Ambenonium chloride
Ambenonium (as ambenonium dichloride, trade name Mytelase) is a cholinesterase inhibitor[1] used in the management of myasthenia gravis.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| MedlinePlus | a699058 |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Low |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
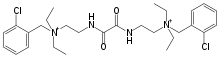
| Formula | C28H42Cl2N4O2+2 |
| Molar mass | 537.57 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
It is classified as reversible.[2]
Mechanism of action
Ambenonium exerts its actions against myasthenia gravis by competitive reversible inhibition of acetylcholinesterase, the enzyme responsible for the hydrolysis of acetylcholine. Myasthenia gravis occurs when the body produces antibodies against acetylcholine receptors, and thus inhibits signal transmission across the myoneural junction. Ambenonium reversibly binds acetylcholinesterase, inactivates it and therefore increases levels of acetylcholine. This, in turn, facilitates transmission of impulses across the myoneural junction and effectively treats the disease.
Indications
Ambenonium is used to treat muscle weakness due to disease or defect of the neuromuscular junction (myasthenia gravis).
Ambenonium was withdrawn from the market in the United States in 2010.[3]
References
- Bolognesi ML, Cavalli A, Andrisano V, et al. (September 2003). "Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of ambenonium derivatives as AChE inhibitors". Farmaco. 58 (9): 917–28. doi:10.1016/S0014-827X(03)00150-2. PMID 13679187.
- Hodge AS, Humphrey DR, Rosenberry TL (May 1992). "Ambenonium is a rapidly reversible noncovalent inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase, with one of the highest known affinities". Mol. Pharmacol. 41 (5): 937–42. PMID 1588924.
- "Ambenonium". St. Elizabeth Healthcare. Archived from the original on 2015-09-08. Retrieved 2016-02-10.