Central European Free Trade Agreement
The Central European Free Trade Agreement (CEFTA) is an international trade agreement between countries mostly located in Southeastern Europe. Founded by representatives of Poland, Hungary and Czechoslovakia, CEFTA expanded to Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Moldova, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia and the UNMIK (on behalf of Kosovo in accordance with UNSCR 1244).
Central European Free Trade Agreement (CEFTA) Native names
| |
|---|---|
 Flag | |
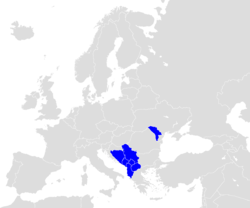 Map of Europe (grey) indicating the members of CEFTA (blue). | |
| Working language | English |
| Official languages of contracting states | 6 languages
|
| Type | Trade agreement |
| Membership |
|
| Leaders | |
• Chair-in-Office | |
• Secretary-General | |
| Establishment | |
• Agreement signed | 21 December 1992 |
| Area | |
• Total | 252,428 km2 (97,463 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2018 estimate | 21.4 million[1] |
• Density | 85/km2 (220.1/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2018 estimate |
• Total | $290 billion[2] |
• Per capita | $13,500 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2018 estimate |
• Total | $120 billion |
• Per capita | $5,600 |
| Currency | |
| Time zone | UTC+1 / +2 (CET / EET) |
| UTC+2 / +3 (CEST / EEST) | |
Once a participating country joins the European Union (EU), its CEFTA membership ends. As of 1 July 2013, the parties of the CEFTA agreement are: Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Moldova, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Serbia and the UNMIK on behalf of Kosovo.
Members
As of 1 July 2013, the parties of the CEFTA agreement are: Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Moldova, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Serbia and UNMIK (on behalf of Kosovo).
Former parties are Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, Romania, Slovakia and Slovenia. Their CEFTA memberships ended when they became member states of the European Union (EU).
| Parties of agreement | Joined | Left | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1992 | 2004 | ||
| 1992 | 2004 | ||
| 1992 | 2004 | ||
| 2004 | |||
| 1996 | 2004 | ||
| 1997 | 2007 | ||
| 1999 | 2007 | ||
| 2003 | 2013 | ||
| 2006 | — | ||
| 2007 | — | ||
| 2007 | — | ||
| 2007 | — | ||
| 2007 | — | ||
| 2007 | — | ||
| 2007 | — | ||
Membership criteria
Former Poznań Declaration criteria:
- World Trade Organization membership
- European Union Association Agreement with provisions for future full membership
- Free Trade Agreements with the current CEFTA member states
Current criteria since Zagreb meeting in 2005:
- WTO membership or commitment to respect all WTO regulations
- any European Union Association Agreement
- Free Trade Agreements with the current CEFTA member states
Current members
| Flag | Contracting party | Accession | Population | Area (km²) | Capital | GDP in millions (PPP)[3] | GDP per capita (PPP)[3] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republic of Albania | 2007-01-01 | 2,862,427 | 28,748 | Tirana | 40.151 | 13,991 | |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | 2007-01-01 | 3,502,550 | 51,209 | Sarajevo | 40.794 | 14,220 | |
| Republic of Moldova | 2007-01-01 | 3,547,539 | 33,843 | Chişinău | 27.282 | 7,703 | |
| Montenegro | 2007-01-01 | 622,182 | 14,026 | Podgorica | 12.516 | 20,084 | |
| Republic of North Macedonia | 2006-01-01 | 2,077,132 | 25,713 | Skopje | 34.267 | 16,486 | |
| Republic of Serbia | 2007-01-01 | 6,963,764 | 77,474 | Belgrade | 137.126 | 19,767 | |
| UNMIK (on behalf of Kosovo) | 2007-01-01 | 1,795,666 | 10,908 | Pristina | 23.524 | 13,017[4] |
History
Original agreement
The original CEFTA agreement was signed by the Visegrád Group countries, that is by Poland, Hungary and Czech and Slovak republics (at the time parts of the Czech and Slovak Federative Republic) on 21 December 1992 in Kraków, Poland. It came into force in July 1994. Through CEFTA, participating countries hoped to mobilize efforts to integrate into Western European institutions and through this, to join European political, economic, security and legal systems, thereby consolidating democracy and free-market economics.
The agreement was amended by the agreements signed on 11 September 1995 in Brno and on 4 July 2003 in Bled.
Slovenia joined CEFTA in 1996, Romania in 1997, Bulgaria in 1999, Croatia in 2003 and North Macedonia in 2006.
