Hyborian Age
The Hyborian Age is a fictional period of Earth's history within the artificial mythology created by Robert E. Howard, serving as the setting for the sword and sorcery tales of Conan the Barbarian.
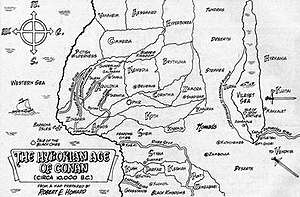
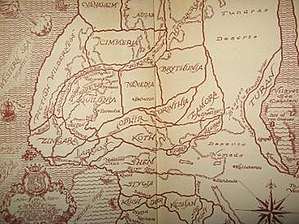
The word "Hyborian" is derived from the legendary northern land of the ancient Greeks, Hyperborea, and is rendered as such in the earliest draft of Howard's essay "The Hyborian Age."[1] Howard described the Hyborian Age taking place sometime after the sinking of Atlantis and before the beginning of recorded ancient history.[2] Most later editors and adaptors such as L. Sprague de Camp and Roy Thomas placed the Hyborian Age around 10,000 BC.[3] More recently, Dale Rippke proposed that the Hyborian Age should be placed further in the past, around 32,500 BC, prior to the beginning of the Last Glacial Maximum.[4] Rippke's date, however, has since been disputed by Jeffrey Shanks, who argues for the more traditional placement at the end of the Last Glacial Maximum.[5]
Howard had an intense love for history and historical dramas; however, at the same time, he recognized the difficulties and the time-consuming research needed in maintaining historical accuracy. By conceiving a timeless setting – a vanished age – and by carefully choosing names that resembled our history, Howard avoided the problem of historical anachronisms and the need for lengthy exposition.[6]
Fictional history
Cataclysmic ancestors
Howard explained the origins and history of the Hyborian civilization in his essay "The Hyborian Age".[7] The essay begins with the end of the Thurian Age (the setting for Howard's King Kull stories) and the destruction of its civilizations, Lemuria and Atlantis, by a geological cataclysm.
After this cataclysm, the surviving humans were reduced to a primitive state and a technological level hardly above the Neanderthal. Several such tribes migrated to the northern areas of what was left of the Thurian continent to escape destruction. They discovered the region to be safe, but covered with snow and already inhabited by a race of vicious white-furred apes. A vicious territorial war ensued until the humans drove the apes further North, past the Arctic Circle. Believing the apes were destined to perish, the humans turned to taming their harsh new home.
Hyborian ancestors
One thousand five hundred years later, the descendants of this initial group were called "Hyborians". They were named after their highest ranking god deity, Bori. The essay mentions that Bori had actually been a great tribal chief of their past who had undergone deification. Their oral tradition remembered him as their leader during their initial migration to the north, though the antiquity of this man had been exaggerated.
By this point, the various related but independent Hyborian tribes had spread throughout the northern regions of their area of the world. Some of them were already migrating south at a "leisurely" pace in search of new areas in which to settle. The Hyborians had yet to encounter other cultural groups, but engaged in wars against each other. Howard describes them as a powerful and warlike race with the average individual being tall, tawny-haired, and gray-eyed. Culturally, they were accomplished artists and poets. Most of the tribes still relied on hunting for their nourishment. Their southern offshoots, however, had been practicing animal husbandry on cattle for centuries.
The only exception to their long isolation from other cultural groups came due to the actions of a lone adventurer, unnamed in the essay. He had traveled past the Arctic Circle and returned with news that their old adversaries, the apes, were never annihilated. They had instead evolved into apemen and, according to his description, were by then numerous. He believed they were quickly evolving to human status and would pose a threat to the Hyborians in the future. He attempted to recruit a significant military force to campaign against them, but most Hyborians were not convinced by his tales; only a small group of foolhardy youths followed his campaign. None of them returned.
Beginnings of the Hyborian Age
With the population of the Hyborian tribes continuing to increase, the need for new lands also increased. The Hyborians expanded outside their familiar territories, beginning a new age of wanderings and conquests. For 500 years, the Hyborians spread towards the south and the west of their nameless continent.
They encountered other tribal groups for the first time in millennia. They conquered many smaller clans of various origins. The survivors of the defeated clans merged with their conquerors, passing on their racial traits to new generations of Hyborians. The mixed-blooded Hyborian tribes were in turn forced to defend their new territories from pure-blooded Hyborian tribes which followed the same paths of migration. Often, the new invaders would wipe away the defenders before absorbing them, resulting in a tangled web of Hyborian tribes and nations with varying ancestral elements within their bloodlines.
The first organized Hyborian kingdom to emerge was Hyperborea. The tribe that established it entered their Neolithic age by learning to erect buildings in stone, largely for fortification. These nomads lived in tents made out of the hides of horses, but soon abandoned them in favor of their crude but durable stone houses. They permanently settled in fortified settlements and developed cyclopean masonry to further fortify their defensive walls.
