Former countries in Europe after 1815
This article gives a detailed listing of all the countries, including puppet states, that have existed in Europe since the Congress of Vienna in 1815 to the present day. Each country has information separated into columns: name of the distinct country, its lifespan, the country or countries that hold all or some of the territory it once did, and further information about it.[1][2]
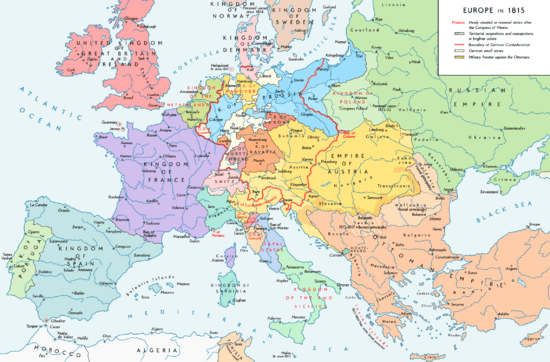
Article scope
The scope of this article begins in 1815, after a round of negotiations about European borders and spheres of influence were agreed upon at the Congress of Vienna.[3] The Congress of Vienna was a nine-month, pan-European meeting of statesmen who met to settle the many issues arising from the destabilising impact of the French Revolutionary Wars, the Napoleonic Wars, and the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire.[4]
The immediate background was Napoleonic France's defeat and surrender in May 1814, which brought an end to twenty-five years of nearly continuous war during which France had caused the annexation or geopolitical reorganisation of myriad European microstates as well as some larger ones. The Congress of Vienna was the first of a series of international meetings that came to be known as the Concert of Europe, which was an attempt to forge a peaceful balance of power in Europe,[5] including restoring or reorganising many of the states which had previously been removed from Europe's political map.
Sovereign countries
This is a list of all the independent countries or puppet states that existed between 1815 and the present day that no longer exist. (Lifespan of each is based on that country's sovereignty. This means that those countries may have existed outside of those dates as well but not under full independence.)
| Former countries | Lifespan of sovereignty | Today part of | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anhalt (Duchy) | 1813–1867 | Germany | Became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State. |
| Armenia (Democratic Republic) | 1918–1920 | Armenia, Azerbaijan and Turkey | The Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic temporarily broke up and the Democratic Republic of Armenia was created as one of its successor states but was reunified with the other two to create the Transcaucasian SSR in 1922. |
| Austrian Empire | 1804–1867 | Austria, Hungary, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Poland, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia, Italy, Slovenia, Croatia | This entity founded on the domains of the Habsburg Monarchy can be regarded in constitutional law as a unitary monarchy on a differentiated federalistic basis, whereby the special position of Hungary within the framework of this federal entity was a separate realm ruled in a personal union that was not annexed or incorporated into the Empire. |
| Austro-Hungarian Empire | 1867–1918 | Austria, Hungary, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Poland, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia, Italy, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia & Herzegovina | By the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867, the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary formed a joint monarchy with a Habsburg Monarch having some common institutions though leaving the status and internal affairs of the two countries separate. |
| Avar Khanate | 13th century–1864 | Russia | Comprised Circassia and Dagestan; it was the last country in the Caucasus to be annexed by the Russian Empire: Dagestan in 1859 and Circassia in 1864. |
| Azerbaijan (Democratic Republic) | 1918–1920 | Azerbaijan | The Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic temporarily broke up and the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic was created as one of its successor states but was reunified with the other two to create the Transcaucasian SSR in 1922. |
| Baden (Grand Duchy) | 1806–1871 | Germany | Joined the German Empire and became one of its members. |
