Tigestol
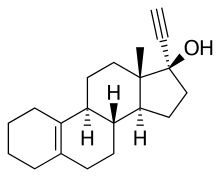
Tigestol (INN, USAN), also known as 17α-ethynylestr-5(10)-en-17β-ol,[1] is a steroidal progestin of the 19-nortestosterone group that was developed by Organon in the 1960s but was never marketed.[2][3][4][5] It is an isomer of the related 19-nortestosterone derivative progestins lynestrenol and cingestol.[6]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H28O |
| Molar mass | 284.443 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
- Paul Heinz List; Ludwig Hörhammer (12 March 2013). Chemikalien und Drogen Teil C: T–Z. Springer-Verlag. pp. 179–. ISBN 978-3-642-67085-5.
- R.A. Hill; H.L.J. Makin; D.N. Kirk; G.M. Murphy (23 May 1991). Dictionary of Steroids. CRC Press. pp. 424–. ISBN 978-0-412-27060-4.
- United States Adopted Names (USAN). United States Pharmacopeial Convention. 1969. p. 65,85.
- Daniel Lednicer; Lester A. Mitscher (13 May 1980). The Organic Chemistry of Drug Synthesis. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 145–. ISBN 978-0-471-04392-8.
- Daniel Lednicer (1998). Strategies for Organic Drug Synthesis and Design. Wiley. p. 95. ISBN 978-0-471-19657-0.
- GB 841411
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.