcar service did not return to Scarborough, instead stopping at the boundary.[14]
Late 20th-century expansion (1989–2000)

The TTC returned to building new streetcar routes in 1989. The first new line was route 604 Harbourfront, starting from Union station, travelling underneath Bay Street and rising to a dedicated centre median on Queen's Quay (along the edge of Lake Ontario) to the foot of Spadina Avenue. This route was lengthened northward along Spadina Avenue in 1997, continuing to travel in a dedicated right-of-way in the centre of the street, and ending in an underground terminal at Spadina station. At this time, the route was renamed 510 Spadina to fit with the numbering scheme of the other streetcar routes. This new streetcar service replaced the former route 77 Spadina bus, and since 1997 has provided the main north–south transit service through Toronto's Chinatown and the western boundary of University of Toronto's main campus. The tracks along Queen's Quay were extended to Bathurst Street in 2000 to connect to the existing Bathurst route, providing for a new 509 Harbourfront route from Union Station to the refurbished Exhibition Loop at the Exhibition grounds, where the Canadian National Exhibition is held.
21st century (2001–present)
By 2003, two-thirds of the city's streetcar tracks were in poor condition as the older track was poorly built using unwelded rail attached to untreated wooden ties lying on loose gravel. The result was street trackage falling apart quickly requiring digging up everything after 10 to 15 years. Thus, the TTC started to rebuild tracks using a different technique. With the new technique, concrete is poured over compacted gravel, and the ties are placed in another bed of concrete, which is topped by more concrete to embed rail clips and rubber-encased rails. The resulting rail is more stable and quieter with less vibration. The new tracks are expected to last 25 years after which only the top concrete layer needs to be removed in order to replace worn rails.[15][16]
Route 512 St. Clair was rebuilt to restore a separated right-of-way similar to that of the 510 on Spadina Avenue, to increase service reliability and was completed on June 30, 2010.[17]
On December 19, 2010, 504 King streetcar service returned to Roncesvalles Avenue after the street was rebuilt to a new design which provided a widened sidewalk "bumpout" at each stop to allow riders to board a streetcar directly from the curb. When no streetcar is present, cyclists may ride over the bumpout as it is doubles as part of a bike lane.[18][19]
On October 12, 2014, streetcar service resumed on 509 Harbourfront route after the street was rebuilt to a new design that replaced the eastbound auto lanes with parkland from Spadina Avenue to York Street. Thus, streetcars since then run on a roadside right-of-way immediately adjacent to a park on its southern edge.[20]
The Toronto Transit Commission eliminated all Sunday stops on June 7, 2015, as these stops slowed down streetcars making it more difficult to meet scheduled stops. Sunday stops, which served Christian churches, were deemed unfair to non-Christian places of worship, which never had the equivalent of a Sunday stop. Toronto originally created Sunday stops in the 1920s along its streetcar routes to help worshippers get to church on Sunday.[21]
_(14918534190).jpg)
The first two Flexity Outlook streetcars entered service on route 510 Spadina, on August 31, 2014; at the same time, all-door boarding and proof-of-payment (POP) was introduced on all 510 Spadina streetcars. Fare payments by Presto on the Flexity cars was introduced on November 30, 2014.[22] On November 22, 2015, the TTC started to operate its new fleet of Flexity Outlook streetcars from its new Leslie Barns maintenance and storage facility.[23]
On December 14, 2015, the TTC expanded Presto, POP and all-door loading to include all streetcars on all routes. All streetcar passengers are required to carry proof that they have paid their fares such as a validated TTC senior, youth or student ticket; paper POP or transfer; Presto card or ticket while riding.[24]
With the January 3, 2016, service changes, 510 Spadina became the first wheelchair-accessible streetcar route using mainly Flexity streetcars. However, CLRV and ALRV streetcars were used, in some cases, as a backup plan in the event there were not enough Flexity streetcars.[25]
On June 19, 2016, the TTC launched the 514 Cherry streetcar route to supplement 504 King service along King Street between Dufferin and Sumach streets. The new route operated every 15 minutes or better and initially used some and later only the Commission's new accessible Flexity streetcars.[26] The eastern end of the 514 route ran on a newly constructed branch, originally named the Cherry Street streetcar line, which is located in a reserved side-of-street right-of-way.[27]
On September 12, 2017, 509 Harbourfront became the first streetcar route in Toronto to operate Flexity streetcars with electrical pickup by pantograph instead of trolley pole.[28] That November, the King Street Transit Priority Corridor, a transit mall, was established along King Street between Bathurst and Jarvis streets.[29][30]
On October 7, 2018, the 514 Cherry route was permanently cancelled. The service it provided was replaced by the 504 King, which was divided into two overlapping branches, each to one of the termini (Dufferin Gate Loop and Distillery Loop) of the former 514 route.[31] That December, the TTC eliminated single-fare payments by credit and debit cards on the Flexity streetcars due to reliability issues with the fare vending machines.[32]
On September 2, 2019, the TTC retired the last of its ALRV streetcars.[33] The next day, due to the construction work at the Queen, Kingston Road, Eastern Avenue intersection, the TTC eliminated the 502 Downtowner service indefinitely. Concordantly, the 503 Kingston Rd service, which used to operate during rush hours only, was upgraded to operate during all daytime hours Monday through Friday. This change also affected the 501 Queen service, with buses replacing streetcars east of Queen street and Greenwood Avenue.[34][35] The construction projects ended that November. While the 501 Queen resumed full streetcar service, the 502 remained eliminated and the consolidation of Kingston Road service into the 503 Kingston Rd route remained in effect.[36]
On December 29, 2019, the TTC retired the last of its high-floor streetcars, the CLRVs. The final day for the CLRVs included a ceremonial farewell voyage along Queen Street, although the TTC plans to retain two CLRVs in Toronto for special events and charters.[37] Since the retirement of the CLRVs, all TTC bus and streetcar routes are served by accessible low-floor vehicles.
Incidents
On December 16, 2010, the TTC suffered its worst accident since the Russell Hill subway crash in 1995. Up to 17 people were sent to hospital with serious but non-life-threatening injuries after a 505 Dundas streetcar heading eastbound collided with a Greyhound bus at Dundas and River Streets.[38]
Routes
Based on 2013 statistics, the TTC operated 304.6 kilometres (189.3 mi)[2] of routes on 82 kilometres (51 mi) streetcar network (double or single track) throughout Toronto.[4][2] There are 10 regular streetcar routes on the TTC network.
| No. | Name | Length[39] | Notes | Fleet[39][40] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 501 | Queen | 24.65 km (15.32 mi) | Operates between Neville Park and Long Branch.[41]
Part of the Blue Night Network service operating as 301 Queen. |
Flexity |
| 503 | Kingston Rd | 10.37 km (6.44 mi)[42] | This route operates during the daytime hours Monday to Friday only.[43] | Flexity |
| 504 | King | 504A: 10.39 km (6.46 mi) 504B: 9.61 km (5.97 mi) | Operates as two overlapping branches:
Stops along Roncesvalles Avenue are not yet accessible due to platform height issues preventing the loading ramp on Flexity streetcars from being deployed.[44] Part of the Blue Night Network service operating as 304 King. |
Flexity |
| 505 | Dundas | 10.92 km (6.79 mi) | Flexity | |
| 506 | Carlton | 15.07 km (9.36 mi) | Aso serves College Street and Gerrard Street. Starting June 21, 2020, the entire 506 route has been replaced by buses until at least the end of 2020 due to a series of construction projects.[45]Part of Blue Night Network as 306 Carlton. | Bus |
| 508 | Lake Shore | 18.88 km (11.73 mi) | Rush hour service only (Monday to Friday); suspended from late March 2020 until further notice due to lower ridership during the COVID-19 pandemic.[46] | Suspended |
| 509 | Harbourfront | 4.40 km (2.73 mi) | Route operates on a dedicated right-of-way | Flexity |
| 510 | Spadina | 5.43 km (3.37 mi) | Route operates on a dedicated right-of-way.