| Bavaria (Kingdom) | 1806–1871 | Germany | Joined the German Empire and became one of its members. |
| Belarus (People's Republic) | 1918–1919 | Belarus | Gained independence from the Russian SFSR and quickly was swallowed by the Russian Soviets. Currently, its Rada (Council) is the oldest government in exile still functioning. |
| Bremen (Free City) | 1813–1867 | Germany | Became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State |
| Brunswick (Duchy) | 1815–1867 | Germany | Became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State |
| Carpatho-Ukraine | 1938–1939 | Ukraine | It was an autonomous region within Czechoslovakia from late 1938 to March 15, 1939. It declared itself an independent republic on March 15, 1939, but was annexed by Hungary between March 15 and March 16, 1939, remaining under Hungarian control until the end of World War II, when it was ceded to the Soviet Union. |
| Cospaia | 1440–1826 | Italy | By error, a small strip of land went unmentioned in a sale treaty, and its inhabitants promptly declared independence; nearly 400 years later it was absorbed into the Papal States and Tuscany equally. |
| Couto Misto | 10th century–1864 | Spain and Portugal | Neutral territory between Portugal and Spain which was divided between Portugal and Spain in 1864. |
| Cretan State | 1898–1913 | Greece | Gained independence after several rebellions against the Ottoman Empire and after only 15 years of independence joined the Kingdom of Greece. |
| Crimea (Republic) | 2014 | Ukraine (disputed with Russia) | Unrecognized state which gained independence after a referendum and then joined Russia a day later. |
| Croatia (puppet state of Nazi Germany) | 1941–1945 | Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia | A puppet state of Nazi Germany during World War II. |
| Czechoslovakia (Democratic Republic) | 1918–1938 1938–1939 1945–1948 |
Czech Republic, Slovakia, Ukraine | Democratic unified government of the Czechs and Slovaks after World War I . |
| Czechoslovakia (People's Republic) | 1948–1992 | Czech Republic, Slovakia | Communist government of the Czechs and Slovaks after World War II behind the Iron Curtain. |
| Danzig (League of Nations) | 1920–1939 | Poland | Protectorate of the League of Nations; annexed by Nazi Germany during the invasion of Poland in World War II. |
| Gurian Republic | 1905-06 | Georgia | Part of the Russian Empire. |
| German Democratic Republic | 1949–1990 | Germany | Also known as East Germany; was the Soviet-controlled government of Germany after World War II. |
| Finnish Democratic Republic | 1939–1940 | Russia | A puppet state of the Soviet Union during World War II created from southern Finland which was quickly annexed into the Soviet Union |
| Fiume (Free State) | 1920–1924 | Croatia | Formed from Austro-Hungarian territory at the end of World War I, it was later divided between the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes and the Kingdom of Italy. |
| Frankfurt (Free City) | 1816–1866 | Germany | Annexed by Prussia in 1866 |
| Georgia (Democratic Republic) | 1918–1921 | Georgia | The Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic temporarily broke up and the Democratic Republic of Georgia was created as one of its successor states but was reunified with the other two to create the Transcaucasian SSR in 1922 |
| Greece (Kingdom) | 1832–1924 1935–1941 1944–1974 |
Greece, Turkey | Wavering between monarchy and dictatorship the Kingdom of Greece existed three times in history always on rocky foundations |
| Hamburg (Free City) | 1813–1867 | Germany | Became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State |
| Hanover (Kingdom) | 1814–1866 | Germany | In personal union with the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland until the ascension of Queen Victoria in 1837; annexed by the Kingdom of Prussia in 1866. |
| Hesse (Grand Duchy) | 1806–1867/1871 | Germany | Northern part became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State and then the German Empire, with the southern part joining the German Empire as well. |