The Hyperboreans were by then the most advanced of the Hyborian tribes and set out to expand their kingdom by attacking their backwards neighbors. Tribes who defended their territories lost them and were forced to migrate elsewhere. Others fled the path of Hyperborean expansion before ever engaging them in war. Meanwhile, the apemen of the Arctic Circle emerged as a new race of light-haired and tall humans. They started their own migration to the south, displacing the northernmost of the Hyborian tribes.
Rulers of the West
For the next thousand years, the warlike Hyborian nations advanced to become the rulers of the western areas of the nameless continent. They encountered the Picts and forced them to limit themselves to the western wastelands, which would come to be known as the "Pictish Wilderness". Following the example of their Hyperborean cousins, other Hyborians started to settle down and create their own kingdoms.
The southernmost of the early kingdoms was Koth, which was established north of the lands of Shem and soon started extending its cultural influence over the southern shepherds. Just south of the Pictish Wilderness was the fertile valley known as "Zing". The wandering Hyborian tribe which conquered them found other people already settled there. They included a nameless farming nation related to the people of the Shem and a warlike Pictish tribe who had previously conquered them. They established the kingdom of Zingara and absorbed the defeated elements into their tribe. Hyborians, Picts, and the unnamed kin of the Shemites would merge into a nation calling themselves Zingarans.
On the other hand, at the north of the continent, the fair-haired invaders from the Arctic Circle had grown in numbers and power. They continued their expansion south while in turn displacing defeated Hyborians to the south. Even Hyperborea was conquered by one of these barbarian tribes. But the conquerors here decided to maintain the kingdom with its old name, merged with the defeated Hyperboreans and adopted elements of Hyborian culture. The continuing wars and migrations would keep the state of the other areas of the continent for another five hundred years.
The world
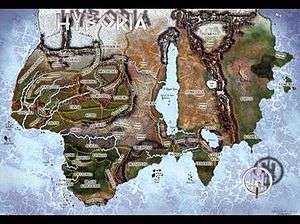
The Hyborian Age was devised by author Robert E. Howard as the post-Atlantean setting of his Conan the Cimmerian stories, designed to fit in with Howard's previous and lesser known tales of Kull, which were set in the Thurian Age at the time of Atlantis. The name "Hyborian" is a contraction of the Greek concept of the land of "Hyperborea", literally "Beyond the North Wind". This was a mythical place far to the north that was not cold and where things did not age.
Howard's Hyborian epoch, described in his essay The Hyborian Age, is a mythical time before any civilization known to anthropologists. Its setting is prehistoric Europe and North Africa (with occasional references to Asia and other continents).
On a map Howard drew conceptualizing the Hyborian Age, his vision of the Mediterranean Sea is dry. The Nile, which he renamed the River Styx, takes a westward turn at right angles just beyond the Nile Delta, plowing through the mountains so as to be able to reach the Straits of Gibraltar. Although his Black Sea is also dry, his Caspian Sea, which he renames the Vilayet Sea, extends northward to reach the Arctic Ocean, so as to provide a barrier to encapsulate the settings of his stories. Not only are his Baltic Sea and English Channel dry, but most of the North Sea and a vast region to the west, easily including Ireland, are, too. Meanwhile, the west coast of Africa on his map lies beneath the sea.
Nations and landmarks
In his fantasy setting of the Hyborian Age, Howard created imaginary kingdoms to which he gave names inspired by or adapted from a variety of mythological and historical sources. Khitai is his version of China, lying far to the east, Corinthia is his name for a Hellenistic civilization, a name derived from the city of Corinth and reminiscent of the imperial fief of Carinthia in the Middle Ages. Howard imagines the Hyborian Picts occupying a large area in the northwest. The probable intended analogues are listed below; notice that the analogues are sometimes very generalized, and are portrayed by non-historical stereotypes. Most of these correspondences are drawn from "Hyborian Names", an appendix featured in Conan the Swordsman by L. Sprague de Camp and Lin Carter.[8]
| Kingdom, region, or ethnic group | Possible analogue(s) |
|---|---|