Part of the Blue Night Network service as 310 Spadina. |
Flexity |
| 511 | Bathurst | 5.33 km (3.31 mi) | Service replaced with buses as of April 2020, due to construction projects including reconstruction of the Bathurst Street Bridge.[47] | Bus |
| 512 | St. Clair | 7.13 km (4.43 mi) | Route operates on a dedicated right-of-way | Flexity |
Due to a shortage of streetcars,[48] as well as various construction projects, some streetcar routes are temporarily supplemented or replaced – partly or entirely – with buses.[49] Some routes operate wholly or partly within their own rights-of-way and stop on demand at frequent stops.
Route numbers
.JPG_-_panoramio.jpg)
Until 1980, streetcar routes had names but not numbers. When the CLRVs were introduced, the TTC assigned route numbers in the 500 series. CLRVs have a single front rollsign showing various combinations of route number and destination, while PCC streetcars showed a route identifier (route name until the 1980s and later route number) and destination on two separate front rollsigns.[50] The digital destination signs on the new Flexity Outlook streetcars show route number, route name and destination.[51] Before 2018, streetcar-replacement bus services indicated route number and destination but not route name, like the CLRVs.
The four streetcar-operated Blue Night Network routes have been assigned 300-series route numbers. The other exception to the 500 series numbering was the Harbourfront LRT streetcar. When introduced in 1990, this route was numbered 604, which was intended to group it with the old numbering scheme for Toronto subway routes. In 1996, the TTC overhauled its rapid transit route numbers and stopped trying to market the Harbourfront route as "rapid transit". The number was changed to 510. The tracks were later extended in two directions to form the 510 Spadina and 509 Harbourfront routes.[52]
During times when streetcar service on all or a portion of a route has been replaced temporarily by buses (e.g., for track reconstruction, major fire, special event, heavy snowfall, lack of available streetcars, disaster), the replacement bus service is typically identified by the same route number as the corresponding streetcar line.
Subway connections
There are underground connections between streetcars and the subway at St. Clair West, Spadina, and Union stations, and streetcars enter St. Clair, Dundas West, Bathurst, Broadview, and Main Street stations at street level. At the eight downtown stations, excepting Union, from Queen's Park to College on Line 1 Yonge–University, streetcars stop on the street outside the station entrances. Union station serves as the hub for both the TTC and the GO Transit system.
Dedicated rights-of-way and transit malls
The majority of streetcar routes in Toronto operate in mixed traffic, generally reflecting the original track configurations of the streetcar system, a system that dates back to the late 19th and early 20th centuries. However, newer trackage has largely been established within dedicated rights-of-way, in order to allow streetcars to operate with fewer disruptions due to delays caused by automobile traffic. Most of the system's dedicated rights-of-way operate within the median of existing streets, separated from general traffic by raised curbs and controlled by specialized traffic signals at intersections. Queen streetcars have operated on such a right-of-way along the Queensway between Humber and Sunnyside loops since 1957. Since the 1990s, dedicated rights-of-way have been opened downtown along Queens Quay, Spadina Avenue, St. Clair Avenue West, and Fleet Street.

Short sections of the track also operate in a tunnel (to connect with Spadina, Union, and St. Clair West subway stations). The most significant section of underground streetcar trackage is a tunnel underneath Bay Street connecting Queens Quay with Union Station; this section, which is approximately 700 m (2,300 ft) long, includes one intermediate underground station at Bay Street and Queens Quay.
During the late 2000s, the TTC reinstated a separated right-of-way — removed between 1928 and 1935[53] — on St. Clair Avenue, for the entire 512 St. Clair route. A court decision obtained by local merchants in October 2005 had brought construction to a halt and put the project in doubt; the judicial panel then recused themselves, and the delay for a new decision adversely affected the construction schedule. A new judicial panel decided in February 2006 in favour of the city, and construction resumed in mid-2006. One-third of the St. Clair right-of-way was completed by the end of 2006 and streetcars began using it on February 18, 2007. The portion finished was from St. Clair station (Yonge Street) to Vaughan Road. The second phase started construction in mid-2007 from Dufferin Street to Caledonia Road. Service resumed using the second and third phases on December 20, 2009 extending streetcar service from St. Clair to Earlscourt Loop located just south and west of Lansdowne Avenue. The fourth and final phase from Earlscourt Loop to Gunns Loop (just west of Keele Street) is completed and full streetcar service over the entire route was finally restored on June 30, 2010.[54][55]

Between September 2007 and March 2008, the tracks on Fleet Street between Bathurst Street and the Exhibition Loop were converted to a dedicated right-of-way and opened for the 511 Bathurst and the 509 Harbourfront streetcars. Streetcar track and overhead power line were also installed at the Fleet loop, which is located at the Queen's Wharf Lighthouse.[56][57]
The eastern portion of the 504A King route runs on a side-of-street right-of-way. It was constructed starting in 2012 to support redevelopment in the West Don Lands and the Distillery District, former industrial areas.[26][27]
As part of the King Street Pilot Project, a temporary transit mall was set up along King Street for a one-year trial period starting in mid-November 2017. Although not a dedicated right-of-way, the transit mall achieves the goal of preventing road traffic from impeding streetcar service. Road traffic is discouraged from using the mall by being forced to leave the mall via a right turn at most signalized intersections.[58] This project has since been extended and made permanent under the name King Street Transit Priority Corridor.[59]
Future expansion
Near future
As of December 2019, the TTC is considering changes to several streetcar routes by 2022. These ideas are not firm plans and some assume approval to purchase additional streetcars, which would also end bus replacement along streetcar routes. The ideas are:[60]
- Splitting 501 Queen into two overlapping branches:
- 501A from Neville Park Loop to Sunnyside Loop
- 501B from Long Branch Loop to a new Riverside Loop, to be constructed along Broadview Avenue just north of Queen Street East
- 502 Downtowner to be definitively cancelled
- 503 Kingston Road to be extended west to Dufferin Gate Loop
- 504B to be extended west to Humber Loop and later to a proposed Park Lawn Loop
Transit City
The City of Toronto's and the TTC's Transit City report[61] released on March 16, 2007, proposed creating new light rail lines. These are mainly separate from the streetcar network as the track gauge and vehicle specifications are quite different. Much of the original proposal has since been cancelled, and those light-rail lines that are proceeding are classified as part of the Toronto subway system. Examples of former Transit City lines that survive include Line 5 Eglinton, which will open in 2021,[62] and Line 6 Finch West, which will open in 2023.[63]
Other proposals
The following are proposals to expand the streetcar system that were under consideration in 2015:
- The Waterfront West LRT would run from Long Branch Loop along Lake Shore Boulevard and the Queensway to Colbourne Lodge Drive and then adjacent to the Lake Shore Boulevard to Exhibition Loop and onto Union subway station via Queens Quay. This line originated from the Transit City proposals. It was shelved in 2013 but recommended for reconsideration in 2015 by city staff. In 2017, the TTC revised the proposal as summarized here.[64]
- The East Bayfront LRT is planned to run along Queens Quay East from Union station to complement the 509 Harbourfront line.[64]
- Waterfront Toronto is recommending the creation or extension of three streetcar lines in the Port Lands. Both the Cherry Street streetcar line and East Bayfront LRT would be extended to Queens Quay and Parliament Street. From there, one line would run south on Cherry Street to the Ship Channel and another east along Commissioners Street to Leslie Street. Another line would be built along an extended Broadview Avenue south from Queen Street to Commissioners Street.[65]
Discontinued streetcar routes
Between late 1921 and 1923, the TTC connected and merged many of the routes it inherited from the Toronto Railway Company and the Toronto Civic Railways. On July 1, 1923, the TTC did a major reorganization of routes whereby 9 new routes were created, 6 routes were discontinued, 13 were modified and 8 routes remained unmodified.[66]:37 The following list shows only those routes discontinued after this reorganization.