| Hesse-Homburg | 1622–1866 | Germany | Annexed by Prussia in 1866 |
| Hesse-Kassel | 1813–1866 | Germany | Annexed by Prussia in 1866 |
| Hohenzollern-Hechingen | 1576–1850 | Germany | Annexed by Prussia in 1850 |
| Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen | 1576–1850 | Germany | Annexed by Prussia in 1850 |
| Italian Social Republic | 1943–1945 | Italy | A puppet state of Nazi Germany during World War II |
| Irish Republic | 1919–1922 | United Kingdom, Ireland | Partly recognized, revolutionary state. Declared its independence after the 1918 election during the Irish War of Independence. Partitioned into the Irish Free State and United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland after the 1921 Anglo-Irish Treaty. |
| Kraków (Free City) | 1815–1846 | Poland | Protectorate of the Kingdom of Prussia, the Russian Empire and the Empire of Austria, later annexed into the Austrian Empire |
| Kuban People's Republic | 1917–1920 | Russia | From the fall of the Russian Empire in 1917 until it was annexed by the Russian SFSR it existed as a small short-lived country in the Northern Caucasus and has never regained its independence |
| Kingdom of Hungary | 1000–1918 1920–1946 |
Hungary, Slovakia, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia, Croatia, Austria, Poland | The historical kingdom's territorial continuity has been altered more times during its lifespan, however was permanently restored after the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867. After WWI, in 1920 by the Treaty of Trianon the classic Kingdom of Hungary with its borders ended and 2/3 of her territory was repartitioned and assigned to other countries. Afterwards, a kingdom without a king, a Regency was established and since 1938 until its lifespan part of her former territories were restored. |
| Lichtenberg (Principality) | 1815–1834 | Germany | Owned by a branch of the Saxe-Coburgs; sold to the Kingdom of Prussia in 1834 |
| Lippe (Principality) | 1123–1867 | Germany | Became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State |
| Lübeck (Free City) | 1815–1867 | Germany | Became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State |
| Lucca (Duchy) | 1815–1847 | Italy | Annexed by Tuscany in 1847 |
| Massa and Carrara (Duchy) | 1473–1829 | Italy | Annexed by Modena and Reggio in 1829 |
| Mecklenburg-Schwerin | 1352–1867 | Germany | Became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State |
| Free Cities of Menton and Roquebrune | 1848-1849 | France | The Free Cities of Menton and Roquebrune seceded from Monaco in 1848. In November 1849 they were annexed by Sardinia, and in 1861 were annexed by France. |
| Modena and Reggio (Duchy) | 1814–1859 | Italy | Joined the United Provinces of Central Italy, (one of the predecessors of the Kingdom of Italy) |
| Moldavian Democratic Republic | 1918 | Moldova | From the fall of the Russian Empire in 1917 until 1918 and the Versailles Treaty which added this territory to the Kingdom of Romania the Moldavian Democratic Republic existed as one of the Imperial Russian successor countries in Europe |
| Montenegro (Kingdom) | 1910–1918 | Montenegro | A kingdom which was annexed by Serbia during the Serbian Expansion after World War I to create Yugoslavia |
| Montenegro (Principality) | 1878–1910 | Montenegro | Predecessor of the Kingdom of Montenegro |
| Mountainous Republic of the Northern Caucasus | 1917–1920 | Russia | From the fall of the Russian Empire in 1917 until 1920 this country existed for a short time before annexation by the Russian SFSR and never has regained independence |
| Nassau (Duchy) | 1806–1866 | Germany | Annexed by Prussia in 1866 |
| North German Confederation Federal State | 1867–1871 | Germany, Poland, Denmark, Russia | First federal German state and predecessor of the German Empire |
| Oldenburg (Grand Duchy) | 1180–1867 | Germany | Became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State |
