Cocke County, Tennessee
Cocke County is a county on the eastern border of the U.S. state of Tennessee. As of the 2010 census, the population was 35,662.[2] Its county seat is Newport.[3]
Cocke County | |
|---|---|
 Cocke County Courthouse in Newport | |
 Location within the U.S. state of Tennessee | |
 Tennessee's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 35°56′N 83°07′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | October 9, 1797 |
| Named for | William Cocke[1] |
| Seat | Newport |
| Largest city | Newport |
| Area | |
| • Total | 443 sq mi (1,150 km2) |
| • Land | 435 sq mi (1,130 km2) |
| • Water | 8.6 sq mi (22 km2) 1.9%% |
| Population | |
| • Estimate (2018) | 35,774 |
| • Density | 82/sq mi (32/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional district | 1st |
| Website | www |
Cocke County comprises the Newport, TN Micropolitan Statistical Area, which is part of the Knoxville-Morristown-Sevierville, Tennessee Combined Statistical Area.[4]
History
Before the arrival of European settlers, the area that is now Cocke County probably was inhabited by the Cherokee. They were the most recent of a series of indigenous cultures who had occupied this country for thousands of years.
The first recorded European settlement in the county was in 1783 when land near the fork of the French Broad and the Pigeon Rivers was cleared and cultivated. The earliest European settlers were primarily Scots-Irish, Dutch, and Germans who came to the area over the mountains from the Carolinas or through Virginia from Pennsylvania and other northern states.
The county was established by an Act of the Tennessee General Assembly on October 9, 1797, from a part of Jefferson County, Tennessee. It was named after William Cocke,[5] one of the state's first Senators. Located within the Appalachian and Great Smoky Mountains, it had difficult conditions for early settlers.
Like many East Tennessee counties, settled by yeomen farmers, Cocke County was largely pro-Union on the eve of the Civil War. In Tennessee's Ordinance of Secession referendum on June 8, 1861, the county's residents voted 1,185 to 518 against secession.[6]
Geography

According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 443 square miles (1,150 km2), of which 435 square miles (1,130 km2) are land and 8.6 square miles (22 km2) (1.9%) are covered by water.[7] The southern part of the county is located within the Great Smoky Mountains, and the lands are protected by the Great Smoky Mountains National Park. The northern part of the county is situated within the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians.[8] The county's highest point is Old Black, which rises to 6,370 feet (1,940 m) in the Smokies along the county's border with North Carolina.[9] English Mountain, a large ridge that peaks at 3,629 feet (1,106 m), dominates the western part of the county.
Cocke County is drained by the French Broad River, which traverses the northern part of the county and forms much of its boundary with Jefferson County. A portion of this river is part of Douglas Lake, an artificial reservoir created by Douglas Dam further downstream. The Pigeon River flows northward across the county and empties into the French Broad north of Newport at Irish Bottoms.