| Route | Began | Ended | Number | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ashbridge | 1917 | 1924 | Former TRC route, replaced by buses after a bridge carrying the streetcar line was declared unsafe[67] | |
| Bay | 1923 | 1954 | Replaced by extended Dupont streetcar[68] | |
| Beach | 1923 | 1948 | Route served today by 501 Queen[69] | |
| Bloor | 1890 | 1966 | Joined former TRC and TCR routes; used multiple unit PCC trains from 1950; replaced by Line 2 Bloor–Danforth subway.[70] | |
| Bloor West | 1914 | 1925 | Former TCR route absorbed into the Bloor streetcar line[70] | |
| Bloor shuttle | 1966 | 1968 | Western end of the Bloor streetcar line replaced an extension of the Bloor–Danforth subway[70] | |
| Cherry | 2016 | 2018 | 514 | Route cancelled as of October 7, 2018, and replaced by branches of 504 King |
| Church | 1881 | 1954 | Former TRC route, replaced by Church bus running until 1979[71] | |
| College | 1923 | 1933 | Replaced by the Carlton streetcar route[72] | |
| Coxwell | 1921 | 1966 | Replaced by 22 Coxwell bus | |
| Danforth shuttle | 1966 | 1968 | Eastern end of the Bloor streetcar line replaced an extension of the Bloor–Danforth subway[70] | |
| Danforth tripper | 1923 | 1966 | Rush-hour variant of the Bloor streetcar route[70] | |
| Davenport | 1892 | 1940 | Former Toronto Suburban Railway route, replaced by Davenport bus due to low ridership[73] | |
| Dovercourt | 1888 | 1947 | Former TRC route replaced by trolley buses due to declining ridership and to avoid replacing deteriorated track[74] | |
| Downtowner | 1973[75] | 2019 | 502 | Merged with 503 Kingston Rd in September 2019 and delisted on TTC website by January 2020[35][36][76] |
| Dundas Exhibition | 1980 | 1986 | 522 | Seasonal route also operated during the 1995 season and the 2013 Canadian National Exhibition |
| Dupont | 1923 | 1963 | Replaced by 6 Bay bus[68] | |
| Earlscourt | 1954 | 1976 | Merged into 512 St. Clair; assigned number 512L. | |
| Fort | 1931 | 1966 | Merged into 511 Bathurst | |
| Harbord | 1911 | 1966 | Replaced by 72 Pape and 94 Wellesley buses | |
| Harbourfront | 1990 | 2000 | 604 | Renumbered as 509 Harbourfront |
| King Exhibition | 1980 | 2000 | 521 | Temporarily reinstated in 2013 and operating as 521 Exhibition East |
| Lake Simcoe | 1927 | 1930 | Former T&Y Radial Metropolitan line[77] | |
| Lambton | 1924 | 1928 | Former Toronto Suburban Railway route, replaced by buses[11] | |
| Lansdowne | 1917 | 1947 | Former TCR line extended south by TTC, replaced by trolley buses[78] | |
| Long Branch | 1928 | 1995 | 507 | Merged into 501 Queen |
| Mimico | 1927 | 1928 | Former T&Y Radial Mimico line replaced by Beach streetcar route and Port Credit route[79][80]:153 | |
| North Yonge | 1930 | 1948 | From Glen Echo to Richmond Hill[77] | |
| Oakwood | 1922 | 1960 | Replaced by 63 Ossington trolleycoach (converted to diesel bus route in 1992 when trolleybus fleet retired)[11] | |
| Parliament | 1910 | 1966 | Replaced by 65 Parliament bus | |
| Port Credit | 1928 | 1935 | Shortened Mimico route running west of Long Branch Loop, replaced by buses[79][80]:153 | |
| Scarboro | 1928 | 1936 | Former T&Y Radial Scarboro line replaced by buses[79][80]:153 | |
| Spadina | 1923 | 1948 | Replaced by the 77 Spadina bus; later replaced by the 510 Spadina streetcar in 1997 | |
| Mount Pleasant | 1975 | 1976 | Split from 512 St. Clair; replaced by 74 Mt. Pleasant trolleycoach until 1991; diesel bus route from St. Clair Station to Mt. Pleasant Loop just north of Eglinton 1976–1977; diesel bus route since 1991. | |
| Rogers Road | 1922 | 1974 | Replaced by 63F Ossington via Rogers trolleycoach and 48 Humber Blvd from 1974 to 1994; diesel buses from 1992 onwards. In 1994, 161 Rogers Road service replaced both 63F Ossington and 48 Humber Blvd.[11] | |
| Sherbourne | 1874 | 1942 | Former TRC route replaced by buses[81] | |
| Weston | 1923 | 1948 | Former Toronto Suburban Railway route, replaced by trolley buses[11] | |
| Winchester | 1910 | 1924 | Replaced by Yonge and Parliament streetcars (former replaced by subway in 1954 and latter by bus route in 1966); bus route from Parliament Street east to Sumach Street from 1924 to 1930. | |
| Yonge | 1861 | 1954 | Replaced by Line 1 Yonge–University subway, Downtown bus (97 Yonge beginning in 1956), and Yonge trolleycoach until 1973, when it was replaced with diesel buses. |
Rolling stock
Streetcars acquired by the TTC

When the TTC was created in 1921, it acquired hundreds of cars from its two predecessor companies: the Toronto Railway Company and the Toronto Civic Railways. In 1927, the TTC acquired the radial cars of the former Toronto & York Radial Railway when it took over operation of that system from the Hydro-Electric Railways.[79]
In the 1920s, the TTC purchased new Peter Witt streetcars, and they remained in use into the 1960s. In 1938, the TTC started to operate its first Presidents' Conference Cars (PCC), eventually operating more than any other city in North America. In 1979, the Canadian Light Rail Vehicles entered revenue service,[82] followed by their longer, articulated variants, the ALRVs, in 1988.[83] The last of the PCC vehicles were retired from full-time revenue service in the 1990s.