| Acheron | A fallen kingdom corresponding to the Roman Empire. Its territory covered Aquilonia, Nemedia, and Argos. In Greek mythology, Acheron was one of the four rivers of Hades (cf. "Stygia"). Acheron was a priest-monarchy ruled by priest-kings who performed human sacrifice with their own hands. |
| Afghulistan | Afghanistan. Afghulistan (sometimes "Ghulistan") is the common name for the habitat of different tribes in the Himelian Mountains. The name itself is a mixture of the historical names of Gulistan and Afghanistan. |
| Alkmeenon | Delphi. Its name derives from the Alcmaeonidae, who funded construction the Temple of Apollo in Delphi, from which the oracle operated. Also, Alcmene is the mother of Hercules. After death, she traveled into Hades and married Rhadamanthys, a chief judge of the underworld.[lower-alpha 1] |
| Amazon | Mentioned in Robert E. Howard's Hyborian Age essay, the kingdom of the Amazons refers to various legends of Greek Amazons, or more specifically to the Dahomey Amazons. In classical legend, Amazonia is a nation of warrior women in Asia Minor and North Africa. The legend may be based upon the Sarmatians, a nomadic Iranian tribe of the Kuban, whose women were required to slay an enemy before they could marry. |
| Aquilonia | Influenced by the Byzantine Empire and elements of Colonial North America. The name is borrowed from Aquilonia, a city of Southern Italy, between modern Venosa and Benevento. It's also an ancient name for Quimper and resembles that of Aquitaine, a French region ruled by England for a long portion of the Middle Ages. The name is derived from Latin aquilo(n–), "north wind". In Italian, aquila means also "eagle", which is the sign used in war by Roman Legion as well as the Aquilonian army. |
| Argos | Various seafaring traders of the Mediterranean, with islands such as Crete and Sardinia being examples. The name comes from the Argo, ship of the Argonauts; or perhaps from the city of Argos, Peloponnesos, reputedly the oldest city in Greece, situated at the head of the Gulf of Argolis near modern Nafplion. Also, hints of Italy in regards to the indigenous population's appearance, names and culture.[lower-alpha 2] In Hyborian Age cartography, Argos takes on the shape of a "shoe" in its border boundaries as compared to Italy appearing as a "boot". The coastal city of Messantia/Massantia derives its name from Massalia, the name given to Marseilles by its Greek founders. |
| Asgard (Aesgaard in comics) | Dark Age Scandinavia. Ásgard is the home of the Æsir in Norse mythology. Howard states that the Baltic Sea would, post-cataclysm, divide his fictional Asgard into the modern Norway, Sweden, and Denmark according to The Hyborian Age essay. |
| Barachan Islands | The Caribbean Islands. Possibly after the Islas Borrachas ("Drunken Isles"). The pirate town of Tortage takes its name from Tortuga. |
| Border Kingdoms | Geographically located over the modern German Baltic Sea coast. A lawless region full of brigands and semi-barbaric peoples. Conan once traveled through the Border Kingdoms on his way to Nemedia. The low countries and the borderlands of Scotland and England could be similar examples. |
| Bossonian Marches | Wales, with an overlay of colonial North America. Possibly from Bossiney, a former parliamentary borough in Cornwall, South West England, which included Tintagel Castle, connected with the Matter of Britain. |
| Brythunia | The continental homelands of the Angles and Saxons who invaded Great Britain, which is the origin of the name, though it is implied the Brythunians of the Hyborian age are a different group that could be related to early slavs. Semantically, the name Brythunia is from the Welsh Brython, "Briton", derived from the same root as the Latin Brito, Britannia, although Howard stated that the name was kept by the Æsir and Nemedians who settled there. The land is depicted geographically over modern Poland, Lithuania, and Latvia. |
| Cimmeria | Howard states in The Hyborian Age that "the Gaels, ancestors of the Irish and Highland Scots, descended from pure-blooded Cimmerian clans." He correlates Cimmeria with the Cymric people, Cimbri, Gimirrai, Scythians, Cimmerians, and the Crimea. Geographically located over modern Ireland, Scotland, and England.[lower-alpha 3] The name is derived from the Greek legends of a northern people, who lived in perpetual mist and darkness near the Land of the Dead. The Cimmerians are named by Howard as the ancestors of the proto-Indo-Europeans. |
| Conajohara (Aquilonia) | The name may have been based on Canajoharie. |
