Iranian nationalism
Iranian nationalism refers to nationalism among the people of Iran and individuals whose national identity is Iranian. Iranian nationalism consists of political and social movements and sentiments prompted by a love for Iranian culture, Iranian languages and history, and a sense of pride in Iran and Iranian people. Whilst national consciousness in Iran can be traced back for centuries, nationalism has been a predominant determinant of Iranian attitudes mainly since the 20th century.[1]
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Iran |
| Government of Islamic Republic of Iran |
|
Leadership |
|
Executive |
|
|
Supreme Councils |
|
Local governments
|
|
|
|
Outside government |
|
During the Pahlavi dynasty (1925–1979), Iranian nationalism experienced a resurgence due to the Pahlavi government's bolstering of patriotic sentiment. After the Iranian revolution, there has been a resurgence of nationalism within the Islamic Republic of Iran in the wake of the Iran student protests, July 1999 and the Islamic Republic's autocratic policies over its forty year existence.
History
Origins
The idea of Iran as a religious, cultural, and ethnic reality goes back as far as the end of the 6th century B.C.E. As a political idea, it first appeared in the twenties of the third century C.E. as an essential feature of Sassanian propaganda.[2]
Third-century Iran was shaken by a conflict between universalism and nationalism that was most clearly manifested in the religious and cultural sphere. The outcome of this conflict is well known: the traditionalistic and nationalistic impulses gained the upper hand, and Manichaean universalism succumbed to the nationalism of the Zoroastrian Magi. Iranian identity, which up to that point had essentially consisted of cultural and religious nature, assumed a definite political value, placing Persia and the Persians at the center of the Ērān-šahr, in other words, at the center of a state based on the twin powers of throne and altar and sustained by an antiquarian and archaizing ideology. This ideology became more and more accentuated during the Sassanian period, reaching its height in the long reign of Khosrow I (531-79 C.E.). Of course, economic and social factors favored the victory of the stronger classes in a society that was based mainly on a rural economy, namely the aristocratic landed and warrior classes and the Magian clergy.[2]
Shu'ubiyya
Iranian identity came under threat after the fall of the Sassanid Empire and the conquest of Iran by the Arab Muslims.The term Shu'ubiyya refers to a response by Persian Muslims to the growing Arabization of Islam in the 9th and 10th centuries in what is now Iran. It was primarily concerned with preserving Persian culture and protecting Persian identity. Some of the famous Iranian Shu'ubi figures are Bashar ibn Burd, Ismail Nisa'i, Zeyad e Ajam, Hissam ibn Ada, Abulhassan Ali Mada'ini, Abu Hatam Sajestani, Ibrahim ibn Mamshad and Abu Abdullah Muhammad Marzbani. Many consider Ferdowsi a Shu'ubi poet.
Iranian Intermezzo
The term Iranian Intermezzo[notes 1] represents a period in Middle Eastern history which saw the rise of various native Iranian Muslim dynasties on the Iranian Plateau. This term is noteworthy since it was an interlude between the decline of Abbāsid Arab rule and power and the eventual emergence of the Seljuq Turks in the 11th century. The Iranian revival consisted of Iranian support based on Iranian territory and most significantly a revived Iranian national spirit and culture in an Islamic form.[3]
Iranian-Shia identity under the Safavids
Iran regained its political unity and was given a new distinct religious identity under the Safavids. Shia became the official state religion and henceforth played an important role in the reconstruction of a new ethno-religious identity for the Iranian people. Furthermore, the rise of the Safavid empire coincided with the rise of the neighbouring Ottoman empire in West Asia and North Africa (and most importantly, for centuries Iran's geo-political as well as ideological arch rival), the Mughal empire in India, and the Uzbek empire in Central Asia, all adhering to Sunni Islam. The formation of these political entities helped create a distinct Iranian-Shia political identity among these polities. It also helped to expand the hegemony of Persian language in much of the Islamic world. Persian literature was, apart from Iran and its territories stretching from the North Caucasus to the Persian Gulf, produced from Anatolia to Central Asia and the Indian subcontinent.[4]
Qajar Era - start of modern nationalism
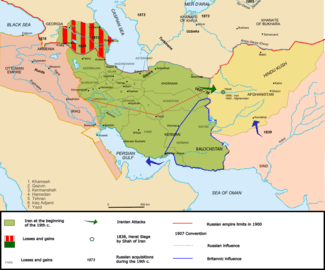
The modern Iranian national movement began in the late 19th century. Iranian nationalism is in origin a reaction to 19th-century European colonialism in the region, which led to the loss of Qajar possessions in the Caucasus.[5] In the course of the 19th century, through the Russo-Persian War (1804-1813) and the Russo-Persian War (1826-1828) and the out-coming Treaty of Gulistan and Treaty of Turkmenchay of 1813 and 1828 respectively, Iran was forced to irrevocably cede swaths of its territory in the North and South Caucasus comprising what is now Georgia, Dagestan, Azerbaijan and Armenia to Imperial Russia.[6] These territories had made, for centuries, part of the concept of Iran until their loss.[7]
The initial objectives of these nationalists e.g. ending the feudalistic landholding system, governmental sloth and corruption and the wholesale distribution of Iranian resources to foreigners also greatly appealed to modernisers.[1]
One of the principal and most noted forerunners of Iranian nationalism of the Qajar era was Mirza Fatali Akhundov, born in the recently taken territories in the Caucasus to a landowner family originally stemming from Iranian Azerbaijan.[8]
Modern nationalism

Modern nationalism in Iran dates back to 1906, when an almost bloodless constitutional revolution created Iran's first parliament. Reza Shah, helped shape Iranian nationalism by infusing it with a distinctly secular ideology, and diminishing the influence of Islam on Iran. By integrating European legal policies in replace of Islamic courts, Shah reassured the efficiency of the state bureaucracy and promoted a strong sense of Iranian nationalism.[9] In addition, Reza Shah sought to change the names of various towns to honor pre-Islamic Persian kings and mythological heroes, and to continue to reduce the power of the mullahs by seeking to modernize Iran. The Pahlavi dynasty thus was set irrevocably down the road towards infusing the country with a form of secular nationalism, a path that would eventually bring it into conflict with the country's clerical class. Iranian nationalism was a deciding force in the 1951 movement to nationalize Iran's oil wealth.
