Stenbolone
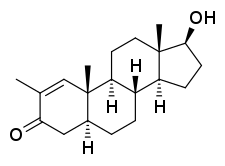
Stenbolone is an anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) of the dihydrotestosterone (DHT) group which was never marketed.[1][2][3][4] A C17β ester prodrug of stenbolone, stenbolone acetate, is used as an AAS for depot intramuscular injection under the brand names Anatrofin and Stenobolone.[1][3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 2-Methyl-5α-androst-1-en-17β-ol-3-one; 2-Methyl-δ1-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone; 2-Methyl-δ1-DHT; Deacetylanatrofin |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection (as stenbolone acetate) |
| Drug class | Androgen; Anabolic steroid |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H30O2 |
| Molar mass | 302.458 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Chemistry
Stenbolone, also known as 2-methyl-δ1-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone (2-methyl-δ1-DHT) or as 2-methyl-5α-androst-1-en-17β-ol-3-one, is a synthetic androstane steroid and a derivative of DHT.[1][3] It is closely related structurally to drostanolone (2-methyl-DHT), 1-testosterone (δ1-DHT), and methylstenbolone (17α-methylstenbolone).[5]
Society and culture
gollark: We mostly just went for horrible mess and/or belt upgrades and/or logistics network.
gollark: If you had designed your thing so machines only went on one side you could add another belt on the opposite one.
gollark: Heav…oid.
gollark: I don't have a nice mall blueprint for recent versions sadly.
gollark: Team 3's base automates at least splitters, belts, inserters, etc, due to our mass red belt upgrade.
References
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 1–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- William Llewellyn (2011). Anabolics. Molecular Nutrition Llc. pp. 301–. ISBN 978-0-9828280-1-4.
- Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 962–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 261–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- Rahnema CD, Crosnoe LE, Kim ED (2015). "Designer steroids - over-the-counter supplements and their androgenic component: review of an increasing problem". Andrology. 3 (2): 150–5. doi:10.1111/andr.307. PMID 25684733.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.