| Corinthia | Ancient Greece. From Corinth (Korinthos), a rich city in Classical Greece. Possibly suggested to Howard by the Epistles to the Corinthians, or by the region of Carinthia. It's a mountainous country located east of Koth. |
| Darfar | Howard derived this name from the region of Darfur, Sudan, in North-Central Africa. Darfur is an Arabic language name meaning "abode (dar) of the Fur", the dominant people of the area.[lower-alpha 4] The original Darfur is now the westernmost part of the Republic of the Sudan. |
| Gunderland | Possibly from Gunderland of Hesbaye, a count in the Merovingian court, or from Gelderland a province in the Netherlands or from Gunther (Gundicar), King of Burgundy or Gunderic, King of the Vandals. |
| Hyperborea | Finland, Russia, and the Baltic countries (Hyperborea). Is a land in the "outermost north" according to Greek historian Herodotus. Howard describes his Hyperborea as the first Hyborian kingdom, "which had its beginning in a crude fortress of boulders heaped to repel tribal attack". |
| Hyrkania | The Eurasian Steppe, specifically the Turco-Mongol peoples, whom Howard names as their descendants in his Hyborian age essay. Hyrkania, in classical geography, was a region southeast of the Caspian Sea or Hyrkanian Sea corresponding to the Iranian provinces of Golestan, Mazandaran, and Gilan. The name is Greek for the Old Persian Varkana, one of the Achaemenid Empire satrapies, and survives in the name of the river Gorgan. The original meaning may have been "wolf land". In Iranian legend, Hyrkania is remarkable for its wizards, demons, wolves, spirits, witches, and vampires. |
| Iranistan | An eastern land corresponding with modern Iran. Historically, the name of the country is derived from Iran + the Persian istan, estan, "country". |
| Kambuja/Kambulja | The original name of Cambodia, also known as Kampuchea. |
| Keshan | The name comes from the "Kesh", the Egyptian name for Nubia. |
| Khauran | The name perhaps derives from the Hauran region of Syria, though its position would place it near Macedonia, with Cretan influences. Apparently, Salome in the New Testament is a descendant of this royal house. |
| Khitai | China. The name is derived from the Khitan Empire (Chinese 遼朝 Liáo cháo or the Liao Dynasty) and the people who ruled northern and northeastern China. The name is derived from the Khitan language for The Khitan Empire, Mos diau-d kitai huldʒi gur; in modern Mandarin Chinese, 契丹國 or Qìdān guó.[lower-alpha 5] In the Hyborian age, Khitai is an ancient empire which is always at war with Kambuja to the south. In ancient times, Khitai was subjugated by an empire of conquerors from a mysterious continent in the eastern ocean. After the cataclysm, this empire made slaves of the Lemurians who fled the destruction. With time, the Lemurian slaves, and perhaps the gentile Khitanians, were able to rise up and overthrow this empire.[lower-alpha 6] The remnants of this white-skinned master race fled westwards, conquering the kingdom of the serpent men and founding Stygia. The people of Khitai are yellow-skinned and of medium height. Khitai is ruled by a God-Emperor whose decisions are greatly influenced by the Scarlet Circle, a clan of some of the most powerful mage lords in all of Hyboria. Khitan laws flow from the overlord of a city-state. The culture of Khitai is similar to that of ancient China. The most prominent feature of Khitai is its Great Wall (similar to the Great Wall of China), which protects it from foreign invasions from the north. The cities of Khitai are Ruo-Chen, Shu-Chen, Shaulum, and the capital, Paikang, which contains the Jade Citadel, from which the God-Emperor rules over all of Khitai. See also Catai. |
| Khoraja | Constantinople and Sicily. Its position places it as the crossroads between the Hyborian kingdoms and the Shemites. The name itself was inspired by the references of Sax Rohmer to the fictional city of Khorassa in the novel The Mask of Fu Manchu. |
| Kosala | From the ancient Indo-Aryan kingdom of Kosala, corresponding roughly in area with the region of Oudh. |
| Kozaki | Semi-barbaric steppe-dwelling raiders analogous to the Cossacks. |
| Koth | From the ancient Italic peoples. The Kothian capital of Khorshemish corresponds with Carchemish, capital of a Neo-Hittite kingdom. Perhaps from The Sign of Koth in The Dream-Quest of Unknown Kadath by H. P. Lovecraft.[lower-alpha 7] Howard also used the same name in his interplanetary novel Almuric. |
| Kusan | Probably from the Kushan Empire. |
| Kush | From the kingdom of Kush, Nubia, North Africa. |
| Meru | Tibet. In Hindu mythology, Meru is the sacred mountain upon which the gods dwell.