| Ottoman Empire | 1299–1923 | Turkey, Bosnia & Herzegovina, Serbia, Romania, Montenegro, Albania, North Macedonia, Bulgaria, Greece, Hungary, Moldova, Ukraine, Iraq, Syria, Kuwait, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria | One of the longest lasting empires of all time this empire rose out of the Near East and fluctuated drastically in territory and economic status throughout its history; it was dissolved after its defeat in World War 1. |
| Papal States | 752–1870 | Italy | The entire eastern region joined the United Provinces of Central Italy, (one of the predecessors of the Kingdom of Italy); however, the remaining strip of land along the west coast did not join Italy until it was annexed in 1870 |
| Parma (Duchy) | 1814–1859 | Italy | joined the United Provinces of Central Italy, (one of the predecessors of the Kingdom of Italy) |
| Prussia (Kingdom) | 1701–1867 | Germany, Poland, Denmark, Russia | Became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State |
| Reuss Junior Line | 1806–1867 | Germany | Became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State (a region of Anhalt) |
| Reuss Elder Line | 1778–1867 | Germany | Became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State (a region of Anhalt) |
| Russian SFSR | 1917–1922 | Russia | From the fall of the Russian Empire in 1917 until 1922 the Russian SFSR was an independent communist state comprising almost all of the territory the Russian Empire had possessed in its final years; in 1922 it became the leading and dominating state in the Soviet Union until the union’s end in 1991 |
| Saar (League of Nations) | 1920–1935 | Germany | League of Nations mandate within Weimar Germany |
| Saar (French protectorate) | 1947–1956 | Germany | French-administered region which was later given to West Germany |
| San Marco Republic | 1848–1849 | Italy | Revolutionary state, existing for 17 months in 1848–49. Based on the Venetian Lagoon, it extended into most of Venetia, or the Terraferma territory of the Venetian Republic. |
| Sardinia (Kingdom) | 1720–1861 | Italy, France | Comprised the Italian regions of Sardinia and Piedmont; the leading state that unified the Italian Peninsula. |
| Saxe-Altenburg | 1826–1867 | Germany | Became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State (a province of Thuringia) |
| Saxe-Coburg and Gotha | 1826–1867 | Germany | Became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State (a province of Thuringia) |
| Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld | 1699–1826 | Germany | Merged to form Saxe-Coburg and Gotha in 1826 |
| Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg | 1680–1826 | Germany | Merged to form Saxe-Coburg and Gotha in 1826 |
| Saxe-Meiningen | 1675–1867 | Germany | Became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State (a province of Thuringia) |
| Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach | 1809–1867 | Germany | Became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State (a province of Thuringia) |
| Saxony (Kingdom) | 1806–1867 | Germany | Became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State |
| Schaumburg-Lippe | 1643–1867 | Germany | Became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State |
| Schleswig (Duchy) | 1864–1866 | Germany, Denmark | Independence from Denmark in 1864; annexed by Prussia in 1866 |
| Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt | 1599–1867 | Germany | Became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State (a province of Thuringia) |
| Schwarzburg-Sondershausen | 1599–1867 | Germany | Became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State (a province of Thuringia) |
| Serbia (Kingdom) | 1882–1918 | Serbia, North Macedonia | Predecessor of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia which was formed from the annexations of other states |
| Serbia (Principality) | 1815–1882 | Serbia | Predecessor of the Kingdom of Serbia |
| Septinsular Republic | 1800–1815 | Greece | An archipelagic republic that existed from 1800 to 1807 under nominal Ottoman sovereignty in the Ionian Islands and then under the French Empire. |
| Slovak State | 1939–1945 | Slovakia | A puppet state of Nazi Germany during World War II |
