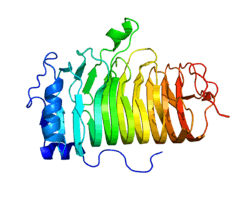
CD20
B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 or CD20 is expressed on the surface of all B-cells beginning at the pro-B phase (CD45R+, CD117+) and progressively increasing in concentration until maturity.[5]
In humans CD20 is encoded by the MS4A1 gene.[6][7]
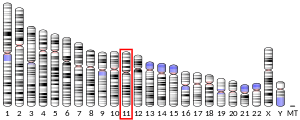
This gene encodes a member of the membrane-spanning 4A gene family. Members of this nascent protein family are characterized by common structural features and similar intron/exon splice boundaries and display unique expression patterns among hematopoietic cells and nonlymphoid tissues. This gene encodes a B-lymphocyte surface molecule that plays a role in the development and differentiation of B-cells into plasma cells. This family member is localized to 11q12, among a cluster of family members. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants that encode the same protein.[7]
Function
The protein has no known natural ligand[8] and its function is to enable optimal B-cell immune response, specifically against T-independent antigens.[9] It is suspected that it acts as a calcium channel in the cell membrane. CD20 is induced in the context of microenvironmental interactions by CXCR4/SDF1 (CXCL12) chemokine signaling and the molecular function of CD20 has been linked to the signaling propensity of B-cell receptor (BCR) in this context. CD20 has also been shown to interact with multiple other surface proteins on B cells (such as CD40, MHCII, CD53, CD81, CD82, and CBP), but the functional relevance of this remains unclear.
Expression
CD20 is expressed on all stages of B cell development except the first and last; it is present from late pro-B cells through memory cells, but not on either early pro-B cells or plasma blasts and plasma cells.[10][11] It is found on B-cell lymphomas, hairy cell leukemia, B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and melanoma cancer stem cells.[12]
Immunohistochemistry can be used to determine the presence of CD20 on cells in histological tissue sections. Because CD20 remains present on the cells of most B-cell neoplasms, and is absent on otherwise similar appearing T-cell neoplasms, it can be very useful in diagnosing conditions such as B-cell lymphomas and leukaemias. However, the presence or absence of CD20 in such tumours is not relevant to prognosis, with the progression of the disease being much the same in either case. CD20 positive cells are also sometimes found in cases of Hodgkins disease, myeloma, and thymoma.[13]
Antibody FMC7 (Flinders Medical Centre) appears to recognise a conformational variant of CD20[14][15] also known as the FMC7 antigen.[16]
Several epigenetic (EZH2, HDAC1/2, HDAC1/4, HDAC6, complex Sin3A-HDAC1) and transcription factors (USF, OCT1/2, PU.1, PiP, ELK1, ETS1, SP1, NFκB, FOXO1, CREM, SMAD2/3) regulating CD20 expression in normal and malignant B cells have been characterized.[17]
Clinical significance
CD20 is the target of the monoclonal antibodies rituximab, ocrelizumab, obinutuzumab, ofatumumab, ibritumomab tiuxetan, tositumomab, and ublituximab, which are all active agents in the treatment of all B cell lymphomas, leukemias, and B cell-mediated autoimmune diseases.
The anti-CD20 mAB ofatumumab (Genmab) was approved by FDA in October 2009 for chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
The anti-CD20 mAB obinutuzumab (Gazyva) was approved by FDA in November 2013 for chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Additional anti-CD20 antibody therapeutics under development (phase II or III clinical trials in 2008) include :
- Obinutuzumab for systemic lupus erythematosus,
- Rituximab for myalgic encephalomyelitis
- Ocaratuzumab for follicular lymphoma and rheumatoid arthritis,
- Ocrelizumab for multiple sclerosis (rheumatoid arthritis discontinued in 2010),
- TRU-015 (by Trubion), (discontinued in 2010[18])
- IMMU-106 (veltuzumab).[19] for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma or (2015) immune thrombocytopenia.
B cells, CD20, and diabetes mellitus
A link between the immune system's B cells and diabetes mellitus has been determined.[20] In cases of obesity, the presence of fatty tissues surrounding the body's major organ systems results in cell necrosis and insulin desensitivity along the boundary between them. Eventually, the contents of fat cells that would otherwise have been digested by insulin are shed into the bloodstream. An inflammation response that mobilizes both T and B cells results in the creation of antibodies against these cells, causing them to become less responsive to insulin by an as-yet unknown mechanism and promoting hypertension, hypertriglyceridemia, and arteriosclerosis, hallmarks of the metabolic syndrome. Obese mice administered anti-B cell CD-20 antibodies, however, did not become less responsive to insulin and as a result did not develop diabetes mellitus or the metabolic syndrome, the posited mechanism being that anti-CD20 antibodies rendered the T cell antibodies dysfunctional and therefore powerless to cause insulin desensitivity by a B cell antibody-modulated autoimmune response. The protection afforded by anti-CD-20 lasted approximately forty days—the time it takes the body to replenish its supply of B cells—after which repetition was necessary to restore it. Hence, it has been argued that diabetes mellitus be reclassified as an autoimmune disease rather than a purely metabolic one and focus treatment for it on immune system modulation.[20]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000156738 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000024673 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Hardy, Richard (2008). "Chapter 7: B Lymphocyte Development and Biology". In Paul, William (ed.). Fundamental Immunology (Book) (6th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 237–269. ISBN 978-0-7817-6519-0.
