Blackfriars station
Blackfriars, also known as London Blackfriars, is a central London railway station and connected London Underground station in the City of London. It provides Thameslink services: local (from North to South London), and regional (Bedford and Cambridge to Brighton) and limited Southeastern commuter services to South East London and Kent. Its platforms span the River Thames, the only one in London to do so, along the length of Blackfriars Railway Bridge, a short distance downstream from Blackfriars Bridge. There are two station entrances either side of the Thames, along with a connection to the London Underground District and Circle lines.
| Blackfriars | |
|---|---|
| London Blackfriars | |
Northern entrance on Queen Victoria Street after renovation in 2012 | |
 Blackfriars Location of Blackfriars in Central London | |
| Location | Blackfriars, Castle Baynard |
| Local authority | City of London |
| Managed by | Thameslink; London Underground |
| Owner | Network Rail Transport for London |
| Station code | BFR |
| DfT category | A |
| Number of platforms | 6 (4 National Rail) (2 London Underground) |
| Accessible | Yes[1][2] |
| Fare zone | 1 |
| OSI | Southwark Blackfriars Millennium Pier |
| London Underground annual entry and exit | |
| 2014 | |
| 2015 | |
| 2016 | |
| 2017 | |
| 2018 | |
| National Rail annual entry and exit | |
| 2014–15 | |
| – interchange | |
| 2015–16 | |
| – interchange | |
| 2016–17 | |
| – interchange | |
| 2017–18 | |
| – interchange | |
| 2018–19 | |
| – interchange | |
| Railway companies | |
| Original company | London, Chatham and Dover Railway |
| Key dates | |
| 10 May 1886 | Opened as St. Paul's (LC&DR) |
| 30 May 1870 | Opened (MDR) |
| 1 February 1937 | Renamed as Blackfriars |
| 30 November 1977 | Rebuilt (British Rail) |
| 20 February 2012 | Rebuilt (Thameslink) |
| Other information | |
| External links | |
| WGS84 | 51.5116°N 0.103°W |
The main line station was opened by the London, Chatham and Dover Railway with the name St. Paul's in 1886, as a replacement for the earlier Blackfriars Bridge station (now the present station's southern entrance) and the earlier Blackfriars railway bridge. This increased capacity of rail traffic through the Snow Hill Tunnel to the rest of the rail network. The Underground station opened in 1870 with the arrival of the Metropolitan District Railway. The station was renamed Blackfriars in 1937 to avoid confusion with St Paul's tube station. It was rebuilt in the 1970s, which included the addition of office space above the station and the closure of the original railway bridge, which was demolished in 1985.
In 2009, the station underwent major refurbishments to improve capacity, which included the extension of the platforms across the railway bridge and a new station entrance on the South Bank. The underground station was rebuilt at the same time, and work was completed in 2012.
Location
Blackfriars station[lower-alpha 1] serves Thameslink rail services that connect suburbs with central London. It straddles the River Thames, running across the length of Blackfriars Railway Bridge parallel to the A201 Blackfriars Bridge.[9] For this reason, it is partly in the City of London and partly in the London Borough of Southwark. The north bank entrance is on the south side of Queen Victoria Street and the south bank entrance, opened in 2011, is adjacent to Blackfriars Road.[10]
The station falls within fare zone 1. The station is run by Thameslink, with Transport for London handling the underground platforms.[11] A Thameslink driver depot is in the station building.[12] London Buses routes 4, 40, 63 and night routes N63 and N89 serve the station.[13] The adjacent Blackfriars Millennium Pier provides river services to Putney and Canary Wharf.[14]
History
London, Chatham and Dover Railway
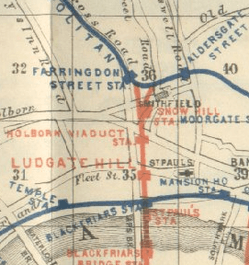
The station was proposed by the London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LC&DR), who had been given parliamentary power to build a line into the City of London. The company wanted to compete with rivals, the South Eastern Railway, and provide the best service into Central London. The line was complete as far as the Thames by 1864; the LC&DR opened a station called Blackfriars Bridge on 1 June, which sat on the south bank adjacent to Blackfriars Road.[15] An underground station at Blackfriars was opened by the Metropolitan District Railway in 1870, before any mainline stations.[16]
The railway bridge across the Thames was delayed because the City's controlling government, the Corporation of London, were unsure as to what it should look like and how many arches there should be. The station was designed by Joseph Cubitt and had a long roof with walls that stretched up to the riverbank. Cubitt subsequently designed the original bridge, which carried four tracks on a 933 feet (284 m) lattice girder bridge, supported by sets of stone piers supporting iron columns. Services began across the bridge on 21 December 1864.[17] Upon completion, trains ended at a temporary terminal, replaced by Ludgate Hill on 1 June 1865.[17] A further station, Holborn Viaduct, opened on 2 March 1874 and the LC&DR line ran via the Snow Hill tunnel to a connection to the Metropolitan Railway near Farringdon, then on to King's Cross and St Pancras stations.[18]
The mainline Blackfriars station was opened by the LC&DR as St. Paul's railway station on 10 May 1886 when the company opened the St. Paul's Railway Bridge across the Thames. The bridge was constructed parallel to the 1864 Blackfriars Railway Bridge, carrying seven tracks across five arched spans between 175 feet (53 m) and 185 feet (56 m) high. It widened past the bridge to the terminus on the south side of Queen Victoria Street. The original station was a small and cheaply designed pink-red brick building, as the LD&CR had financial difficulties throughout its lifetime attempting to drive a railway through Central London.[19] The station's frontage backed onto the District Railway, making a cab access and forecourt impossible owing to lack of space. It did, however, allow St Paul's a direct interchange with the rest of the underground, unlike all the other LC&DR stations. On 13 November 1886, a direct connection was made between the mainline and underground stations.[16]