On August 31, 2014, the TTC started operating its first Bombardier Flexity Outlook vehicles. As more of these new vehicles arrived and entered service, older CLRV and ALRV vehicles were gradually retired from service.[84]
The following table summarizes streetcars purchased by the TTC since 1921. The main article has more details on rosters, including streetcars inherited from the Toronto Railway Company and the Toronto Civic Railways which are not summarized here.
| Type | Quantity | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peter Witt | 250 | 1921–1954 | "Large" Witts – with rear coupler to haul a trailer |
| Peter Witt | 100 | 1922–1965 | "Small" Witts – without coupler; one vehicle retained by the TTC for special occasions. |
| 2-door trailer | 60 | 1921–1938 | |
| 3-door trailer | 165 | 1923–1954 | "Harvey" trailers |
| PCC | 317 | 1938–1971 | Air-electric |
| PCC | 428 | 1947–1995 | All-electric; two PCCs retained by the TTC for charters and special occasions.[85] |
| CLRV | 196 | 1979–2019 | Retired from regular TTC service on December 29, 2019, with three heritage vehicles retained by the TTC for special events.[86][37] A number of vehicles were also bought by heritage museums. In October 2019, prior to the fleet's retirement, CLRV 4178 was wrapped with special "A streetcar named Toronto" colours in partnership with Cityfund and the TTC – this vehicle was subsequently donated to the Halton County Radial Railway.[87][88] |
| ALRV | 52 | 1988–2019 | Articulated, two-section streetcars; all ALRVs were officially retired on September 2, 2019, with one retained by the TTC for special events and the other sold to the Halton County Radial Railway.[89] |
| Flexity | 204 | 2014–present | Articulated, with five modules per vehicle, low-floor and wheelchair-accessible; prototypes arrived in 2012 for extensive testing; they first entered service on August 31, 2014, with final deliveries taken in January 2020.[39] |
Streetcar shortage (2016–present)
Since 2016, the TTC has faced a streetcar shortage because of:
- Delays in the delivery of the new Flexity streetcars[84]
- The declining reliability and retirement of the aging CLRV/ALRV fleet[90]
- A 20 percent increase in streetcar ridership since 2008[84]
- Warranty repairs on 67 Flexity streetcars requiring the shipment of several streetcars at a time to a Bombardier plant[91]
In January 2017, the TTC claimed that delays in delivery of the new Flexity Outlook streetcars had resulted in both streetcar and bus shortages. Because the CLRV/ALRV streetcars required extra maintenance, only 170 of the 200 CLRVs and ALRVs could be put into service. This shortage led to the replacement of streetcars by buses on some routes, which in turn led to a reduction of service on some bus routes.[90][92]
To address the streetcar shortage, as well as construction projects, the TTC has used bus substitution at various times on several streetcar routes.[93][94] The first bus substitution due to the streetcar shortage occurred for the 502 Downtowner route on October 11, 2016.[95]
Ridership on the 504 King increased by 25 percent after the implementation of the King Street Transit Priority Corridor through downtown King Street. Thus, in February 2018, the TTC replaced the CLRV streetcars on routes 505 Dundas and 506 Carlton with buses and reassigned those streetcars to other routes, such as 504 King and 511 Bathurst, to handle crowding from increased ridership.[96][93]
The streetcar fleet capacity had not grown for almost three decades after the CLRVs and ALRVs were introduced. After delivery of the last of the initial 204 Flexity cars ordered, the TTC planned to purchase another 60 cars; however, the TTC estimated that would only satisfy demand until 2023 instead of 2027 as originally planned. Bombardier may end up being the chosen supplier for additional Flexity cars solely because, if the TTC went with another supplier, a prototype modified for Toronto's track characteristics would not be ready until 2023, with first delivery in 2024 or 2025.[84]
By June 2020, the streetcar shortage had been alleviated by the reduction in ridership due to the COVID-19 pandemic in conjunction with temporary bus replacements on routes 511 Bathurst and 506 Carlton to accommodate construction projects. With more streetcars available, the TTC could ship up 19 extra streetcars to a Bombardier plant for warranty repairs, as well as introduce Flexity streetcars for the first time on route 503 Kingston Rd.[97][43][98]
Track characteristics
The track on the Toronto streetcar system has characteristics of non-standard gauge, tight curve radii and single-point switches that previous generations of high-floor streetcars were adept at handling. Some of these characteristics were problematic for Bombardier when it adapted its low-floor Flexity Outlook for Toronto's streetcar system.[99][100]
Track gauge


All streetcar lines use the unique Toronto gauge of 4 ft 10 7⁄8 in (1,495 mm) which is 2 3⁄8 inches (60 mm) wider than the 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge used by most other rail lines in Canada. This broad gauge was adopted in 1861 for the city's horse-drawn streetcar lines to allow horse-drawn wagons and carriages to use the inside of the rail for a smoother ride through muddy, unpaved streets. The gauge also had the effect of precluding the movement of standard-gauge freight cars along streetcar lines. The unique gauge has remained to this day because it is easier to adapt new rail vehicles to this gauge than to convert the entire system to standard gauge. The three heavy-rail lines of the Toronto subway also use the unique gauge; however, the light-metro Line 3 Scarborough and two light rail lines under-construction (Line 5 Eglinton and Line 6 Finch West) use standard gauge.[101][102]
Track curvature
Curved track on the streetcar system has a very low minimum radius of curvature, with streetcars designed for a minimum radius of 10.973 metres (36 ft).[50] The tightest curves are 11.3 metres (37.1 ft) at Roncesvalles Carhouse and Russell Carhouse.[103] Almost all turning loops on the system have curves of less than 15 metres (49.2 ft).[104]
The Flexity Outlook, as modified for Toronto, is designed for a minimum radius of 10.973 metres (36 ft).[50] In contrast, the standard Flexity Outlook, as well as the Flexity Freedom (used on Line 5 Eglinton), both require a minimum radius of 25 metres (82 ft).[105][106]
Track switches
As with most legacy streetcar systems in North America, the TTC uses single-point switches in special work throughout the system. In contrast, most light-rail systems use double-point switches, with a movable blade on each track. With single-point switches, the blade is only on the inner rail of the curve, and streetcars must have a rigid, continuous axle to pull the wheel on the outer rail through the curve without the blade. Thus, low-floor streetcars with split axles cannot operate through single-point switches. In the early days of the CLRV, Bochum wheels with rubber rings holding the axle caused derailments due to a lack of rigidity, and had to be replaced with SAB wheels.[100]
Streetcar switches are either manual or automatic. For automatic switches, there are loop antennae buried in the road and two transmitters onboard the vehicles. One transmitter is located at the front of the car to set and lock the switch; the second is at the rear to unlock the switch.[lower-alpha 1] Because of failing electronics, defective attennae or the failure of the system to unlock after passage of a car, there is the risk of a streetcar taking the wrong path at a switch.[107]