NOTE: Meru is not an original Hyborian Age country and was created by L. Sprague de Camp and Lin Carter for "The City of Skulls". |
| Nemedia | A cross between the Holy Roman Empire and Byzantium. Nemedia is the rival of Aquilonia, and depended on Aesir mercenaries for their defence (as the Byzantine Empire hired Vikings as the Varangian Guard). The name comes from Nemed, leader of colonists from Scythia to Ireland in Irish mythology.[lower-alpha 8] |
| Ophir | The Etruscans, an ancient people also stereotyped for their wealth. Howard saw it as situated somewhere in Italy, namely in the North, as opposed to the more southern Koth. |
| Pelishtim | Philistines (P'lishtim in Hebrew). The Pelishti city of Asgalun derives its name from Ashkelon. The Pelisti god Pteor or Baal-Pteor derives his name from the Moabite Baal-Peor. |
| Pictish Wilderness | Pre-Columbian America, with an overlay of North America during the European colonization of the Americas, possibly even colonial-era New York. Howard bestows names from the Iroquoi language on many of his Hyborian-Age Picts (but not the quasi-historical Picts featuring Bran Mak Morn).[lower-alpha 9] |
| Poitain | A combination of Poitou and Aquitaine, two regions in southwestern France. From the 10th to the mid-12th century, the counts of Poitou were also the dukes of Aquitaine. |
| Punt | The Land of Punt on the Horn of Africa. A place in which the ancient Egyptians traded with, probably Somalia. |
| Shem | Mesopotamia, Syria, Palestine, and Arabia. In the Bible, Shem is Noah's eldest son, the ancestor of the Hebrews, Arabs and Assyrians; hence, the modern "Semite" and Semitic languages (via Greek Sem), used properly to designate the family of languages spoken by these peoples. |
| Stygia | Egypt. The name comes from the Styx, a river of the Greek underworld in Greek mythology. In earlier times the territory of Stygia included Shem, Ophir, Corinthia, and part of Koth. Stygia is ruled by a theocracy of sorcerer-kings. The people are brown-skinned. They worship the serpent god Set. Stygia's terrain is a mix of mountains, deserts, and marshes. The River Styx flows through Stygia into the sea; the map provided makes clear that the Styx is the Nile, but since the Mediterranean did not yet exist, it had a very long additional westward bend, following what is now the coast of North Africa, until finally emptying into the Atlantic. .[lower-alpha 10] The commoners of Stygia may still, in spirit, be the original human slaves or slave races of the serpent men who ruled this kingdom centuries before.[lower-alpha 11] The white skinned elite may still worship "The great dark nameless one" (Skelos?). |
| Turan | Persian name for Turkestan. A Turkish land, possibly referring to the Gokturk Empire, the Timurid Empire, or the Seljuq Sultanate. The name derives from Turan, the areas of Eurasia occupied by speakers of Ural–Altaic languages. The names of the various Turanian cities (e.g. Aghrapur, Sultanapur, Shahpur) are often in Persian language. King Yezdigerd is named after Yazdegerd III, ruler of the Sassanid Empire.[lower-alpha 12] The city of Khawarizm takes its name from Khwarezm, and Khorusun from Khorasan. |
| Uttara Kuru | From the medieval Uttara Kuru Kingdom in the north and central reaches of Pakistan.
NOTE: Uttara Kuru is not an original Hyborian Age country, it appear in Conan the Avenger by Björn Nyberg. |
| Vanaheim | Dark Age Scandinavia. Vanaheim is the home of the Vanir in Norse mythology. The red-haired vanir will finally oust the evil aristocracy of Stygia and found pharaonic Egypt. They are red-haired as a reference to pharaohs like Ramses and his father Seti, who had red hair. |
| Vendhya | India (the Vindhya Range is a range of hills in central India). The name means "rent" or "ragged", i.e. having many passes. This very ancient kingdom worships the god Asura.[lower-alpha 13] This cult has spread westwards and is present, albeit often persecuted, in the Hyborian lands. In Aquilonia, the cult finds a protector in King Conan. |
| Yamatai | Japan. Probably inspired by the historical name of Yamatai. The land of Yamatai is described as "a cluster of islands east of Khitai", ruled by the "Witch Queen of Yamatai" in the omonymous The Savage Sword of Conan story,[9] herself possibly inspired by the historical shaman-queen Himiko.
NOTE: Yamatai is not an original Hyborian Age country. |
| Wadai (tribe) | The Wadai Empire in present-day Chad. |
| Wazuli (tribe) | The Waziri tribe in northwest Pakistan. |
| Zamora | The Romani people. The name comes from the city of Zamora, Zamora province, Castile-León, Spain, alluding to the Gitanos of Spain (see Zingara for discussion); or possibly it is based on the word "Roma". There may also be some reference to southern Italy, as Zamorans dance the tarantella in honor of their Spider-Gods (variously known as Omm and Zath). Also hints of Ancient Israel and Palestine. |
| Zembabwei | The Munhumutapa Empire. The name comes from Great Zimbabwe, a ruined fortified town in Rhodesia, first built around the 11th century and used as the capital of the Munhumutapa Empire. The modern Republic of Zimbabwe has taken its name from the same ruined fortified town, when seeking to replace the name "Rhodesia" which commemorated a British Empire-builder. |
| Zingara | The Iberian Peninsula as a whole, with overt influences from Spain. Zingara is also Italian for "Gypsy woman"; this may mean that Howard mixed up the source names of Zingara and Zamora, with Zingara originally meant to apply to the Roma kingdom, and Zamora to the Spanish kingdom. |
| Zuagir (tribe) | The name is perhaps derived from a combination of Tuareg and Uyghur. |
| Other geographic features | |
| Amir Jehun Pass | Takes its name from a combination of the Amu Darya river and the Gihon river (Jayhoun in Arabic), which has been identified by some with the Amu Darya. Perhaps corresponds to the Broghol Pass, which is near the headwaters of the Amu Darya in Wakhan. |
| The Himelian Mountains | Take their name from the Himalayas, but correspond more closely with the Hindu Kush or Karakoram ranges. |
| The Karpash Mountains | The Carpathian Mountains. |
| The Poitanian Mountains | The Pyrenees, which are just south of the Aquitaine region of France. |
| The River Styx | The River Styx runs northward through Stygia, following the course of the historical Nile river. Then it turns and runs westward through Shem, following the historical Mediterranean Sea, finally emptying into the western ocean. Styx, in classical mythology, is the River of the Dead and this symbolism is used in The Hour of the Dragon. |
| The River Alimane | Alamana river, (present Spercheios) in Greece. It may also be a reference to the Alemanni. |
| Vilayet Sea | Geographically, the Caspian Sea. The name comes from vilayet, the term for administrative regions in the Ottoman Empire. |
| Zhaibar Pass | The Khyber Pass which has been the traditional borderline between Afghanistan and Pakistan. |
| Zaporoska River | The Dnieper river and/or the Don and/or the Volga. The river's name was probably influenced by Zaporizhian Sich, a settlement of the Ukrainian Cossacks in Zaporizhzhia (region). It was situated on the Dnieper river, below the Dnieper rapids (porohy, poroz.a), hence the name, translated as "territory beyond the rapids". |
Deities
Crom
Crom /ˈkrɒm/ is a deity in Robert E. Howard's fantasy tales of the Hyborian Age. He is ackowledged as the chief god by the lead character Conan, and his proto-Celtic Cimmerian people.