After the opening of St. Paul's station, the earlier Blackfriars Bridge station was closed to passengers but remained as a goods station until 1965.[20][lower-alpha 2] Most mainline trains called at St Paul's, including those stopping at Holborn Viaduct. Local commuters continued to use Ludgate Hill where possible, as it was closer to where they were going, but it did not have sufficient capacity.[16]
Southern Railway and Southern Region
London, Chatham and Dover Railway City Branch | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depicted as at 1900 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
St. Paul's station was renamed by the Southern Railway as Blackfriars on 1 February 1937. This was partly done to avoid confusion after the London Passenger Transport Board renamed Post Office tube station on the Central line to St Paul's, and partly so that the mainline and underground stations would have the same name.[19] It suffered significant bomb damage during World War II.[22] Overnight on 16–17 April 1941, the signalbox on the south side of the bridge was destroyed, along with a bridge over Southwark Street.[23] The signals were not fully restored until 11 August 1946, after the war.[24]

After the creation of British Railways in 1948, the station was managed by British Railways (Southern Region).[25] Gradually, the structure of the original Blackfriars Railway Bridge deteriorated until it was unsound. In 1961, two tracks were removed from the bridge to ease its load. The station had little investment and still supported some of the original architecture and design up to the 1960s. By this time, services were reduced to a handful of commuter services.[26] The bridge was closed to trains on 27 June 1971 and the deck was removed in 1985, and only the piers in the river and the orange bridge abutments remain.[25][27]
The station began to be rebuilt along with the Underground station in 1971, which included an additional 150,000 square feet (14,000 m2) of office space. Reconstruction was problematic, as the original station building had sat on top of a cold store, which had frozen the ground below it. The District Line tunnel had to be removed and replaced with a new supporting structure that could accommodate the redesigned station building. The work was formally reopened on 30 November 1977 by the Lord Mayor of London, Peter Vanneck (though the station had never actually closed). A part of the stonework elevation from the 1886 LC&DR station has been preserved at platform level in the main line station indicating many destinations in the south-east of England and in Europe.[28]
Station rebuild

Blackfriars station was significantly renovated between 2009 and 2012 in a £500m redevelopment programme to modernise the station and increase capacity.[29] The terminal platforms at the station were closed on 20 March 2009 in order for work to begin.[22] The original concept for the project was designed by Pascall+Watson architects, with execution by Jacobs and Tony Gee and Partners; it was built by Balfour Beatty.[30] The office building above the station was demolished and replaced as part of the Thameslink programme. The new station is the same height and has a combined National Rail and London Underground ticket hall and ventilation shaft together with escalators and lifts between a mezzanine level for main line railway services and the sub-surface level for London Underground services.[25] The Underground station also received major enhancements, with a new roof of glazed north lights and partial-height glazed side panels installed along the entire length of the bridge.[31][32]

On the south bank of the river a new station entrance was built at Bankside, containing a second ticket hall.[33] The through platforms were moved to the east side and extended along Blackfriars Railway Bridge to accommodate 12-carriage trains (in place of the previous eight). The layout has been altered by building new bay platforms on the west side, avoiding the need for through trains between City Thameslink and London Bridge crossing the paths of terminating ones.[29]