Adjacent counties
- Hamblen County (north)
- Greene County (northeast)
- Madison County, North Carolina (east)
- Haywood County, North Carolina (south)
- Sevier County (southwest)
- Jefferson County (northwest)
National protected areas
- Appalachian Trail (part)
- Cherokee National Forest (part)
- Foothills Parkway (part)
- Great Smoky Mountains National Park (part)
State protected areas
- Rankin Wildlife Management Area (part)
- Martha Sundquist State Forest
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1810 | 5,154 | — | |
| 1820 | 4,892 | −5.1% | |
| 1830 | 6,017 | 23.0% | |
| 1840 | 6,992 | 16.2% | |
| 1850 | 8,300 | 18.7% | |
| 1860 | 10,408 | 25.4% | |
| 1870 | 12,458 | 19.7% | |
| 1880 | 14,808 | 18.9% | |
| 1890 | 16,523 | 11.6% | |
| 1900 | 19,153 | 15.9% | |
| 1910 | 19,399 | 1.3% | |
| 1920 | 20,782 | 7.1% | |
| 1930 | 21,775 | 4.8% | |
| 1940 | 24,083 | 10.6% | |
| 1950 | 22,991 | −4.5% | |
| 1960 | 23,390 | 1.7% | |
| 1970 | 25,283 | 8.1% | |
| 1980 | 28,792 | 13.9% | |
| 1990 | 29,141 | 1.2% | |
| 2000 | 33,565 | 15.2% | |
| 2010 | 35,662 | 6.2% | |
| Est. 2018 | 35,778 | [10] | 0.3% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[11] 1790-1960[12] 1900-1990[13] 1990-2000[14] 2010-2014[2] | |||
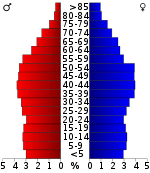
As of the census[16] of 2000, 33,565 people, 13,762 households, and 9,715 families were residing in the county. The population density was 77 people per square mile (30/km²). The 15,844 housing units averaged 36 per mi2(14/km²). The racial makeup of the county was 96.16% White, 1.99% African American, 0.40% Native American, 0.15% Asian, 0.33% from other races, and 0.96% from two or more races. About 1.05% of the population was Hispanic or Latino of any race.
Of the 13,762 households, 29.50% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 53.10% were married couples living together, 13.00% had a female householder with no husband present, and 29.40% were not families. About 25.70% of all households were made up of individuals, and 10.10% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.41 and the average family size was 2.87.
In the county, the population was distributed as 22.80% under the age of 18, 8.30% from 18 to 24, 28.80% from 25 to 44, 26.40% from 45 to 64, and 13.60% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 39 years. For every 100 females, there were 94.60 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 92.80 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $25,553, and for a family was $30,418. Males had a median income of $26,062 versus $18,826 for females. The per capita income for the county was $13,881. About 18.70% of families and 22.50% of the population were below the poverty line, including 31.80% of those under age 18 and 18.70% of those age 65 or over.
Communities
City
- Newport, county seat
Towns
Unincorporated communities
- Allen Grove
- Baltimore
- Boomer
- Briar Thicket
- Bridgeport
- Bybee
- Cosby
- Del Rio
- Hartford
- Midway
- Reidtown (partial)
- Tom Town
- Wasp
Notable residents
- Ben W. Hooper, governor of Tennessee from 1911 to 1915
- Popcorn Sutton, moonshiner[17]
- Marshall Teague, actor
In popular culture
The novel Christy and the television series of the same name are based on historical events, people, and localities of Cocke County. The fictional small town of El Pano, where the novel begins, is based on the existing village of Del Rio, Tennessee. The fictional Cutter Gap, where most of the plot unfolds, represents the locale now known as Chapel Hollow. Several area landmarks associated with the story are marked for visitors, including the site of the Ebenezer Mission in Chapel Hollow, which is located off the Old Fifteenth Rd., about 5 miles (8.0 km) from Del Rio.
