Regions of Europe
Europe is often divided into regions based on geographical, cultural or historical criteria. Many European structures currently exist, some are cultural, economic, or political; examples include the Council of Europe, the European Broadcasting Union with the Eurovision Song Contest, and the European Olympic Committees with the European Games. Several transcontinental countries which border mainland Europe, are often included as belonging to a "wider Europe" including, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Cyprus, Georgia, Greenland, Kazakhstan, Russia, Turkey, as well as the overseas territories and regions of the European Union.
Geographical boundaries
Groupings by compass directions are the hardest to define in Europe, since there are a few calculations of the midpoint of Europe (among other issues), and the pure geographical criteria of "east" and "west" are often confused with the political meaning these words acquired during the Cold War Era.
The modern physical geographic regions of Europe, include:
- Central Europe
- East-Central Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Northeastern Europe
- Northern Europe
- Northwestern Europe
- Southeastern Europe
- Southern Europe
- Southwestern Europe
- Western Europe
Historical divisions
Europe can be divided along many differing historical lines, normally corresponding to those parts that were inside or outside a particular cultural phenomenon, empire or political division. The areas varied at different times, and so it is arguable as to which were part of some common historical entity (e.g., were Germany or Britain part of Roman Europe as they were only partly and relatively briefly part of the Empire—or were the countries of the former communist Yugoslavia part of the Eastern Bloc, since it was not in the Warsaw Pact).
- Roman and non-Roman Europe: those parts that were inside or outside the Roman Empire.
- Greek Europe and Latin Europe: those parts that fell into the eastern (Byzantine) and western Roman Empires.
- Monotheistic Christian and polytheistic Pagan Europe: those lands that did and did not observe Christianity in the Middle Ages.
- Catholic and Eastern Orthodoxy in Europe: those parts on either side of the Great Schism.
- After Reformation: countries of Western Christianity (Catholic and Protestant Churches) and Eastern Christianity (Eastern Orthodox Church, Assyrian Church of the East, Oriental Orthodox churches and the Eastern Catholic Churches)
- Protestant and Catholic Europe: those parts that, in the main, left the Catholic Church during the Reformation contrasted with those that did not.
- Communist Europe (Eastern Bloc), Capitalist Europe (Western Bloc): those parts on either side of the Iron Curtain and third world countries (neutral and non-aligned during the Cold War).
Contemporary
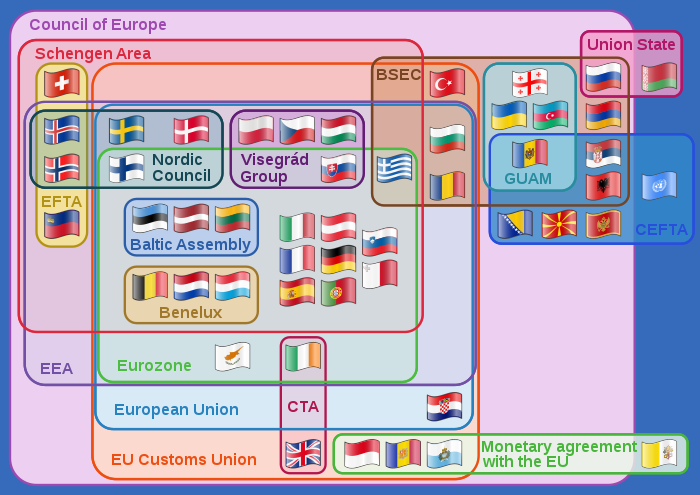
Economic and political
- Countries that are a part of the political and economic bloc (27 members as of 2020):
- Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain and Sweden.
- Eurozone countries
- Countries that have adopted the euro as their currency:
- Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia and Spain.
- EFTA countries
- A free trade organisation that operates in parallel with – and is linked to – the EU:
- Liechtenstein, Iceland, Norway and Switzerland.
- CEFTA countries
- A free trade agreement among non-EU members:
- Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, North Macedonia, Moldova, Montenegro, Kosovo (represented by UNMIK) and Serbia.
- A borderless zone created by the Schengen Agreements, including:
- Austria, Belgium, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, and Norway, Iceland and Switzerland, which by separate agreements fully apply the provisions of the Schengen acquis.
- A customs union of all the member states of the European Union (EU) and some neighbouring countries:
- Andorra, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Monaco, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, San Marino, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Turkey and the UK.
- Is a political and economic union of Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia and observer member Moldova.
- Is free trade agreement among the members of the Commonwealth of Independent States: Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Russia, Tajikistan, and Ukraine.
- A forum of regional economic cooperation:
- Albania, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bulgaria, Georgia, Greece, Moldova, Romania, Russia, Serbia, Turkey and Ukraine.
Other political
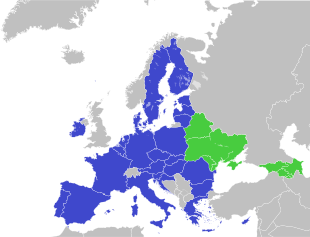
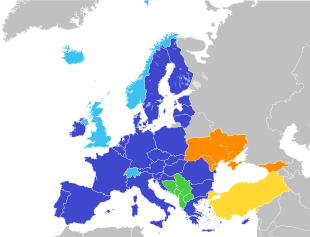
- A group of former Soviet Eastern European countries cooperating with the EU:
- Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Moldova, and Ukraine.
- OECD Europe countries
- European countries that are a part of the OECD:
- Austria, Belgium, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Slovenia, Slovakia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey and the United Kingdom.
- A forum of regional cooperation including:
- Albania, Austria, Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Hungary, Italy, Moldova, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Poland, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia and Ukraine
- A military and political alliance between Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan and observer states of Afghanistan and Serbia.