- Tedder TF, Streuli M, Schlossman SF, Saito H (January 1988). "Isolation and structure of a cDNA encoding the B1 (CD20) cell-surface antigen of human B lymphocytes". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 85 (1): 208–12. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.1.208. PMC 279513. PMID 2448768.
- "Entrez Gene: MS4A1 membrane-spanning 4-domains, subfamily A, member 1".
- Cragg MS, Walshe CA, Ivanov AO, Glennie MJ (2005). The biology of CD20 and its potential as a target for mAb therapy. Current Directions in Autoimmunity. 8. pp. 140–74. doi:10.1159/000082102. ISBN 978-3-8055-7851-6. PMID 15564720.
- Kuijpers TW, Bende RJ, Baars PA, Grummels A, Derks IA, Dolman KM, Beaumont T, Tedder TF, van Noesel CJ, Eldering E, van Lier RA (January 2010). "CD20 deficiency in humans results in impaired T cell-independent antibody responses" (PDF). The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 120 (1): 214–22. doi:10.1172/JCI40231. PMC 2798692. PMID 20038800.
- Walport M, Murphy K, Janeway C, Travers PJ (2008). Janeway's Immunobiology (7th ed.). New York: Garland Science. ISBN 978-0-8153-4123-9.
- Bonilla FA, Bona CA (1996). "5". Textbook of Immunology. Boca Raton: CRC. p. 102. ISBN 978-3-7186-0596-5.
- Fang D, Nguyen TK, Leishear K, Finko R, Kulp AN, Hotz S, Van Belle PA, Xu X, Elder DE, Herlyn M (October 2005). "A tumorigenic subpopulation with stem cell properties in melanomas". Cancer Research. 65 (20): 9328–37. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1343. PMID 16230395.
- Cooper K, Anthony Leong AS-Y (2003). Manual of diagnostic antibodies for immunohistology (2nd ed.). London: Greenwich Medical Media. ISBN 978-1-84110-100-2.
- Polyak MJ, Ayer LM, Szczepek AJ, Deans JP (July 2003). "A cholesterol-dependent CD20 epitope detected by the FMC7 antibody". Leukemia. 17 (7): 1384–9. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2402978. PMID 12835728.
- Serke S, Schwaner I, Yordanova M, Szczepek A, Huhn D (April 2001). "Monoclonal antibody FMC7 detects a conformational epitope on the CD20 molecule: evidence from phenotyping after rituxan therapy and transfectant cell analyses". Cytometry. 46 (2): 98–104. doi:10.1002/cyto.1071. PMID 11309819.
- Deans JP, Polyak MJ (February 2008). "FMC7 is an epitope of CD20". Blood. 111 (4): 2492, author reply 2493–4. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-11-126243. PMID 18263793.
- Pavlasova G, Mraz M (June 2020). "The regulation and function of CD20: an "enigma" of B-cell biology and targeted therapy". Haematologica. 105 (6): 1494–1506. doi:10.3324/haematol.2019.243543. PMID 32482755.
- "Trubion announces Pfizer's decision to discontinue development of TRU-015 for RA". Trubion Pharmaceuticals, Inc. press release. 15 June 2010.
- Note: information included in this article only found in table present in print version of article. K. John Morrow Jr (15 June 2008). "Methods for Maximizing Antibody Yields". Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News. Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. p. 36. Retrieved 6 July 2008.
- Winer DA, Winer S, Shen L, Wadia PP, Yantha J, Paltser G, Tsui H, Wu P, Davidson MG, Alonso MN, Leong HX, Glassford A, Caimol M, Kenkel JA, Tedder TF, McLaughlin T, Miklos DB, Dosch HM, Engleman EG (May 2011). "B cells promote insulin resistance through modulation of T cells and production of pathogenic IgG antibodies". Nature Medicine. 17 (5): 610–7. doi:10.1038/nm.2353. PMC 3270885. PMID 21499269. Lay summary – Stanford School of Medicine.
Further reading
- Macardle PJ, Nicholson IC (2003). "CD20". Journal of Biological Regulators and Homeostatic Agents. 16 (2): 136–8. PMID 12144126.