In 2002, the TTC instituted a "stop, check, go" rule for all facing point switches. Streetcar operators, when approaching such switches, must stop and check the switch-blade setting before proceeding. In 2008, an operator forgot to make this check, which resulted in two streetcars colliding.[107] About 2015, the TTC modified the "stop, check, go" process to include pointing a finger. Each streetcar operator, upon arriving at a facing switch-point, is to stop short of the switch, point with their finger toward the switch's position to confirm that the switch is aligned properly for the streetcar's intended movement, and then proceed.[108]
Electrical pickup

The older CLRV and ALRV streetcars have only a trolley pole. New Flexity Outlook streetcars are delivered with both a pantograph as well as a trolley pole. All streetcars in service had been using the trolley pole until September 12, 2017, when 509 Harbourfront became the first route to use the pantograph.[28]
With the introduction of the new Flexity streetcars, the TTC plans to convert the entire system to be pantograph-compatible. The new streetcars need 50% more electrical current than the older streetcars, and use of the trolley pole limits the amount of electricity the new cars can draw from the overhead wire, resulting in reduced performance. One consequence of trolley pole use on the Flexity streetcars is that air conditioning does not function in summer.[109]
Since 2008, the TTC has been converting the streetcar overhead wire to be compatible for pantograph electrical pickup as well as for trolley poles. The overhead over the Fleet Street tracks was the first to be so converted. The new overhead uses different hangers so that pantographs do not strike supporting crosswires. It also uses a different gauge of wire to handle the higher electrical demands of Flexity Outlook streetcars.[110]
.jpg)
During a rainy period in February 2018, the TTC received an incentive to expedite the conversion of the electrical overhead for pantograph use by the Flexity streetcars. On February 20, 2018, Flexity streetcars using trolley poles were pulling down some of the overhead. In Toronto, the tip of the trolley pole has a shoe with a carbon insert to collect current. The carbon insert also lowers the trolley shoe so that it does not strike hangers that are not yet pantograph-compatible. During wet weather, these carbon inserts wear out faster, needing replacement after a day or two for older streetcars. However, because the Flexity streetcars draw more current than older streetcars, their carbon inserts wore out faster in less than eight hours in the wet weather. (There was also an issue with the quality of carbon the TTC purchased.) With pantographs, this would be less of a problem as the pantograph blades have a larger contact area than a trolley shoe to absorb wear. Because of this incident, the TTC decided it should accelerate the conversion of overhead for pantograph use.[111]
The first three routes to operate with pantographs were 509 Harbourfront on September 12, 2017, 510 Spadina on May 14, 2018, and 512 St. Clair on October 1, 2018.[112][111]
Winter operational issues
Extreme cold weather
The fleet of CLRV and ALRV streetcars experienced several operational issues during extreme cold temperatures during late 2013 and early 2014, late 2014 and early 2015, late 2017 and early 2018, and late 2018 and early 2019, as doors and brakes failed as moisture in the pneumatic lines froze. Moisture also caused track sanders to fail. Buses were used to replace streetcars unfit for service, some of which had failed while in service. The new Flexity Outlook streetcars were unaffected by the weather, as they use electronic braking and door operations.[113][114][115][116] During an extreme cold snap between January 20 and 22, 2019, none of the CLRV/ALRV streetcars were in service due to the high risk of breakdowns in the cold weather. Instead, Flexity streetcars, along with buses, were used to provide service. The remaining ALRVs stayed out of service for the rest of that winter season.[117]
By 2020, the CLRV/ALRV vehicles had been entirely replaced by new Flexity Outlook streetcars, mitigating these operational issues from occurring in future years.[113][114][115][116]
Freezing rain
The streetcar overhead is vulnerable during freezing rain storms. During such storms, the TTC applies anti-freeze to the overhead wire to prevent ice from interrupting electrical contact. In addition, the TTC attaches "sliders" to trolley poles on every fifth streetcar to knock ice off the overhead wire. The TTC places overhead crews on standby at various locations around the streetcar network to address problems of power loss or overhead wires coming down.[118]
The anti-freeze used on the overheard wire is also applied to streetcar switches on the network. In addition, the TTC runs "storm cars" on all routes to prevent any ice build-up on switches that the anti-freeze could not prevent.[118]
These measures are applied only during freezing rain. However, during the ice storm of April 14–16, 2018, the TTC also used bus substitution on portions of the streetcar network outside the downtown area in order to concentrate streetcars and emergency crews into a smaller area.[118]
Properties

Dedicated station
Queens Quay is the one standalone underground station that does not connect to the subway. It is located in the tunnel, shared by the 509 Harbourfront and 510 Spadina routes, between Queens Quay West and Union subway station.
Loops
Since all of Toronto's current streetcars are single-ended, turning loops are provided at the normal endpoints of each route and at likely intermediate turnback locations. A routing on-street around one or more city blocks may serve as a loop, but most loops on the system are wholly or partly off-street. Many of these are also interchange points with subway or bus services.
Carhouses
Toronto's streetcars are housed and maintained at various carhouses or "streetcar barns":
| Yard | Location | Year opened | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hillcrest Complex | Davenport Road and Bathurst Street | 1924 | Newly built by TTC on former site of farm and later Toronto Driving Club track; services streetcars and buses, repair facilities |
| Roncesvalles Carhouse | Queen Street West and Roncesvalles Avenue | 1895 (for TRC); rebuilt 1921 (by TTC) | Property acquired Toronto Railway Company, but new carbarn built in 1921 with indoor inspection and repair facility and outdoor streetcar storage tracks |
| Russell (Connaught Avenue) Carhouse | Connaught Avenue and Queen Street East | 1913 (by TRC and 1916 carhouse added); 1924 (rebuilt by TTC) | Built for the Toronto Railway Company as paint shop and 1916 carhouse built to replace King carhouse lost to a fire in 1916; acquired by the TTC in 1921 and rebuilt in 1924 with indoor maintenance facility and outdoor streetcar storage tracks |
| Leslie Barns | Leslie Street and Lake Shore Boulevard East – southeast corner | November 2015 | Carhouse opened November 2015 and receiving some of Flexity fleet (100 of the 204 cars);[119] fully opened in early 2016 |
Inactive carhouses once part of the TTC's streetcar operations:
| Yard | Location | Year opened | Year closed | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Danforth Carhouse | Danforth Avenue and Coxwell Avenue | 1915; 1921–22 (additions by TTC) | 2002 | built for the Toronto Civic Railways in 1915 and additional indoor storage added by TTC in 1921–22; re-purposed as bus garage in 1967; closed in 2002 but still used by TTC for storage and office space[120] |