Mosadeqq goal of nationalizing Iran’s oil came into effect in the year 1951. By allowing Iran to have full power and control over their prime resource, the AIOC and other European programs participated in an international boycott which eventually caused a deter in Iran’s economy.[10] After Mosadeqq deposition guided by the help from the U.S., Reza Shah redeemed control and used the increased gas prices to expand modernization in Iran.[11]
Iranian nationalist discourse often focuses on the pre-Islamic history of Iran.[12] In the 20th century, different aspects of this romantic nationalism would be referenced by both the Pahlavi monarchy, which employed titles such as Āryāmehr "Light of the Aryans", and by some leaders of the Islamic Republic that followed it.[13]
Nationalist parties of Iran
- Active parties
- Pan-Iranist Party (founded 1941, banned, operating inside Iran)
- National Front (founded 1949, banned, operating inside Iran)
- Iran Party (founded 1944, banned, operating inside Iran)
- Party of the Iranian People (founded 1949, banned, operating inside Iran)
- Nation Party of Iran (founded 1951, banned, operating inside Iran)
- Freedom Movement of Iran (founded 1961, banned, operating inside Iran)
- Marze Por Gohar (founded 1998, banned, exiled)
- Council of Nationalist-Religious Activists of Iran (founded 2000, banned, operating inside Iran)
- Historic parties
- Society for the Progress of Iran (1909–1911)
- Revival Party (1920–1927)
- Iran-e-No Party (1927)
- Progress Party (1927–1932)
- Motherland Party (1940–1946)
- Justice Party (1941–1946)
- Azure Party (1942–1953)
- National Will Party (1943–1951)
- Movement of God-Worshipping Socialists (1943–1960)
- Democrat Party of Iran (1946–1984)
- Aria Party (1946–1953)
- Iran Unity Party (1946–1948)
- Society of Muslim Warriors (1948–1955)
- Third Force (1948–1960)
- National Socialist Workers Party of Iran (1952–1953)
- Nationalists’ Party (1957–1963)
- League of Iranian Socialists (1960–1982)
- The Liberation Movement of People of Iran (1964–1988)
- National Democratic Front (1979–1981)
- Iranians' Party (1970–1975)
- Rastakhiz Party (1975–1979)
Footnotes
- Such an obviously coined designation was introduced by Vladimir Minorsky, "The Iranian Intermezzo", in Studies in Caucasian history (London, 1953) and has been taken up by Bernard Lewis, among others, in his The Middle East: A brief history of the last 2,000 years (New York, 1995).
References
- Cottam, Richard W. (1979). Nationalism In Iran: Updated through 1978. Pittsburg: University of Pittsburgh Press. ISBN 0-8229-5299-8. Retrieved 2011-01-31.
- Gnoli, Gherardo. "IRANIAN IDENTITY ii. PRE-ISLAMIC PERIOD". Encyclopædia Iranica. Archived from the original on 2011-11-17. Retrieved 2011-09-11.CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link)
- Lewis, Bernard. The Middle East: 2,000 Years of History from the Rise of Christianity to the Present Day. pp. 81–82.
- Ashraf, Ahmad. "IRANIAN IDENTITY iii. MEDIEVAL ISLAMIC PERIOD". Encyclopedia Iranica. Retrieved 2012-02-08.
- Patrick Clawson writes:
- "Since the days of the Achaemenids, the Iranians had the protection of geography. But high mountains and vast emptiness of the Iranian plateau were no longer enough to shield Iran from the Russian army or British navy. Both literally, and figuratively, Iran shrank. At the beginning of the nineteenth century, Azerbaijan, Armenia, much of Georgia were Iranian, but by the end of the century, all this territory had been lost as a result of European military action. Iran translated her territorial losses into a sense of both victimization and a propensity to interpret European action through the lens of conspiracy. This in turn has helped shape Iranian nationalism into the twenty first century." Clawson, Patrick; Rubin, Michael (2005). Eternal Iran ([Online-Ausg.]. ed.). New York: Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 31–32. ISBN 1-4039-6276-6.
- Timothy C. Dowling Russia at War: From the Mongol Conquest to Afghanistan, Chechnya, and Beyond pp 728-729 ABC-CLIO, 2 dec. 2014 ISBN 1598849484
- Fisher et al. 1991, p. 329.
- Tadeusz Swietochowski, Russia and Azerbaijan: A Borderland in Transition (New York: Columbia University Press), 1995, page 27-28:
- Hunt, Michael (2014). The World Transformed 1945 to the Present. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 279. ISBN 9780199371020.
- Hunt, Michael (2014). The World Transformed 1945 to the Present. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 280–281. ISBN 9780199371020.
- Hunt, Michael (2014). The World Transformed 1945 to the Present. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 282.
- Adib-Moghaddam, Arshin (2006). "Reflections on Arab and Iranian Ultra-Nationalism". Monthly Review Magazine. 11/06..
- Keddie, Nikki R.; Richard, Yann (2006). Modern Iran: Roots and Results of Revolution. Yale University Press. pp. 178f. ISBN 0-300-12105-9..
Sources
- Fisher, William Bayne; Avery, P.; Hambly, G. R. G; Melville, C. (1991). The Cambridge History of Iran. 7. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521200954.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)