The name Crom is probably derived from the ancient Celtic deity Crom Cruach or Crom Dubh.
Nature of Crom
Queen of the Black Coast by Robert E. Howard
Crom is the chief god of the Cimmerian pantheon, and he lives on a great mountain, from where he sends forth doom or death. It's useless to call upon Crom, because he is a gloomy and savage god who despises the weak. However, Crom gives a man courage, free-will, and the strength to kill their enemies at birth.[10] Crom doesn't care if individuals live or die, and he despises weakness, therefore the name of Crom is typically only invoked during an oath or curse. He is the only member of the Cimmerian pantheon named with any regularity.
The Tower of the Elephant by Robert E. Howard
The Stygian followers of Set worship their deity with human sacrifice and actively venerate serpents, while Ishtar's worshippers follow the pleasures of the flesh. In Vendhya, the followers of Asura seek truth beyond the illusions of the physical world, and the Hyborian devotees of Mitra are almost Christian in their merging of asceticism with a commitment to compassion and justice. By contrast, Conan remarks in conversation that it is best to avoid doing anything that would draw Crom's attention, as the god brings down only trouble and doom.[11] As a result, he is not so much worshipped in Howard's works as invoked in curses and expletives (for instance, Conan exclaims things like "Crom and his devils"), or when trying to gather one's courage.
Crom is never depicted as directly intervening or otherwise explicitly causing any event to occur in the original Conan stories by Robert E. Howard. There is little consistent evidence in his works that Crom actually exists; the existence of demons and highly advanced aliens is confirmed (as in the stories "The God in the Bowl" and "The Tower of the Elephant"), while the story "The Phoenix on the Sword" implies that Set is one of H. P. Lovecraft's Great Old Ones. Howard's story "Black Colossus" features a princess vocally directed by Mitra to transform Conan into her champion,[12] yet Crom makes no such appearances.
Using Crom's name as an expletive immediately identifies Conan as being a Cimmerian. Crom is specifically and uniquely considered a Cimmerian god, with other civilizations paying him little attention.
In other works
In Conan stories by authors other than Howard, there is some evidence that Crom definitely exists. For example, in The Return of Conan, Crom intervenes directly to save Conan from death and eternal damnation - evidently, because in that story Conan takes a quest around the world, braving countless dangers and doing all that a human could possibly do by human means, and it would have been unfair for him to succumb to magic which he was not equipped to counter.
Conan also mentions the Celtic deity, Manannán mac Lir, in Conan the Valorous by John Maddox Roberts. In this story, Crom is worshipped in, and reportedly lives in, a great cave in the east face of the mountain called Ben Morgh in Cimmeria where he (or a giant statue of him) is seated on a throne overlooking the Cimmerian burial grounds known as the Field of the Dead.
In other media
Crom is briefly mentioned in Conan the Barbarian, a 1982 film directed by John Milius, co-written by Oliver Stone, and loosely based on Robert E. Howard's works. The film's Crom is similar to the god described in Howard's works, although elements of Norse mythology, in particular the mythos of Odin, are introduced. During a theological discussion, Conan says that when he dies, he will go in front of Crom, who will ask of him the Riddle of Steel, and if he does not know the answer, Crom will cast him away from Valhalla and laugh at him. (The Riddle of Steel is never mentioned in any of Howard's stories.)