| Dundas Carhouse[121] | Dundas Street West and Howard Park Avenue | 1907 | 1936 | Original acquired from TRC (built in 1907), but carhouse was demolished in 1921 but retained for storage for 60 cars; wye and runaround loop since disappeared and area re-developed with cars moving to Roncesvalles |
| Eglinton (Yonge) Carhouse | Eglinton Avenue West and Yonge Street | 1922 | 2002; demolished | Built to replace TRC Yorkville Carhouse and retired as carhouse in 1948 to become bus garage until 2002; most of facility now demolished and remainder used as temporary bus terminal |
| George Street Yard | 170 The Esplanade East | 1894? | 1960s | Used to store and scrap streetcars; now part of David Crombie Park built along with the St. Lawrence housing project (built between 1960s to 1990s) |
| Harbour Yard | Lakeshore Boulevard between Bay and York Streets | 1951 | 1954 | Built as temporary outdoor storage space for Peter Witt cars after Eglinton Carhouse closed to streetcars; tracks removed 1954; now site of parking lot and office towers |
| Lansdowne Carhouse | Lansdowne Avenue and Paton Avenue | 1911 | 1996; demolished 2003 | Built for the Toronto Railway Company and acquired by TTC in 1921; became a trolley bus garage in 1947 and streetcar storage ended 1967; abandoned after 1996 and demolished 2003 |
| TRC Motor Shops | 165 Front Street East | 1886–1887 | 1924 | Built for Toronto Street Railway near St Lawrence Market as horse stables and became electrical generating plant 1891 after horsecar converted to electric car operations by Toronto Railway Company; later as storage space 1906 and acquired by TTC in 1921; used until 1924 and deemed surplus in 1970s; sold to Young People's Theatre 1977 |
| St. Clair (Wychwood) Carhouse | Wychwood Avenue south of St. Clair Avenue West | 1914 | 1978 | Built for the Toronto Civic Railways in 1914 and expanded 1916. Acquired by TTC in 1921 with renovations and renamed as Wychwood Barns; closed in 1978 after cars moved to Roncesvalles but continued to be used for storage until the 1990s; tracks removed and restored as community centre. |
| Yorkville Carhouse | Between Scollard Street and Yorkville Avenue west of Yonge Street | 1892 | 1922 | The TRC demolished the Toronto Street Railway's Yorkville stables in order to build the carhouse.[122]:114 In 1922, the TTC closed the carhouse; it was later demolished and is now site of a condominium and Townhall Square Park. |
Source: The TTC's Active Carhouses
Advertising
Pattison Outdoor Advertising is responsible for posters outside and inside the streetcars, as well as outside and inside the buses and the subway system.[123]
See also
- Toronto Transit Commission bus system
- Urban rail transit in Canada
- Metrolinx light rail projects in Toronto:
- Queen subway line (a streetcar tunnel)
- Birney (Toronto streetcar) (a model of streetcar operated by the TTC)
- Streetcars in North America (for other streetcar lines in North America)
Notes
- This explanation is from several years prior to the delivery of the first Flexity Outlook streetcar.
References
Inline citations
- "TTC Streetcars". TTC. Archived from the original on January 12, 2020. Retrieved January 11, 2020.
- "2013 TTC Operating Statistics". Toronto Transit Commission. 2014. Retrieved October 4, 2014.
- "Public Transportation Ridership Report: Fourth Quarter 2019" (PDF). American Public Transit Association. February 27, 2020. Retrieved May 12, 2020.
- "Toronto's Streetcar Network – Past to Present – History". 2013. Retrieved July 26, 2013.
- http://www.urbanrail.net/am/toro/tram/toronto-tram.htm
- The Canadian Light Rail Vehicles – Transit Toronto
- Costa, Alvaro; Fernandes, Ruben (February 2012). "Urban public transport in Europe: Technology diffusion and market organisation". Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice. 46 (2): 269–284. doi:10.1016/j.tra.2011.09.002.
- Bragg, William (November 13, 1967). "Our Streetcars are Near the End of the Line". Toronto Star. p. 7.
- Thompson, John (April 5, 2017). "Renewing TTC's surface-running streetcar track". Railway Age. Retrieved April 7, 2017.
The Toronto Transit Commission (TTC) owns and operates more than 200 single-track miles of surface streetcar track, including loops, yards and carhouses.
- Cal, Craig (December 1, 2007). "Streetcars for Toronto – 35th Anniversary". Spacing. Archived from the original on November 28, 2010.
- Bow, James (August 14, 2017). "The Township Of York Railways (Deceased)". Transit Toronto. Retrieved June 28, 2020.
- Bow, James (April 21, 2013). "The Mount Pleasant Streetcar (Deceased)". Transit Toronto. Retrieved October 20, 2017.
- "Kipling". Transit Toronto. Retrieved December 14, 2017.
A cutaway of the elevations of Kipling and Kennedy station, showing planned LRT platforms. Image courtesy the Toronto Archives and Nathan Ng's Station Fixation web site.
- "Frequently Asked Questions About Toronto's Subway And The Scarborough RT". Transit Toronto. July 20, 2017. Retrieved December 14, 2017.
Why was the Kennedy RT station renovated so soon after it was built?
- Munro, Steve (October 25, 2009). "Streetcar Track Replacement Plan 2010–2014". Steve Munro. Retrieved October 25, 2009.
- Abbate, Gay (July 14, 2003). "State of tracks forces streetcars to crawl". The Globe and Mail. Retrieved July 14, 2003.
- Alter, Lloyd (November 25, 2013). "Streetcars save cities: A look at 100 years of a Toronto streetcar line". TreeHugger. Archived from the original on November 26, 2013. Retrieved November 25, 2013.
A hundred years ago, a new streetcar line was installed on St. Clair Avenue in Toronto in a dedicated right-of-way. In 1928 they got rid of the right-of-way to make more room for cars; In 2006 they rebuilt it again, putting the right of way back.
- "Lanes, tracks and bikes". Roncesvalles Village BIA.
- Munro, Steve (December 19, 2010). "Parliament and Roncesvalles 2010 Track Work". Steve Munro. Retrieved December 19, 2010.
- Munro, Steve (October 12, 2014). "Streetcars Return to Queens Quay". Steve Munro. Retrieved October 12, 2014.
- Andrew-Gee, Eric (May 7, 2015). "Sunday streetcar stops near churches to be shuttered in June". Toronto Star. Retrieved May 7, 2015.
- Freeman, Joshua (November 28, 2014). "Presto card readers to roll out soon on some streetcars : Metrolinx". CP24. Retrieved January 12, 2020.
- "TTC's new streetcar facility to enter service this Sunday". Toronto Transit Commission. November 20, 2015.
- "Proof-of-Payment (POP)". Toronto Transit Commission. Archived from the original on December 7, 2015. Retrieved December 6, 2015.
- Munro, Steve (December 4, 2015). "TTC Service Changes Effective January 3, 2016". Retrieved December 6, 2015.
- "Introducing 514 Cherry". Toronto Transit Commission. June 20, 2016. Retrieved December 14, 2017.
- Morrow, Adrian (May 25, 2012). "A tiny perfect streetcar line is being laid along Cherry Street". The Globe and Mail. Retrieved July 19, 2012.
- Munro, Steve (September 12, 2017). "Pantographs Up On Harbourfront". Steve Munro. Retrieved September 15, 2017.
- "King Street pilot to launch in November — but not everyone's happy about it". Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. October 26, 2017. Retrieved October 30, 2017.
- Spurr, Ben (November 8, 2017). "Street overhaul that puts transit first set to launch on King St". Toronto Star. Retrieved November 9, 2017.
- "The current section is Service Advisories 504 King and 514 Cherry route changes". Toronto Transit Commission. October 7, 2018. Archived from the original on September 25, 2018. Retrieved October 7, 2018.
- Jones, Alexandra (December 5, 2018). "Debit/credit pay option to be removed from new streetcars' on-board machines by Dec. 20". Toronto Star. Retrieved January 12, 2020.