| State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs | 1918 | Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia & Herzegovina, Serbia | A short-lived, independent country which was annexed by Serbia during the Serbian Expansion after World War I to create Yugoslavia |
| Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic | 1918 | Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan | From the fall of the Russian Empire in 1917 until 1918 and the temporary breakup of the Transcaucasian DFR, it was an independent state comprising Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan all three of which gained independence and then rejoined together in 1922 to form the Transcaucasian SSR. |
| Trieste (Free Territory) | 1947–1975 | Italy, Slovenia, Croatia | De facto split in 1954 between neighbouring countries Italy and Yugoslavia, it was formally removed in 1975 with an agreement between these two countries |
| Tuscany (Grand Duchy) | 1815–1859 | Italy | Joined the United Provinces of Central Italy, (one of the predecessors of the Kingdom of Italy) |
| Two Sicilies (Kingdom) | 1816–1860 | Italy | Comprised the Italian regions of Naples and Sicily; was annexed by the Kingdom of Sardinia in March 1860 |
| Ukraine (People’s Republic) | 1917–1921 | Ukraine | Gained independence from the Russian SFSR and quickly was swallowed by the Russian Soviets |
| Union of Soviet Socialist Republics | 1922–1991 | Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, Moldova, Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan | One of the greatest superpowers in modern times comprising most of the territory that once was under the Russian Empire including some new territory after World War II in Europe annexed from Germany, Poland and Czechoslovakia |
| United Kingdom of the Netherlands | 1815–1839 | Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg | Unified sovereign state of the Dutch lands after the crush of Napoleon; only the area of Luxembourg was part of the German Confederation |
| United Provinces of Central Italy | 1859–1860 | Italy | First step of Italian unification comprising Tuscany, Parma, Modena and Reggio, and the eastern region of the Papal States; was annexed by the Kingdom of Sardinia in March 1860 |
| United States of the Ionian Islands | 1815–1864 | Greece | Was a state and amical protectorate of the United Kingdom. It was the successor state of the Septinsular Republic |
| Waldeck-Pyrmont | 1180–1867 | Germany | Became a member of the North German Confederation Federal State |
| Weimar Germany | 1919–1933 | Germany, Poland, Russia | First German democracy |
| West Ukrainian People's Republic | 1918–1919 | Ukraine | Unrecognized successor state of Ukrainians after the fall of the Austro-Hungarian Empire |
| Württemberg (Kingdom) | 1806–1871 | Germany | Joined the German Empire and became one of its members |
| Yugoslavia (Federal Republic) | 1992–2006 | Serbia, Montenegro, Bosnia & Herzegovina | Democratic Yugoslavia after the fall of communism; Bosnia & Herzegovina gained independence between 1991 and 1993; Renamed to Serbia and Montenegro in 2003. |
| Yugoslavia (Kingdom) | 1918–1941 | Serbia, Slovenia, Kosovo, Croatia, Bosnia & Herzegovina, Montenegro, North Macedonia | Unified Slavic country after World War I |
| Yugoslavia (Socialist/Peoples's Federal Republic) | 1944–1992 | Serbia, Slovenia, Kosovo, Croatia, Bosnia & Herzegovina, Montenegro, North Macedonia | Communist government of the south Slavic ethnicities after World War II outside of the Iron Curtain |
| Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia | 1938–1945 | Czech Republic | A puppet state of Nazi Germany during World War II. |
| First Austrian Republic | 1918–1934 | Austria | |
| Federal State of Austria | 1934–1938 | Austria |
Autonomous countries or incorporated protectorates
This is a list of all the dependencies of countries that existed between 1815 and the present day that no longer exist. (Lifespan of each is based on that country’s autonomy. This means that those countries may have existed outside of those dates as well but as independent countries.)