Conan is shown having a strained, distant relationship with Crom. The only time he sincerely prays in the film (and, it is implied, in his entire life) is when he faces the men who killed his people, his family, and his lover, Valeria. His prayer is as follows:
"Crom, I have never prayed to you before. I have no tongue for it. No one, not even you will remember if we were good men or bad, why we fought, or why we died. No, all that matters is that two stood against many, that's what's important. Valor pleases you, Crom, so grant me one request, grant me revenge! And if you do not listen, then to hell with you!"[13]
In the 1984 sequel Conan the Destroyer, Conan, having avenged Valeria's death, appears to have reconciled with his god. At one point, Conan is seen praying to Crom for the return of Valeria; he tells one character that "She sits by the side of my god." He also uses "Crom" as an expletive or expression of surprise at numerous points in the film.
Crom is also mentioned in Conan the Adventurer animated series, though there he is referred to as a "guardian spirit." In the animated series, Crom is also mostly portrayed as he is in Howard's stories, a distant deity that Conan invokes in exclamations but not in formal worship. Not irreligious, though, Conan is shown to make solemn vows in the name of his god.
In the 1997 live action television series Conan the Adventurer starring Ralph Moeller, Crom is shown as being real and active in mortal affairs having directed Conan to the location of an Atlantian sword wielded by him for the run of the series.
In the 2011 film, Conan The Barbarian, Crom is mentioned but only in passing and in expletives.
Crom is also referenced in passing in Earnest Cline's 2011 Sci-Fi novel "Ready Player One". The main character says "Thanks be to Crom" at the beginning of chapter 0027.
In Marvel Comics' What If? #39 "What If ... Thor Battled Conan?" Thor travels to the Hyborian past and, suffering from amnesia, climbs the mountain of Crom to seek answers from the god. Later, at his death, Thor passes Mjolnir to Conan. At the end, Conan then climbs up the mountain of Crom as well. His fate is left untold.
Mitra
Mitra is a deity from the fictional Hyborian Age created by Robert E. Howard in his Conan series of stories. Mitra is a personification of good popular amongst people of the era.

He is probably loosely based on the Vedic and Zoroastrian figure by the same name, and in the Hyborian universe, his worship generally represents Christianity. In the essay "The Hyborian Age", Howard notes that followers of Mitra are urged to forgive their enemies (though many of them fail to do so). Mitra's religion is missionary; its adherents sometimes lose their lives trying to spread their faith to hostile peoples.
The god's worship is strong and dominant, effectively the state religion, in the Hyborian countries corresponding to modern Western Europe. In other parts of the world, corresponding to Asia and Africa, Mitra is, at best, one god among many, while in Stygia (Egypt and North Africa), worship of Mitra is altogether banned.
Mitra is the chief god of most of the civilized Hyborian kingdoms, including Aquilonia, Ophir, Nemedia, Brythunia, Corinthia, and Zingara. His worshippers are monolatristic, since at least one tale depicts priests of Mitra recognizing the existence of another deity (Set). He is depicted as a "gentle" god.[14] In Khoraja, which is on the border between the Hyborian kingdoms and the Semite ones, the worship of Mitra was largely forgotten in favor of the Semite gods – but in hours of great need, Khorajans still call on Mitra and are answered ("Black Colossus").
While Mitra and his followers are in general presented favorably in the Conan stories, in Howard's The Hour of the Dragon they show prejudice and persecution those of Asura. Conan, being a "barrbarian", does not share this "civilized" prejudice and protects the Asura followers, who prove benefit in his hour of need.
The Mitran cult never practice sacrifice and values aesthetic simplicity. Thus, his shrines are usually unadorned and feature little or no iconography except for a single idol. The idol itself has the appearance of an idealized, bearded male figure and is the primary direction of Mitran worship. However, being omnipresent and incorporeal, Mitra is not considered to reside in the icon, nor share its appearance.[15] He is also symbolically represented by a phoenix in Howard's writing,[16] by an Ankh in the Age of Conan MMORPG, and by a bronze colossus in the survival video game Conan Exiles.[17]
Mitra appears directly in Howard's "Black Colossus", where he speaks to Princess Yasmela of Khoraja and helps her in an hour of desperate need. Mitra's involvement has a significant effect on Conan's career. Due to the god's involvement, Conan – who hitherto had never commanded more than a "company of cut-throats" – gets the chance to become a general and emerge victorious from a major battle involving tens of thousands of soldiers and affecting the future of the whole world. Though Conan's career would know many more ups and downs, this was an important step towards him eventually becoming a king – for which he could thank Mitra. From Mitra's point of view, the god evidently considered Conan as the fighter best fitted to fight and defeat a sworn enemy of the Hyborian kingdoms, who had an ancient grudge against Hyborians and who intended to lead his armies to conquer and devastate the Hyborian kingdoms, the center of Mitra worship.
Black Colossus
Mitra is also mentioned by the pirate Valeria in Howard's story "Red Nails".