Politics
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third Parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 80.7% 9,791 | 16.3% 1,981 | 2.9% 354 |
| 2012 | 73.9% 8,459 | 24.5% 2,804 | 1.7% 191 |
| 2008 | 71.7% 8,945 | 26.8% 3,340 | 1.6% 196 |
| 2004 | 67.4% 8,297 | 32.0% 3,935 | 0.6% 79 |
| 2000 | 60.4% 6,185 | 37.8% 3,872 | 1.8% 182 |
| 1996 | 51.6% 4,481 | 38.3% 3,326 | 10.2% 884 |
| 1992 | 53.0% 5,298 | 35.0% 3,495 | 12.1% 1,207 |
| 1988 | 71.7% 5,430 | 27.9% 2,115 | 0.5% 34 |
| 1984 | 75.5% 6,665 | 23.4% 2,068 | 1.1% 95 |
| 1980 | 74.4% 6,802 | 23.4% 2,139 | 2.2% 203 |
| 1976 | 60.9% 5,004 | 38.2% 3,141 | 0.9% 74 |
| 1972 | 85.6% 5,268 | 13.1% 805 | 1.3% 80 |
| 1968 | 72.8% 5,645 | 12.3% 950 | 15.0% 1,159 |
| 1964 | 70.7% 5,084 | 29.3% 2,109 | |
| 1960 | 81.3% 6,581 | 17.8% 1,442 | 0.9% 72 |
| 1956 | 82.3% 5,526 | 16.7% 1,121 | 1.0% 68 |
| 1952 | 82.0% 5,688 | 18.0% 1,247 | |
| 1948 | 77.5% 3,576 | 20.4% 939 | 2.2% 99 |
| 1944 | 78.1% 3,554 | 21.8% 989 | 0.1% 5 |
| 1940 | 75.4% 3,521 | 23.5% 1,098 | 1.2% 54 |
| 1936 | 75.3% 3,731 | 24.6% 1,217 | 0.1% 6 |
| 1932 | 59.4% 2,324 | 39.8% 1,557 | 0.9% 34 |
| 1928 | 80.0% 2,908 | 19.9% 722 | 0.1% 5 |
| 1924 | 73.1% 2,556 | 26.4% 921 | 0.5% 18 |
| 1920 | 77.4% 3,283 | 21.9% 929 | 0.8% 32 |
| 1916 | 70.9% 1,478 | 28.5% 595 | 0.6% 13 |
| 1912 | 39.6% 757 | 31.2% 597 | 29.2% 559 |
Like all of Unionist East Tennessee, Cocke County has been overwhelmingly Republican ever since the Civil War. Since the first postwar election in 1868, Cocke County has voted for every Republican Presidential candidate, even supporting William Howard Taft during the divided 1912 election. No Democratic Presidential candidate has managed to receive forty percent of the county's vote in this time, although Franklin D. Roosevelt in his 1932 landslide got within 0.23 percent of this figure.
References
- E.R. Walker III, "Cocke County," Tennessee Encyclopedia of History and Culture. Retrieved: June 24, 2013.
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 8, 2011. Retrieved November 29, 2013.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on May 31, 2011. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- Office of Management and Budget, Update of Statistical Area Definitions and Guidance on Their Uses Archived April 24, 2009, at the Wayback Machine, December 5, 2005
- Gannett, Henry (1905). The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States. Govt. Print. Off. pp. 86.
- Oliver Perry Temple, East Tennessee and the Civil War, (R. Clarke Company, 1899), p. 199.
- "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Retrieved April 2, 2015.
- Tennessee Department of Environment and Conservation, et al., "Ambient Air Monitoring Plan," Environmental Protection Agency website, July 1, 2010, p. 6. Accessed: March 18, 2015.
- Tennessee County Highpoints, Tennessee Landforms. Retrieved: June 24, 2013.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved July 20, 2019.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved April 2, 2015.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved April 2, 2015.
- Forstall, Richard L., ed. (March 27, 1995). "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved April 2, 2015.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. April 2, 2001. Retrieved April 2, 2015.
- Based on 2000 Census data
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved May 14, 2011.
- Robertson, Campbell (February 20, 2012). "Yesterday's Moonshiner, Today's Microdistiller". The New York Times. Retrieved February 21, 2012.
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved March 10, 2018.
Further reading
- Goodspeed Publishing Company, "History of Cocke County", pages 864–867 in History of Tennessee, 1887. Retrieved November 26, 2006.
- Walker, E.R. III. Cocke County, Tennessee: Pages from the Past. Charleston: The History Press (2007). ISBN 1-59629-398-5
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cocke County, Tennessee. |
- Official site
- Cocke County Partnership – Chamber of Commerce
- Cocke County Schools
- Cocke County, TNGenWeb – genealogy resources
- Cocke County at Curlie