- Bañares, Ilya (August 28, 2019). "Monday is your last chance to ride the TTC's old, articulated streetcars". Toronto Star. Retrieved August 30, 2019.
- "503 Kingston Rd – Route update". TTC. Archived from the original on August 31, 2019. Retrieved September 3, 2019.
- "Editorial – September Board Period Service Changes". The Coupler. Toronto Transit Commission. July 31, 2019. Archived from the original on September 1, 2019. Retrieved September 1, 2019.
- "Editorial – November Board Period Service Changes". The Coupler. Toronto Transit Commission. October 27, 2019. Archived from the original on November 15, 2019. Retrieved November 15, 2019.
- Aguilar, Bryann (November 21, 2019). "TTC to retire its CLRV streetcars on Dec. 29". CP24. Retrieved November 29, 2019.
- Schoolchildren returning from field trip hurt in streetcar crash: report
- "February 16, 2020 to March 28, 2020" (PDF). Toronto Transit Commission.
- "Service Changes". Toronto Transit Commission. Retrieved March 29, 2020. Showing late changes not reflected in the TTC service summary
- "Service Summary - February 18, 2018 to March 31, 2018" (PDF). Toronto Transit Commission.
- "Seasonal service changes and improvements". Toronto Transit Commission. June 18, 2020. Archived from the original on June 20, 2020. Retrieved June 20, 2020.
- "504 King". Toronto Transit Commission. Retrieved May 7, 2020.
- "506 Carlton - Temporary route change during infrastructure renewal". Toronto Transit Commission. June 21, 2020. Archived from the original on June 20, 2020. Retrieved June 20, 2020.
- "Coronavirus update". Toronto Transit Commission. March 27, 2020. Retrieved March 29, 2020.
- "Upcoming City Construction on Bathurst Street" (PDF). City of Toronto. May 7, 2020. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 21, 2020. Retrieved May 21, 2020.
- Byford, Andy (December 20, 2016). "New Streetcar Delivery and Claim Negotiation Update" (PDF). Toronto Transit Commission. Retrieved April 4, 2017.
- "Accessible streetcar service updates". Toronto Transit Commission. November 12, 2017. Retrieved December 13, 2017.
- Bow, James (February 7, 2017). "The Canadian Light Rail Vehicles (The CLRVs)". Transit Toronto. Retrieved October 21, 2017.
Some Torontonians also didn't like it when the streetcar route names like QUEEN and KING were removed from the front rollsigns, in favour of route numbers like 501 and 504, and some blamed the CLRV's single rollsign design for this change.
- Bow, James (September 14, 2017). "The Toronto Flexity Light Rail Vehicles (LRVs)". Transit Toronto. Retrieved October 21, 2017.
Photographer Patrick Duran captured this image of Flexity LRV #4416 operating in 501 QUEEN service eastbound at Queen and Bay on May 7, 2016. The streetcar is likely coming off duty from Spadina Avenue, but the destination sign suggests it's still picking up passengers.
photo - Bow, James (November 10, 2006). "Route 509 – The New Harbourfront Streetcar". Transit Toronto. Retrieved July 21, 2007.
- Route 512 – The St Clair Streetcar
- http://www3.ttc.ca/Service_Advisories/Construction/St_Clair_Avenue_West_Transit_Improvements_Project_-_Phase_4.jsp
- Kalinowski, Tess (June 30, 2010). "Finally, St. Clair streetcar fully restored". The Star. Toronto.
- https://transittoronto.ca/archives/weblog/2007/09/03-fleet_stre.shtml
- https://transittoronto.ca/archives/weblog/2008/03/29-streetcars.shtml
- Rider, David (December 12, 2017). "King St. pilot project moving streetcar riders quicker, city says". Toronto Star. Retrieved December 13, 2017.
- https://globalnews.ca/news/4759182/king-street-pilot-project-extended/
- Munro, Steve (December 10, 2019). "TTC Annual Service Plan for 2020". Steve Munro. Retrieved December 10, 2019.
- "Transit City". City of Toronto. Retrieved July 21, 2007.
- "FAQs". Eglinton Crosstown: The Project. Metrolinx. Retrieved February 12, 2017.
Q: What is the timeline for the project? A:The project will be complete in 2021
- "Ontario LRT Update". Railway Age. September 18, 2019.
- "Waterfront Transit Update" (PDF). Toronto Transit Commission. November 13, 2017. Retrieved November 13, 2017.
- "Port Lands + South of Eastern – Transportation + Servicing" (PDF). Waterfront Toronto. November 11, 2015. Retrieved November 20, 2015.
- Bromley, John F.; May, Jack (1978) [1973]. Fifty Years of Progressive Transit: A History of the Toronto Transit Commission (2 ed.). New York: Electric Railroaders' Association. LCCN 73-84892.
- Bow, James (June 25, 2015). "The Ashbridge Streetcar (Deceased)". Transit Toronto. Retrieved June 27, 2020.
- Bow, James (June 25, 2015). "The Dupont And Bay Streetcars (Deceased)". Transit Toronto. Retrieved June 25, 2020.
- Bow, James (June 26, 2015). "Route 501 - The Queen Streetcar". Transit Toronto. Retrieved June 27, 2020.
- Bow, James (January 23, 2017). "The Bloor Streetcar (Deceased)". Transit Toronto. Retrieved June 28, 2020.
- Bow, James (June 29, 2017). "The Church Streetcar (Deceased)". Transit Toronto. Retrieved June 28, 2020.
- Bow, James (October 15, 2019). "Route 506 - The Carlton Streetcar". Transit Toronto. Retrieved June 28, 2020.
- Bow, James (August 26, 2017). "The Davenport Streetcar (Deceased)". Transit Toronto. Retrieved June 28, 2020.
- Bow, James (October 29, 2018). "The Dovercourt Streetcar (Deceased)". Transit Toronto. Retrieved June 28, 2020.
- Bow, James (January 17, 2018). "Route 502 And 503 – The Kingston Road Streetcars". Transit Toronto. Retrieved January 22, 2018.
- "Streetcars". Toronto Transit Commission. Archived from the original on January 12, 2020. Retrieved January 12, 2020.
- Bow, James (June 25, 2015). "A History Of Interurban Service On Yonge Street". Transit Toronto. Retrieved June 28, 2020.
- Bow, James (June 26, 2016). "The Lansdowne Streetcar (Deceased)". Transit Toronto. Retrieved June 29, 2020.
- Bromley, John F. (1979). TTC '28; the electric railway services of the Toronto Transportation Commission in 1928. Upper Canada Railway Society. pp. 10–12: The Radial Network, 23: Year in review, 27: Lake Shore project, 28: Radial shuttles. Retrieved May 5, 2016.
- Stamp, Robert M. (1989). Riding the Radials, Toronto's Suburban Electric Streetcar Lines. The Boston Mills Press. ISBN 1-55046-008-0. Retrieved April 16, 2016.
- Bow, James (May 17, 2017). "Remembering The Sherbourne Streetcar (1874-1942)". Transit Toronto. Retrieved June 28, 2020.
- Thompson, John (January 5, 2018). "The car that saved Toronto's streetcars". Railway Age. Retrieved January 11, 2018.
