Estriol dihexanoate
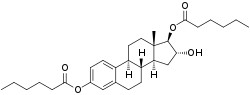
Estriol dihexanoate, or estriol 3,17β-dihexanoate, is a synthetic estrogen and estrogen ester – specifically, the C3 and C17β dihexanoate ester of estriol – which was first described in 1963 and was never marketed.[1][2][3] Following a single intramuscular injection of 8.90 mg estriol dihexanoate (equivalent to 5.0 mg estriol) in an oil solution, peak levels of estriol occurred after 2.1 to 3.4 days, an elimination half-life of 187 to 221 hours was observed, and estriol levels remained elevated for up to 20 to 50 days.[1][3] For comparison, the durations of estriol and estriol dipropionate were far shorter.[1][3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Oestriol dihexanoate; Estriol 3,17β-dihexanoate; 16α-Hydroxyestra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diyl dihexanoate |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
| Drug class | Estrogen; Estrogen ester |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C30H44O5 |
| Molar mass | 484.677 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
- Michael Oettel; Ekkehard Schillinger (6 December 2012). Estrogens and Antiestrogens II: Pharmacology and Clinical Application of Estrogens and Antiestrogen. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 273–. ISBN 978-3-642-60107-1.
- Tsuneda K, Yamada J, Yasuda K, Mori H (April 1963). "Preparation of some estriol esters". Chem. Pharm. Bull. 11: 510–514. doi:10.1248/cpb.11.510. PMID 13994597.
- Heithecker R, Aedo AR, Landgren BM, Cekan SZ (1991). "Plasma estriol levels after intramuscular injection of estriol and two of its esters". Horm. Res. 35 (6): 234–8. doi:10.1159/000181911. PMID 1819548.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.