The works exploited the disused piers west of the existing railway bridge which once supported the former West Blackfriars and St. Paul's Railway Bridge. The easternmost row of disused piers was strengthened, tied into the existing bridge and clad in stone.[34] The longer platforms allow longer trains on the Thameslink route to pass through London.[35] Thameslink services began using the newly constructed platforms in early 2011. The station's new entrance and ticket hall on the south side of the river opened on 5 December.[10] The tube station reopened on 20 February 2012. The Mayor of London, Boris Johnson, visited the works on the same day, saying "the rebirth of this central London station will improve the journeys of thousands of passengers every single day". The reconstruction work provided jobs for around 13,000 people, with a maximum of 2000 per day at the busiest times.[35] The Thameslink redevelopment work at Blackfriars has been well received.[34] In January 2014 the Blackfriars Railway Bridge became the world's largest solar-powered bridge having been covered with 4,400 photovoltaic panels providing up to half of the energy for the station.[36] In 2017, the station won a Major Station of the Year award at the National Rail Awards.[34]
The Waterloo & City line, a deep-level tube line which runs non-stop between Waterloo and Bank, runs almost directly under Blackfriars station and there have been suggestions to construct an interchange station for the line at Blackfriars. The Department for Transport considers this to have "no significant transport benefit".[37]
Accidents
- On 19 May 1938, a SECR B1 class locomotive was derailed, causing several hours disruption at the station.[38]
- On 2 January 2014, a train's pantograph struck the roof of the station due to a technical fault.[39] The accident[40] involving a First Capital Connect service from St Albans City to Sevenoaks did not result in any injuries but caused delays of around 45 minutes.[41]
Services

Blackfriars main-line station is served by through services on the Thameslink route operated by Thameslink and Southeastern. This includes trains from Bedford, St Albans City and Luton to the north, and Brighton, Sutton and Sevenoaks to the south. Southbound trains run via London Bridge or Elephant & Castle; northbound trains next call at City Thameslink. Before March 2009 some services from the south terminated at three bay platforms, which were then removed during renovation works. Two new bay platforms opened in May 2012 and are used during peak hours and at weekends.[42] Southeastern provides direct services to Kent during peak hours Monday to Friday.
The new Thameslink timetable was introduced in May 2018. The current off peak service is as follows:
- 4 tph to Brighton via Gatwick Airport
- 2 tph to Horsham via Gatwick Airport
- 2 tph to Gatwick Airport via Redhill
- 2 tph to Rainham via Greenwich, Charlton, Abbey Wood, Dartford, Gravesend and Gillingham
- 2 tph to Orpington
- 4 tph to Sutton, 2 tph via Wimbledon and 2 tph via Mitcham Junction.
- 4 tph to Bedford via St Pancras International, St Albans City, Luton Airport and Luton Town.
- 2 tph to Luton via St Pancras International, St Albans City and Luton Airport
- 4 tph to St Albans City via St Pancras International
- 2 tph to Kentish Town via St Pancras International
- 2 tph to Cambridge via St Pancras International, Stevenage and Hitchin
- 2 tph to Peterborough via St Pancras International, Stevenage and Hitchin