- Tamayose K, Sato N, Ando J, Sugimoto K, Oshimi K (December 2002). "CD3-negative, CD20-positive T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia: case report and review of the literature". American Journal of Hematology. 71 (4): 331–5. doi:10.1002/ajh.10224. PMID 12447967.
- Küster H, Zhang L, Brini AT, MacGlashan DW, Kinet JP (June 1992). "The gene and cDNA for the human high affinity immunoglobulin E receptor beta chain and expression of the complete human receptor". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 267 (18): 12782–7. PMID 1535625.
- Einfeld DA, Brown JP, Valentine MA, Clark EA, Ledbetter JA (March 1988). "Molecular cloning of the human B cell CD20 receptor predicts a hydrophobic protein with multiple transmembrane domains". The EMBO Journal. 7 (3): 711–7. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02867.x. PMC 454379. PMID 2456210.
- Tedder TF, Disteche CM, Louie E, Adler DA, Croce CM, Schlossman SF, Saito H (April 1989). "The gene that encodes the human CD20 (B1) differentiation antigen is located on chromosome 11 near the t(11;14)(q13;q32) translocation site". Journal of Immunology. 142 (7): 2555–9. PMID 2466898.
- Tedder TF, Klejman G, Schlossman SF, Saito H (April 1989). "Structure of the gene encoding the human B lymphocyte differentiation antigen CD20 (B1)". Journal of Immunology. 142 (7): 2560–8. PMID 2466899.
- Loken MR, Shah VO, Dattilio KL, Civin CI (November 1987). "Flow cytometric analysis of human bone marrow. II. Normal B lymphocyte development". Blood. 70 (5): 1316–24. PMID 3117132.
- Stamenkovic I, Seed B (June 1988). "Analysis of two cDNA clones encoding the B lymphocyte antigen CD20 (B1, Bp35), a type III integral membrane protein". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 167 (6): 1975–80. doi:10.1084/jem.167.6.1975. PMC 2189672. PMID 3260267.
- Bofill M, Janossy G, Janossa M, Burford GD, Seymour GJ, Wernet P, Kelemen E (March 1985). "Human B cell development. II. Subpopulations in the human fetus". Journal of Immunology. 134 (3): 1531–8. PMID 3871452.
- Deans JP, Kalt L, Ledbetter JA, Schieven GL, Bolen JB, Johnson P (September 1995). "Association of 75/80-kDa phosphoproteins and the tyrosine kinases Lyn, Fyn, and Lck with the B cell molecule CD20. Evidence against involvement of the cytoplasmic regions of CD20". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 270 (38): 22632–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.38.22632. PMID 7545683.
- Valentine MA, Licciardi KA, Clark EA, Krebs EG, Meier KE (January 1993). "Insulin regulates serine/threonine phosphorylation in activated human B lymphocytes". Journal of Immunology. 150 (1): 96–105. PMID 7678037.
- Bubien JK, Zhou LJ, Bell PD, Frizzell RA, Tedder TF (June 1993). "Transfection of the CD20 cell surface molecule into ectopic cell types generates a Ca2+ conductance found constitutively in B lymphocytes". The Journal of Cell Biology. 121 (5): 1121–32. doi:10.1083/jcb.121.5.1121. PMC 2119683. PMID 7684739.
- Shirakawa T, Li A, Dubowitz M, Dekker JW, Shaw AE, Faux JA, Ra C, Cookson WO, Hopkin JM (June 1994). "Association between atopy and variants of the beta subunit of the high-affinity immunoglobulin E receptor". Nature Genetics. 7 (2): 125–9. doi:10.1038/ng0694-125. PMID 7920628.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (January 1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Szepetowski P, Perucca-Lostanlen D, Gaudray P (June 1993). "Mapping genes according to their amplification status in tumor cells: contribution to the map of 11q13". Genomics. 16 (3): 745–50. doi:10.1006/geno.1993.1257. PMID 8325649.
- Algino KM, Thomason RW, King DE, Montiel MM, Craig FE (July 1996). "CD20 (pan-B cell antigen) expression on bone marrow-derived T cells". American Journal of Clinical Pathology. 106 (1): 78–81. doi:10.1093/ajcp/106.1.78. PMID 8701937.
- Szöllósi J, Horejsí V, Bene L, Angelisová P, Damjanovich S (October 1996). "Supramolecular complexes of MHC class I, MHC class II, CD20, and tetraspan molecules (CD53, CD81, and CD82) at the surface of a B cell line JY". Journal of Immunology. 157 (7): 2939–46. PMID 8816400.
- Kanzaki M, Lindorfer MA, Garrison JC, Kojima I (June 1997). "Activation of the calcium-permeable cation channel CD20 by alpha subunits of the Gi protein". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 272 (23): 14733–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.23.14733. PMID 9169438.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (October 1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
External links
- CD20+antigen at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- representations of the shape are found here and more detail here
- Human MS4A1 genome location and MS4A1 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
- Human MS4A2 genome location and MS4A2 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.