- Bow, James (January 30, 2017). "The Articulated Light Rail Vehicles (The ALRVs)". Transit Toronto. Retrieved January 11, 2018.
- Spurr, Ben (June 6, 2018). "Bombardier has inside track for TTC's next streetcar order". Toronto Star. Retrieved June 6, 2018.
- "A History of Toronto's Presidents' Conference Committee Cars (the PCCs) – Transit Toronto – Content". transittoronto.ca. Retrieved April 18, 2016.
- "TTC to retire last of its 40-year-old streetcars today". CP24. December 29, 2019. Retrieved December 29, 2019.
- "TTC partners with CityFund and local artists to create A Streetcar Named Toronto". TTC. September 25, 2019. Archived from the original on September 26, 2019. Retrieved October 20, 2019.
- "TTC's legacy CLRV streetcars reach the end of the line on Dec 29". TTC. November 21, 2019. Archived from the original on November 22, 2019. Retrieved November 22, 2019.
- Fox, Chris (August 29, 2019). "TTC to retire its final two articulated streetcars on Monday". CP24. Retrieved August 29, 2019.
- Spurr, Ben (January 9, 2017). "TTC blames service cuts on streetcar delays". Toronto Star. Archived from the original on January 9, 2017. Retrieved January 9, 2017.
- Spurr, Ben (July 3, 2018). "Most new TTC streetcars to be recalled to fix welding defect, Bombardier says". Toronto Star. Retrieved July 4, 2018.
- Munro, Steve (December 11, 2016). "TTC Service Changes Effective Sunday, January 8, 2017". Archived from the original on January 10, 2017. Retrieved January 9, 2017.
- "Accessible streetcar service updates". Toronto Transit Commission. Archived from the original on January 14, 2018. Retrieved January 12, 2018.
- Munro, Steve (October 22, 2016). "TTC Service Changes Effective Sunday, November 20, 2016". Steve Munro. Retrieved January 27, 2018.
The continued shortage of streetcars will trigger the following arrangement for service to Exhibition Loop: 511 Bathurst will be operated with buses, and these will run through to the Exhibition grounds.
- "Accessible streetcar service updates". Toronto Transit Commission. Archived from the original on January 14, 2018. Retrieved January 12, 2018.
- Moore, Oliver (January 11, 2018). "Toronto's King streetcar sees 'spectacular' rise in ridership". The Globe and Mail. Archived from the original on January 12, 2018. Retrieved January 12, 2018.
- "505 Dundas and 511 Bathurst service changes". Toronto Transit Commission. April 20, 2020. Retrieved May 31, 2020.
- "Chief Executive Officer's Report – June 2020 Update" (PDF). Toronto Transit Commission. June 17, 2020. p. 14. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 21, 2020. Retrieved June 21, 2020.
- Spurr, Ben (October 24, 2019). "Poor planning at the start bedevilled Bombardier's delivery of streetcars, TTC meeting hears". Toronto Star. Retrieved October 26, 2019.
- Munro, Steve. "TTC Unveils New Streetcar Design and Mockup (Update 2)". Steve Munro. Archived from the original on March 4, 2015. Retrieved November 10, 2011.
- Kalinowski, Tess (January 6, 2010). "Transit City measures up to international standard". Toronto Star. Archived from the original on September 30, 2013. Retrieved August 6, 2013.
- "Frequently Asked Questions About Toronto's Streetcars". Transit Toronto. April 4, 2020. Retrieved May 8, 2020.
- Lam, Stephen (January 12, 2016). "Transportation Research Board" (PDF). Transportation Research Board. p. 9. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 11, 2018. Retrieved November 10, 2018.
- "LF LRV Procurement Project - Cancellation of RFP & Way Forward" (PDF). Toronto Transit Commission. August 27, 2008. p. 17. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 6, 2018. Retrieved November 5, 2018.
- Karl-Heinrich Grote, Erik K. Antonsson (2009). Springer Handbook of Mechanical Engineering, Volume 10. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 1089. Retrieved May 19, 2020.
- Metrolinx (March 16, 2013). "LRV Comparison Chart". Archived from the original (PDF) on March 16, 2013.
- Munro, Steve (June 12, 2008). "Streetcar Track Switching". Steve Munro. Retrieved May 19, 2020.
- "TTC Audit & Risk Management Committee" (PDF). Toronto Transit Commission. September 11, 2015. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 14, 2019. Retrieved June 20, 2020.
- "New Streetcar Implementation Plan" (PDF). Toronto Transit Commission. June 24, 2013. p. 22. Retrieved April 28, 2018.
New cars draw over 50% more current than the old cars. Low voltage problems will result in reduced performance (i.e. no A/C in summer).
- Mackenzie, Robert (September 29, 2008). "Streetcars Roll Along Fleet Street Tomorrow". Transit Toronto. Retrieved April 25, 2018.
- Munro, Steve (April 27, 2018). "Problems With Trolley Shoes on Flexity Cars". Steve Munro. Retrieved April 27, 2018.
- Bow, James (October 13, 2018). "The Toronto Flexity Light Rail Vehicles (LRVs)". Transit Toronto. Retrieved October 19, 2018.
- "Some TTC streetcars out of service due to cold weather". Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. January 8, 2015. Retrieved October 19, 2017.
- Kalinowski, Tess (January 7, 2015). "TTC warns of chilly waits as cold freezes streetcar service". Toronto Star. Retrieved October 19, 2017.
- "Nearly one-third of old streetcars were unable to leave yard due to frigid weather: TTC". Retrieved January 7, 2018.
- Fox, Chris (January 5, 2018). "Frigid temperatures impacting transit service". CP24. Retrieved January 7, 2018.
- Wilson, Codi (January 21, 2019). "Bitterly cold temperatures continue in Toronto". CP24. Retrieved March 15, 2019.
- "Service changes in the event of an ice storm". Toronto Transit Commission. April 16, 2018. Archived from the original on April 16, 2018. Retrieved April 16, 2018.
- "Ashbridges Bay Light Rail Vehicle (LRV) Maintenance and Storage Facility". ttc.ca. Toronto Transit Commission. May 2010. Retrieved August 16, 2011.
- Mallion, Godfrey (August 26, 2017). "Danforth Carhouse And Garage". Transit Toronto. Retrieved March 12, 2019.
- http://www.stevemunro.ca/?p=392
- Pursley, Louis H. (1958). Street Railways of Toronto: 1861–1921. Los Angeles: Interurbans Press.
- https://www.pattisonoutdoor.com/products/transit/
Other references
- Gray, Jeff (June 23, 2005). "TTC to shop for new streetcars". The Globe and Mail.
- "Future Streetcar Fleet Requirements and Plans". Toronto Transit Commission. June 22, 2005.
- Livett, Christopher. "Toronto's Streetcar System (schematic track map)". Transit Toronto.
- Kalinowski, Tess (April 28, 2009). "A streetcar named Inspire?". Toronto Star. Retrieved October 4, 2014. – includes a timeline of the history of the Toronto streetcar system
- "Opportunities for New Streetcar Routes" (PDF). Toronto Transit Commission. January 21, 1997.
- "North America – Canada – Ontario – Toronto Streetcar (Tram)". UrbanRail.Net. 2012. Retrieved July 26, 2013.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Toronto streetcar system. |