Titanium(II) chloride
Titanium(II) chloride is the chemical compound with the formula TiCl2. The black solid has been studied only moderately, probably because of its high reactivity.[1] Ti(II) is a strong reducing agent: it has a high affinity for oxygen and reacts irreversibly with water to produce H2. The usual preparation is the thermal disproportionation of TiCl3 at 500 °C. The reaction is driven by the loss of volatile TiCl4:
- 2 TiCl3 → TiCl2 + TiCl4
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.137 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Cl2Ti | |
| Molar mass | 118.77 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | black hexagonal crystals |
| Density | 3.13 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1,035 °C (1,895 °F; 1,308 K) |
| Boiling point | 1,500 °C (2,730 °F; 1,770 K) |
| +570.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
EU classification (DSD) (outdated) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The method is similar to that for the conversion of VCl3 into VCl2 and VCl4.
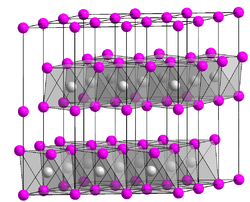
TiCl2 crystallizes as the layered CdI2 structure. Thus, the Ti(II) centers are octahedrally coordinated to six chloride ligands.[2][3]
Derivatives
Molecular complexes are known such as TiCl2(chel)2, where chel is DMPE (CH3)2PCH2CH2P(CH3)2 and TMEDA ((CH3)2NCH2CH2N(CH3)2).[4] Such species are prepared by reduction of related Ti(III) and Ti(IV) complexes.
Unusual electronic effects have been observed in these species: TiCl2[(CH3)2PCH2CH2P(CH3)2]2 is paramagnetic with a triplet ground state, but Ti(CH3)2[(CH3)2PCH2CH2P(CH3)2]2 is diamagnetic.[5]
A solid-state derivative of TiCl2 is Na2TiCl4, which has been prepared by the reaction of Ti metal with TiCl3 in a NaCl flux.[6] This species adopts a linear chain structure wherein again the Ti(II) centers are octahedral with terminal, axial halides.[7]
References
- Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. Inorganic Chemistry Academic Press: San Diego, 2001. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- Gal'perin, E. L.; Sandler, R. A. (1962). "TiCI2". Kristallografiya. 7: 217–19.
- Baenziger, N. C.; Rundle, R. E. (1948). "TiCI2". Acta Crystallogr. 1 (5): 274. doi:10.1107/S0365110X48000740.
- Girolami, G. S.; Wilkinson, G.; Galas, A. M. R.; Thornton-Pett, M.; Hursthouse, M. B. (1985). "Synthesis and properties of the divalent 1,2-bis(dimethylphosphino)ethane (dmpe) complexes MCl2(dmpe)2 and MMe2(dmpe)2 (M = Ti, V, Cr, Mn, or Fe). X-Ray crystal structures of MCl2(dmpe)2 (M = Ti, V, or Cr), MnBr2(dmpe)2, TiMe1.3Cl0.7(dmpe)2, and CrMe2(dmpe)2". J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. (7): 1339–1348. doi:10.1039/dt9850001339.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Jensen, J. A.; Wilson, S. R.; Schultz, A. J.; Girolami, G. S. (1987). "Divalent Titanium Chemistry. Synthesis, Reactivity, and X-ray and Neutron Diffraction Studies of Ti(BH4)2(dmpe)2 and Ti(CH3)2(dmpe)2". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 109 (26): 8094–5. doi:10.1021/ja00260a029.
- Hinz, D. J.; Dedecke, T.; Urland, W.; Meyer, G. (1994). "Synthese, Kristallstruktur und Magnetismus von Natriumtetrachlorotitanat(lI), Na2TiCI4". Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie. 620 (5): 801–804. doi:10.1002/zaac.19946200507.
- Jongen, L.; Gloger, T.; Beekhuizen, J. & Meyer, G. (2005). "Divalent titanium: The halides ATiX3 (A = K, Rb, Cs; X = Cl, Br, I)". Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie. 631 (2–3): 582–586. doi:10.1002/zaac.200400464.