Although many services are Thameslink through trains, Blackfriars is considered a central London terminus and is a valid destination for a ticket marked "London Terminals".[43]
| Preceding station | Following station | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thameslink Thameslink | London Bridge |
|||
| Preceding station | Following station | |||
| Circle line | ||||
| District line | towards Upminster |
|||
| Disused railways | ||||
| Ludgate Hill Line open, station closed |
London, Chatham & Dover Railway City Branch |
Blackfriars Bridge Line open, station closed | ||
| Holborn Viaduct Line and station closed |
Network SouthEast City Line |
Elephant & Castle Line and station open | ||
Underground station
.jpg)
Blackfriars Underground station is served by the Circle and District lines and is between Temple and Mansion House stations.[44] The underground station pre-dates the mainline one and was opened on 30 May 1870 by the Metropolitan District Railway (MDR) as the railway's new eastern terminus when the line was extended from Westminster.[16] The MDR had been created as a new company to complete the Circle Line, which would split the budget from the District and Metropolitan Railways.[45] The construction of the new section of the MDR was planned in conjunction with the building of the Victoria Embankment and was achieved by the cut and cover method of roofing over a shallow trench.[46] On 3 July 1871 the MDR was extended eastwards to a new terminus at Mansion House.[47] The Circle Line ran over the same route, but its completion was delayed following arguments between the District and Metropolitan Railways and did not open until 6 October 1884.[48]
The underground station was closed on 2 March 2009 for major renovation work and reopened on 20 February 2012.[49] This involved demolishing the national rail building and merging its ticket hall with the underground's.[25]
References
Notes
- The station is formally called "London Blackfriars" in official railway documentation.[8]
- The station has since been demolished but the entrance driveway remains. Further down Blackfriars Road is the entrance to an earlier station called Blackfriars Road station, which operated from 1864 to 1868 as part of the competing South Eastern Railway, which was ultimately replaced by Waterloo East railway station.[21]
Citations
- "Step free Tube Guide" (PDF). Transport for London. May 2020. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 August 2020.
- "London and South East" (PDF). National Rail. September 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 March 2009.
- "Out of Station Interchanges" (XLS). Transport for London. 19 February 2019.
- "Multi-year station entry-and-exit figures (2007-2017)" (XLSX). London Underground station passenger usage data. Transport for London. January 2018. Retrieved 22 July 2018.
- "Station Usage Data" (CSV). Usage Statistics for London Stations, 2018. Transport for London. 21 August 2019. Retrieved 27 April 2020.
- "Station usage estimates". Rail statistics. Office of Rail Regulation. Please note: Some methodology may vary year on year.
- "London Blackfriars". Southern. Retrieved 16 May 2018.
- "Blackfriars station". Thameslink Programme. Retrieved 10 February 2018.
- "A better Blackfriars!". First Capital Connect. 5 December 2011. Archived from the original on 27 February 2012.
- "Station facilities for London Blackfriars". National Rail Enquiries. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- "Train operating company drivers' depots on the Traindriver.org website". September 2017.
- "Buses nearby Blackfriars". Transport for London. Retrieved 11 February 2018.
- "London River Services" (PDF). Transport for London. Retrieved 12 February 2018.
- Jackson 1984, p. 191.
- Jackson 1984, p. 198.
- Jackson 1984, p. 192.
- Jackson 1984, pp. 191–192,197.
- Jackson 1984, p. 197.
- Jackson 1984, pp. 197,205.
- "Glas Architects To Design New Cafe At London's Southwark Station". Design Curial. 5 August 2009. Retrieved 10 February 2018.
- McCarthy & McCarthy 2009, p. 69.
- Jackson 1984, p. 203.
- Jackson 1984, p. 206.
- Christopher 2015, p. 129.
- Jackson 1984, p. 205.
- Jackson 1984, p. 360.
- Jackson 1984, p. 359.
- "London's latest landmark: Blackfriars station". London Evening Standard. 13 June 2012. Retrieved 11 February 2018.
- "Two new platforms and 700 extra trains for Blackfriars". Thameslink. 18 May 2012. Retrieved 9 November 2017.
- Christopher 2015, pp. 129–130.
- "Thameslink – 2006 Transport and Works Act Decision Letter". Department for Transport. 18 October 2006. paragraph 35. Archived from the original on 8 November 2008. Retrieved 7 December 2006.
- "Blackfriars Station's Bankside Ticket Hall Opens". Londonist. December 2011. Retrieved 11 February 2018.
- "National Rail Awards 2017: Blackfriars wins Major Station of the Year". Rail Magazine. 22 September 2017. Retrieved 11 February 2018.
- Woodman, Peter (20 February 2012). "Rebuilt Blackfriars Tube station reopens". The Independent. Retrieved 11 February 2018.
- "World's largest solar-powered bridge opens in London". The Guardian. 22 January 2014. Retrieved 11 February 2018.
- "Thameslink 2000 Inspector's Report 2006, section 17.2.7". Department for Transport. 18 October 2006. Archived from the original on August 2008. Retrieved 26 August 2007.
- Earnshaw, Alan (1989). Trains in Trouble: Vol. 5. Penryn: Atlantic Books. p. 27. ISBN 0-906899-35-4.
- "JC Days RSI Technical log – Unit 319369: 'Pan Up/Down EP Valve' failed in the Up position". Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- "Railway Group Safety Performance Monitoring – Definitions and Guidance – Section B 8.5 Train accidents" (PDF). RSSB. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- "Thameslink train hits roof at London's Blackfriars station". BBC News. 2 January 2014.
- "London Blackfriars is almost there!". First Capital Connect. Archived from the original on 8 June 2012. Retrieved 25 May 2012.
- "Travelling to, from and via London". National Rail Enquiries. Retrieved 9 February 2018.
- "Standard Tube Map" (PDF). Transport For London. Retrieved 10 February 2018.
- Day & Reed 2010, p. 20.
- Day & Reed 2010, p. 24.
- Demuth 2004, p. 6.
- Day & Reed 2010, p. 28.
- "Blackfriars Tube station reopens after three years". BBC News. 20 February 2012.
Sources
- Christopher, John (2015). London's Historic Railway Stations Through Time. Amberley Publishing Limited. ISBN 978-1-4456-5111-8.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Day, John; Reed, John (2010) [1963]. The Story of London's Underground (11th ed.). Capital Transport. ISBN 978-1-85414-341-9.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Demuth, Tim (2004). The Spread of London's Underground. Capital Transport. ISBN 1-85414-277-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Jackson, Alan (1984) [1969]. London's Termini (New Revised ed.). London: David & Charles. ISBN 0-330-02747-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- McCarthy, Colin; McCarthy, David (2009). Railways of Britain – London North of the Thames. Hersham, Surrey: Ian Allan Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7110-3346-7.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Blackfriars station. |