In other media
Mitra, along with Crom, is mentioned in the animated series Conan the Adventurer. Here, he serves as the patron deity of Conan's love interest Jezmine, Conan's love interest, who says, "By Mitra!" in times of danger.
See also
| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
- Bran Mak Morn
- Hyborian War
- Kull of Atlantis
- Thurian Age
Footnotes
- An princess named Yelaya, who presumably becomes a consort for the lord of the underworld, plays a important role in this story. Yelalla is the name of a series of rapids and water falls in the Congo, roughly where the story takes place. In the philistine (Pelishtia) city of Ekron, there was an important oracle of Baal-Zevul (Beelzebuul). This may also have inspired the role of Bit-Yakin in the story
- Howard labels the populace of his Argos as "Argosseans", whereas the folk of the historical Argos are known as "Argives".
- According to Robert E. Howard's essay "The Hyborian Age", Cimmeria partially sinks during the cataclysm which marks the end of the said Hyborian Age, surrounded by what would be the North Sea, with its mountain-tops remaining above water as the British Isles.
- In changing the name to Darfar, Howard unwittingly changed the Arabic meaning to "the abode of mice".
- Khita is also the origin of the Russian name for China, "Kitai" (Китай), which is related to the English word "Cathay" and Marco Polo's Cathay (/kæˈθeɪ/).
- Perhaps Vendhya had something to do with this?
- There is a town called Koth in Gujarat, India, but the connection is doubtful.
- Perhaps the name Nemedia is also meant to allude to Nemea, home to the Nemean Lion of Greek mythology. The name may also be suggestive of various names for Germany in Slavic languages, e.g. Czech Německo.
- Note that the name "Pict" comes from the Latin language term for "painted one", which could be applicable to a number of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas. The historical termed Picts were a confederation of Celtic tribes in central and northern Scotland which bordered Roman Britain.
- Hellenistic Egypt had a political religion of state, the Cult of Serapis, a blending together of Hades (Styx) and Osiris, mostly the former. Perhaps this has inspired the Serpent Cult of Howard's Stygia.
- Maybe the exchange of a non-human master-race for an inhuman one was nothing for these people to be happy or grateful for, but the conquerors from the east slyly understood to play on this and turn it to their own advantage.
- The name of King Yildiz means star in the Turkish language.
- Asura is the Indian version of Persian "Ahura", as in Ahura Mazda (father of the god Mithra).
References
- Shanks (2011, p. 74)
- Howard (2002b)
- Shanks (2012, p. 27)
- Rippke (2004, pp. 82–86)
- Shanks (2012, pp. 27–29)
- Louinet (2002, p. 434)
- Howard (2002a)
- de Camp et. al (1978)
- "The Witch Queen of Yamatai (Issue)". Comic Vine. The Savage Sword of Conan. Retrieved 4 April 2018.
- The Tower of the Elephant by Robert E. Howard
- Queen of the Black Coast by Robert E. Howard
- Black Colossus by Robert E. Howard
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W5K3AKl5qpc
- Howard, Robert E. (2003), The Hyborian Age (The Coming of Conan the Cimmerian)
- Howard, Robert E. (1933), Black Colossus, USA: Weird Tales
- Howard, Robert E. (1932), The Phoenix on the Sword, USA: Weird Tales
- Conan Exiles Wiki (12 February 2017). "Religion". Archived from the original on 2017-01-14. Retrieved 12 February 2017.
Bibliography
- de Camp, L. Sprague; Carter, Lin; Nyberg, Björn (1978), "Hyborian Names", Conan the Swordsman, Bantam Books, ISBN 0-553-20582-X
- Howard, Robert, E. (2002a) [1936, 1938], "The Hyborian Age", The Coming of Conan the Cimmerian, Del Rey Books, ISBN 0-345-46151-7
- Howard, Robert, E. (2002b) [1932], "The Phoenix on the Sword", The Coming of Conan the Cimmerian, Del Rey Books, ISBN 0-345-46151-7
- Louinet, Patrice (2002), "Hyborian Genesis Part I", The Coming of Conan the Cimmerian, Del Rey Books, ISBN 0-345-46151-7
- Rippke, Dale (2004), The Hyborian Heresies, Wild Cat Books, ISBN 978-1-4116-1608-0
- Shanks, Jeffrey (2011), "Theosophy and the Thurian Age: Robert E. Howard and the Works of William Scott-Elliot", The Dark Man: The Journal of Robert E. Howard Studies, 6 (1–2), pp. 53–90
- Shanks, Jeffrey (2012), "Hyborian Age Archeology: Unearthing Historical and Anthropological Foundations", in Prida, Jonas (ed.), Conan Meets the Academy: Multidisciplinary Essays on the Enduring Barbarian, McFarland & Co, ISBN 978-0786461523