| Former dependencies | Lifespan of dependency | Within present-day countries | Further information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abkhazia (Principality) | 1810–1864 | Georgia | the principality was actually in existence since the 12th century and even managed to keep its autonomous home rule after being conquered by the Ottoman Empire in the 15th and 16th centuries; the autonomous principality was transferred to the Russian Empire in 1810 and was completely dissolved and assimilated into Russia by 1864 |
| Bulgaria (Principality) | 1878–1908 | Bulgaria, Serbia | during the Russian-Turkish Wars of 1878, and the independence of Montenegro, Serbia and Romania, Bulgaria gained autonomous status within the Ottoman Empire; the principality gained complete independence in 1908 |
| Erivan (Khanate) | 1604–1828 | Armenia | it was an autonomous region of the Persian Empire since 1604 and was annexed by the Russian Empire in 1828 |
| Finland (Grand Duchy) | 1809–1918 | Finland, Russia | was an autonomous monarchy of the Russian Empire with the Russian Tsar as its grand duke |
| Guria (Principality) | 1810–1829 | Georgia | the principality was actually in existence since the 15th century and even managed to keep its autonomous home rule after being conquered by the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century; the autonomous principality was transferred to the Russian Empire in 1810 and was completely dissolved and assimilated into Russia by 1829 |
| Lombardy–Venetia (Kingdom) | 1815–1866 | Italy | comprised the Italian regions of Lombardy and Venetia; an autonomous kingdom within the Austrian Empire |
| Montenegro (Principality) | 1815–1878 | Montenegro | after being a puppet state of Napoleon’s Europe it regained autonomous status within the Ottoman Empire until its independence in 1878 with Russian support |
| Moresnet | 1816–1919 | Belgium | In 1816 Neutral Moresnet became a territory under common administration of the Netherlands and Prussia. The Netherlands were replaced by Belgium in 1830. After World War I in 1919 the territory was ceded to Belgium by Germany under Treaty of Versailles and formally annexed in 1920. |
| Nakhchevan (Khanate) | 1747–1828 | Azerbaijan, Armenia | it was an autonomous region of the Persian Empire since 1747 and was annexed by the Russian Empire in 1828 |
| Poland (protectorate) | 1815–1830 | Poland, Lithuania | was an autonomous monarchy of the Russian Empire with the Russian Tsar as its king; at home it was called the ‘Kingdom of Poland’ but internationally known as Congress Poland and functioned more like a protectorate |
| Romania (Principality) | 1859–1878 | Romania | in 1859 Moldovia and Wallachia unified into the United Principalities and gained autonomous status within the Ottoman Empire until its independence in 1878 with Russian support |
| Samegrelo (Principality) | 1803–1857 | Georgia | the principality was actually in existence since the 4th century BC and even managed to keep its autonomous home rule after being conquered by the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century; the autonomous principality was transferred to the Russian Empire in 1803 and was completely dissolved and assimilated into Russia by 1857 |
| Serbia (Principality) | 1817–1878 | Serbia | a rebellion broke out in 1804 and 1817 Serbia gained autonomous status within the Ottoman Empire until its independence in 1878 with Russian support |
Proposed states
This is a list of all the independent countries that could or would have existed between 1815 and the present day that for some reason or another never did.
| Proposed states | Proposed formation | Current states | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| United Baltic Duchy | 1918 | Estonia and Latvia | idea first brought forth by the Germans but was rejected after the Versailles Treaty and the Baltic Region became the three present day countries |
| United States of Greater Austria | 1905 | Austria, Hungary, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Poland, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia, Italy, Slovenia, Croatia | concept brought forth by the Habsburgs in reaction to tensions within the empire of autonomy; the autocratic empire would be changed into a united autonomous country where each nation governed itself with some support from a much weaker Habsburg monarchy |
| Intermarium | 1918 | Poland, Lithuania Latvia, Estonia, Finland Belarus Ukraine Hungary Romania Yugoslavia and Czechoslovakia. | was a geopolitical project conceived by politicians in successor states of the former Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in several iterations, some of which anticipated the inclusion as well of other, neighboring states. The proposed multinational polity would have extended across territories lying between the Baltic and Black Seas, hence the Latinate name Intermarium, meaning "Between-Seas". |
See also
General:
- List of extinct states
References
- This information is based on the main articles on these former countries.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2009-11-01. Retrieved 2010-02-25.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Bloy, Marjie (30 April 2002). "The Congress of Vienna, 1 November 1814 – 8 June 1815". The Victorian Web. Retrieved 2009-01-09.
- Bloy, Marjie (30 April 2002). "The Congress of Vienna, 1 November 1814 – 8 June 1815". The Victorian Web. Retrieved 2009-01-09.
- Bloy, Marjie (30 April 2002). "The Congress of Vienna, 1 November 1814 – 8 June 1815". The Victorian Web. Retrieved 2009-01-09.