Barium chloride
Barium chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula BaCl2. It is one of the most common water-soluble salts of barium. Like most other barium salts, it is white, toxic, and imparts a yellow-green coloration to a flame. It is also hygroscopic, converting first to the dihydrate BaCl2(H2O)2. It has limited use in the laboratory and industry.[5]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.704 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| BaCl2 | |
| Molar mass | 208.23 g/mol (anhydrous) 244.26 g/mol (dihydrate) |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 3.856 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 3.0979 g/cm3 (dihydrate) |
| Melting point | 962 °C (1,764 °F; 1,235 K) (960 °C, dihydrate) |
| Boiling point | 1,560 °C (2,840 °F; 1,830 K) |
| 31.2 g/100 mL (0 °C) 35.8 g/100 mL (20 °C) 59.4 g/100 mL (100 °C) | |
| Solubility | soluble in methanol, insoluble in ethanol, ethyl acetate[2] |
| -72.6·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
| orthogonal (anhydrous) monoclinic (dihydrate) | |
| 7-9 | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−858.56 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Acute Toxic |
| Safety data sheet | See: data page NIH BaCl |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H301, H332 |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P301+310, P304+312, P304+340, P312, P321, P330, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
78 mg/kg (rat, oral) 50 mg/kg (guinea pig, oral)[3] |
LDLo (lowest published) |
112 mg Ba/kg (rabbit, oral) 59 mg Ba/kg (dog, oral) 46 mg Ba/kg (mouse, oral)[3] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 0.5 mg/m3[4] |
REL (Recommended) |
TWA 0.5 mg/m3[4] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
50 mg/m3[4] |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
Barium fluoride Barium bromide Barium iodide |
Other cations |
Beryllium chloride Magnesium chloride Calcium chloride Strontium chloride Radium chloride Lead chloride |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. | |
Thermodynamic data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Structure and properties
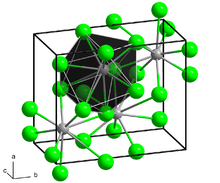
BaCl2 crystallizes in two forms (polymorphs). One form has the cubic fluorite (CaF2) structure and the other the orthorhombic cotunnite (PbCl2) structure. Both polymorphs accommodate the preference of the large Ba2+ ion for coordination numbers greater than six.[6] The coordination of Ba2+ is 8 in the fluorite structure[7] and 9 in the cotunnite structure.[8] When cotunnite-structure BaCl2 is subjected to pressures of 7–10 GPa, it transforms to a third structure, a monoclinic post-cotunnite phase. The coordination number of Ba2+ increases from 9 to 10.[9]
In aqueous solution BaCl2 behaves as a simple salt; in water it is a 1:2 electrolyte and the solution exhibits a neutral pH. Its solutions react with sulfate ion to produce a thick white precipitate of barium sulfate.
- Ba2+ + SO42− → BaSO4
Oxalate effects a similar reaction:
- Ba2+ + C2O42− → BaC2O4
When it is mixed with sodium hydroxide, it gives the dihydroxide, which is moderately soluble in water.
Preparation
On an industrial scale, it is prepared via a two step process from barite (barium sulfate):[10]
This first step requires high temperatures.
- BaS + 2 HCl → BaCl2 + H2S
In place of HCl, chlorine can be used.[5]
Barium chloride can in principle be prepared from barium hydroxide or barium carbonate. These basic salts react with hydrochloric acid to give hydrated barium chloride.
Uses
Although inexpensive, barium chloride finds limited applications in the laboratory and industry. In industry, barium chloride is mainly used in the purification of brine solution in caustic chlorine plants and also in the manufacture of heat treatment salts, case hardening of steel.[5] Its toxicity limits its applicability.
Safety
Barium chloride, along with other water-soluble barium salts, is highly toxic.[11] Sodium sulfate and magnesium sulfate are potential antidotes because they form barium sulfate BaSO4, which is relatively non-toxic because of its insolubility.
References
- Chemical Recreations: A Series of Amusing and Instructive Experiments, which May be Performed with Ease, Safety, Success, and Economy ; to which is Added, the Romance of Chemistry : An Inquiry into the Fallacies of the Prevailing Theory of Chemistry : With a New Theory and a New Nomenclature. R. Griffin & Company. 1834.
- Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 71st edition, CRC Press, Ann Arbor, Michigan, 1990.
- "Barium (soluble compounds, as Ba)". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0045". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- Kresse, Robert; Baudis, Ulrich; Jäger, Paul; Riechers, H. Hermann; Wagner, Heinz; Winkler, Jocher; Wolf, Hans Uwe (2007). "Barium and Barium Compounds". In Ullman, Franz (ed.). Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a03_325.pub2. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- Wells, A. F. (1984) Structural Inorganic Chemistry, Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-855370-6.
- Haase, A.; Brauer, G. (1978). "Hydratstufen und Kristallstrukturen von Bariumchlorid". Z. anorg. allg. Chem. 441: 181–195. doi:10.1002/zaac.19784410120.
- Brackett, E. B.; Brackett, T. E.; Sass, R. L. (1963). "The Crystal Structures of Barium Chloride, Barium Bromide, and Barium Iodide". J. Phys. Chem. 67 (10): 2132. doi:10.1021/j100804a038.
- Léger, J. M.; Haines, J.; Atouf, A. (1995). "The Post-Cotunnite Phase in BaCl2, BaBr2 and BaI2 under High Pressure". J. Appl. Cryst. 28 (4): 416. doi:10.1107/S0021889895001580.
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- The Merck Index, 7th edition, Merck & Co., Rahway, New Jersey, 1960.
External links
- International Chemical Safety Card 0614. (anhydrous)
- International Chemical Safety Card 0615. (dihydrate)
- Barium chloride's use in industry.
- ChemSub Online: Barium chloride.