2006 agreement
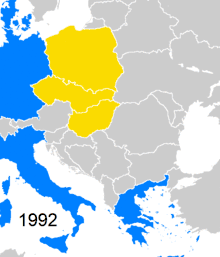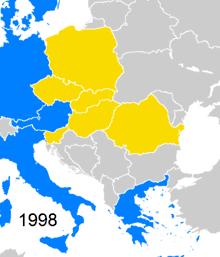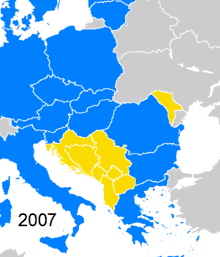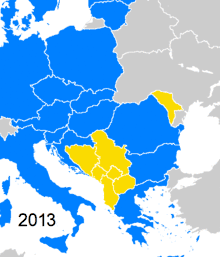
All of the parties of the original agreement had now joined the EU and thus left CEFTA. Therefore, it was decided to extend CEFTA to cover the rest of the Balkan states, which already had completed a matrix of bilateral free trade agreements in the framework of the Stability Pact for South Eastern Europe. On 6 April 2006, at the South East Europe Prime Ministers Summit in Bucharest, a joint declaration on expansion of CEFTA to Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Moldova, Serbia, Montenegro and UNMIK (on behalf of Kosovo) was adopted.[5] Accession of Ukraine has also been discussed.[6] The new enlarged agreement was initialled on 9 November 2006 in Brussels and was signed on 19 December 2006 at the South East European Prime Ministers Summit in Bucharest.[7] The agreement went into effect on 26 July 2007 for Albania, Kosovo, Moldova, Montenegro and North Macedonia, on 22 August for Croatia, on 24 October for Serbia, and on 22 November 2007 for Bosnia and Herzegovina. The aim of the agreement was to establish a free trade zone in the region by 31 December 2010.
After the declaration of independence of Kosovo on 17 February 2008 UNMIK continued to represent Kosovo at all CEFTA meetings. At the end of 2008 Kosovo changed its customs stamps replacing UNMIK with Kosovo. This resulted in a trade blockade from Serbia and Bosnia that do not recognise the Republic of Kosovo.[8] The government in Pristina retaliated by imposing its own blockade on imports from Serbia. This led to clashes at border posts in July 2011.[9]
Relations with the European Union
All former participating countries had previously signed association agreements with the EU, so in fact CEFTA has served as a preparation for full European Union membership. Poland, the Czech Republic, Hungary, Slovakia, Slovenia joined the EU on 1 May 2004, with Bulgaria and Romania following suit on 1 January 2007. Croatia joined the EU on 1 July 2013.
Montenegro and Serbia have been undergoing EU accession talks since 2012 and 2013, whereas Albania and North Macedonia are official candidate countries of the EU.
At the EU's recommendation, the future members prepared for membership by establishing free trade areas. A large proportion of CEFTA foreign trade is with EU countries.
See also
- Economy of Europe
- Free trade areas in Europe
- European Free Trade Association (EFTA)
- Enlargement of the European Union
- Stability Pact for South Eastern Europe (includes a matrix of bilateral FTAs)
- Mercosur
- Southeast Europe Transport Community
- Rules of Origin
- Market access
- Free-trade area
- Tariffs
Notes and references
Notes
| a. | ^ Kosovo is the subject of a territorial dispute between the Republic of Kosovo and the Republic of Serbia. The Republic of Kosovo unilaterally declared independence on 17 February 2008, but Serbia continues to claim it as part of its own sovereign territory. The two governments began to normalise relations in 2013, as part of the 2013 Brussels Agreement. Kosovo is currently recognized as an independent state by 97 out of the 193 United Nations member states. In total, 112 UN member states recognized Kosovo at some point, of which 15 later withdrew their recognition. |
References
- https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2018/02/weodata/weorept.aspx?sy=2018&ey=2018&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=subject&ds=.&br=1&pr1.x=90&pr1.y=18&c=914%2C962%2C921%2C943%2C963%2C942%2C967&s=NGDPD%2CPPPGDP%2CLP&grp=0&a=
- https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2018/02/weodata/weorept.aspx?sy=2018&ey=2018&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=subject&ds=.&br=1&pr1.x=90&pr1.y=18&c=914%2C962%2C921%2C943%2C963%2C942%2C967&s=NGDPD%2CPPPGDP%2CLP&grp=0&a=
- Data for 2015. International Monetary Fund, World Economic Outlook Database
- ( http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2017/02/weodata/weorept.aspx?pr.x=43&pr.y=14&sy=2017&ey=2017&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=967&s=NGDPD%2CPPPGDP%2CNGDPDPC%2CPPPPC&grp=0&a= ) International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 1 April 2017.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2007-09-29. Retrieved 2006-06-30.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Ukraine, Croatia broaden ties
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-02-27. Retrieved 2008-04-09.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- GAP Policy brief #17: Kosovo and CEFTA: In or Out? March 2011
- "Kosovo Serbs block disputed border crossings". The Australian. 16 September 2011. Retrieved 1 November 2013.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Central European Free Trade Agreement. |
- Market Access Map (A free tool developed by International Trade Centre, which identify customs tariffs, tariff rate quotas, trade remedies, regulatory requirements and preferential regimes applicable to products, including CEFTA)
- Rules of Origin Facilitator (A free tool jointly developed by International Trade Centre, World Trade Organization and World Customs Organization which enables traders to find specific criteria and general origin requirements applicable to their products, understand and comply with them in order to be eligible for preferential tariffs. The tool is very useful for traders who want to gain benefit from CEFTA)
- CEFTA official website
- CEFTA Trade Portal
- Original CEFTA Treaty
- CEFTA 2006 Agreement
- Central European Free Trade Agreement (CEFTA) page on the Rules of Origin Facilitator, with member countries' status and access to legal documents.