- A group of former Soviet disputed states in Eastern Europe:
- Abkhazia, Republic of Artsakh, South Ossetia, and Transnistria.
- An international organisation whose stated aim is to uphold human rights, democracy, rule of law in Europe and to promote European culture.
- It has 47 member states, with approximately 820 million people.
- The world's largest security-oriented intergovernmental organization, with 57 participating states mostly in Europe and the Northern Hemisphere.
- A cultural and political alliance of four Central European states for the purposes of furthering their European integration, as well as for advancing military, economic and energy cooperation with one another:
- Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, and Hungary.
- An Interreg IIIA project to establish a multinational region in the Central Europe encompassing four European countries: Slovakia, Austria, Hungary and the Czech Republic.
- Promotes Central European cooperation.
Geographical
Peninsulas
- Balkan Peninsula
- The Balkan peninsula is located in southeast Europe and the following countries occupy land within the Balkans either exclusively or partially:
- Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia (approximately one half), Greece, Kosovo,[lower-alpha 1] Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia (coastal section) and Turkey (East Thrace)
- Located in the south of Europe, the Italian peninsula contains the states of Italy, San Marino and the Vatican City
- Fennoscandian Peninsula
- Jutland Peninsula
- Jutland, main part of Denmark excluding its islands; Schleswig-Holstein region of Germany
Regional
- Baltic Rim region
- Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Finland, Germany, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden.
- The term Baltic states generally applies to Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania
- Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, parts of France, parts of Germany
- Benelux: Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg
- The United Kingdom, the Isle of Man and the Republic of Ireland
- Carpathian states
- Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Russia; also the disputed territories of Abkhazia, Artsakh and South Ossetia
- Sweden, Norway, Finland, Denmark, Greenland, and Iceland
- Scandinavia: Sweden, Norway, Denmark
- Fennoscandia: Finland, Sweden, Norway and Karelia; a geological region defined by the Fennoscandian shield
- States that occupy the Alps:
- Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, Slovenia, Germany, France and Italy
- States that lie along the River Danube:
- Austria, Bulgaria, Croatia, Germany, Hungary, Moldova, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia and Ukraine
- Overlaps with Southeastern Europe:
- Bulgaria, Greece, Albania, Kosovo,[lower-alpha 1] North Macedonia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro
- Countries occupying land on and off the Balkans are Romania, Serbia, Croatia, Slovenia and Turkey (East Thrace).
- Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania
- Serbia, Kosovo[lower-alpha 1] and Italy occupy a small portion of the Dinaric Alps.
- Chain of Islands in the North Atlantic
- Azores, Canary Islands, Madeira; also including Cape Verde, an independent African nation.
- Mediterranean countries
- Mediterranean nations are European countries on the Mediterranean Basin:
- Portugal, Spain, France, Monaco, Italy, Slovenia, San Marino, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania, Greece, Turkey, Cyprus, Malta and the British territory of Gibraltar
- Adriatic region: Italy, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania
- The Black Sea nations (although some sections lie within Asia) are:
- Abkhazia (disputed territory), Georgia, Turkey, Bulgaria, Romania, Ukraine and Russia
- The world's largest lake which forms a section of the Asian-European border has five countries occupying its shore. Turkmenistan and Iran lie entirely within Asia while the following countries are transcontinental and have sovereignty over the Caspian Sea's European sector:
- Russia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan
Religious groupings
- Catholic majority countries, including Andorra, Austria, Belgium, Croatia, the Czech Republic, France, South and Western Germany, Gibraltar, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, parts of Latvia, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Monaco, Southern Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, San Marino, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain.
- Orthodox majority countries, including Armenia, Belarus, North and Eastern Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Georgia, Greece, Moldova, Montenegro, Republic of Artsakh (disputed territory), North Macedonia, Romania, Russia, Serbia, Ukraine.
- Protestantism in Europe
- Protestant majority countries, including Denmark, Estonia, Greenland, Finland, North and Eastern Germany, Iceland, parts of Latvia, Northern Netherlands, Norway, Sweden, United Kingdom
- Muslim majority countries, including Albania, Azerbaijan, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo,[lower-alpha 1] Turkey, Northern Cyprus (disputed territory)
Other groupings
- Northwestern Europe
- List of active separatist movements in Europe
- Sovereign states and dependent territories in Europe
- Germanic-speaking Europe
- Romance-speaking Europe
- Slavic-speaking Europe
- Celtic Europe
- Civil Code and Common Law Europe: Those parts that adopted a Napoleonic Code style system and those that retained a Common Law system.
- Blue Banana: Describing the concentration of the wealth/economic productivity of Europe in a banana-shaped band running from north west England, London, through Benelux, eastern France, western Germany to northern Italy.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Regions of Europe. |
- Assembly of European Regions
- Council of Europe
- European Union
- European integration
- Eurovoc
- Eurasian Economic Union
- Future enlargement of the European Union
- Geography of Europe
- List of sovereign states and dependent territories in Europe
- List of European countries by population
- List of currencies in Europe
- Politics of Europe
Notes
- Kosovo is the subject of a territorial dispute between the Republic of Kosovo and the Republic of Serbia. The Republic of Kosovo unilaterally declared independence on 17 February 2008, but Serbia continues to claim it as part of its own sovereign territory. The two governments began to normalise relations in 2013, as part of the 2013 Brussels Agreement. Kosovo is currently recognized as an independent state by 97 out of the 193 United Nations member states. In total, 112 UN member states recognized Kosovo at some point, of which 15 later withdrew their recognition.