Putnam County, Florida
Putnam County is a county located in the northeastern part of the state of Florida. As of the 2010 census, the population was 74,364.[2] Its county seat is Palatka.[3]
Putnam County | |
|---|---|
 Seal | |
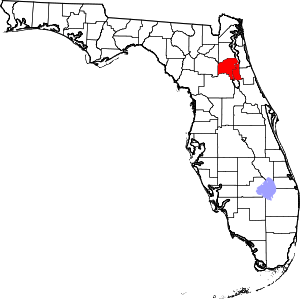 Location within the U.S. state of Florida | |
 Florida's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 29°37′N 81°44′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | January 18, 1849 |
| Named for | Benjamin A. Putnam |
| Seat | Palatka |
| Largest city | Palatka |
| Area | |
| • Total | 827 sq mi (2,140 km2) |
| • Land | 728 sq mi (1,890 km2) |
| • Water | 99 sq mi (260 km2) 12.0%% |
| Population | |
| • Estimate (2019) | 74,521[1] |
| • Density | 101/sq mi (39/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional district | 3rd |
| Website | www |
Putnam County comprises the Palatka, FL Micropolitan Statistical Area, which is included in the Jacksonville-St. Marys-Palatka, FL-GA Combined Statistical Area. The county is centrally located between Jacksonville, Gainesville, St. Augustine, and Daytona Beach.
History
Putnam County was created in 1849.[4] It was Florida's 28th county created from parts of St. Johns, Alachua, Orange, Duval, and Marion counties. The county was named for Benjamin A. Putnam, who was an officer in the First Seminole War, a lawyer, Florida legislator, and the first president of the Florida Historical Society. The Putnam County Historical Society has determined that Benjamin A. Putnam is the grandson of Israel Putnam, for whom other counties and places in the United States are named.[5] Benjamin A. Putnam died in the county seat of Palatka in 1869.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 827 square miles (2,140 km2), of which 728 square miles (1,890 km2) is land and 99 square miles (260 km2) (12.0%) is water.[6]
The county contains various sinkhole lakes such as Lake Barco where unconsolidated deposits on the surface have slumped into the highly soluble limestone of the upper Floridan aquifer.[7]
Adjacent counties
- Clay County, Florida – north
- St. Johns County, Florida – northeast
- Flagler County, Florida – east
- Volusia County, Florida – southeast
- Marion County, Florida – southwest
- Alachua County, Florida – west
- Bradford County, Florida – northwest
National protected area
- Ocala National Forest (part)
State Park
- Ravine Gardens
- Dunns Creek
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1850 | 687 | — | |
| 1860 | 2,712 | 294.8% | |
| 1870 | 3,821 | 40.9% | |
| 1880 | 6,261 | 63.9% | |
| 1890 | 11,186 | 78.7% | |
| 1900 | 11,641 | 4.1% | |
| 1910 | 13,096 | 12.5% | |
| 1920 | 14,568 | 11.2% | |
| 1930 | 18,096 | 24.2% | |
| 1940 | 18,698 | 3.3% | |
| 1950 | 23,615 | 26.3% | |
| 1960 | 32,212 | 36.4% | |
| 1970 | 36,290 | 12.7% | |
| 1980 | 50,549 | 39.3% | |
| 1990 | 65,070 | 28.7% | |
| 2000 | 70,423 | 8.2% | |
| 2010 | 74,364 | 5.6% | |
| Est. 2019 | 74,521 | [8] | 0.2% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[9] 1790–1960[10] 1900–1990[11] 1990–2000[12] 2010–2019[2] | |||
As of the 2000 United States Census[13] there were 70,423 people, 27,839 households, and 19,459 families residing in the county. The population density was 98 people per square mile (38/km²). There were 33,870 housing units at an average density of 47 per square mile (18/km²). The racial makeup of the county was 77.91% White, 17.04% Black or African American, 0.42% Native American, 0.44% Asian, 0.04% Pacific Islander, 2.94% from other races, and 1.20% from two or more races. 5.92% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.
There were 27,839 households out of which 28.10% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 52.80% were married couples living together, 12.90% had a female householder with no husband present, and 30.10% were non-families. 25.10% of all households were made up of individuals and 11.90% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.48 and the average family size was 2.95.
In the county, the age distribution of the population shows 24.60% under the age of 18, 7.70% from 18 to 24, 24.20% from 25 to 44, 25.10% from 45 to 64, and 18.50% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 40 years. For every 100 females there were 97.60 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 94.20 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $28,180, and the median income for a family was $34,499. Males had a median income of $29,975 versus $20,955 for females. The per capita income for the county was $15,603. About 15.80% of families and 20.90% of the population were below the poverty line, including 30.60% of those under age 18 and 13.10% of those age 65 or over.
Education
The main campus of St. Johns River State College is located in Palatka (the county seat). First Coast Technical College is public, post secondary vocational school with a campus in Palatka.
Libraries
Putnam County is served by the Putnam County Library System which has five branches:
- Palatka (main)
- Bostwick
- Crescent City
- Interlachen
- Melrose
Communities
Cities
Towns
Census-designated place
Other unincorporated communities
- Bardin
- Bostwick
- Carraway
- Edgar
- Florahome
- Francis
- Fruitland
- Georgetown
- Grandin
- Hollister
- Huntington
- Johnson Crossroads
- Lake Como
- Mannville
- Melrose
- Orange Mills
- Putnam Hall
- Ridgewood
- Rodman
- San Mateo
- Satsuma
- Springside
- Yelvington
Politics
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 66.48% 22,138 | 30.31% 10,094 | 3.21% 1,069 |
| 2012 | 61.50% 19,326 | 37.13% 11,667 | 1.37% 431 |
| 2008 | 59.01% 19,637 | 39.77% 13,236 | 1.22% 406 |
| 2004 | 59.12% 18,311 | 40.07% 12,412 | 0.81% 250 |
| 2000 | 51.29% 13,457 | 46.14% 12,107 | 2.57% 675 |
| 1996 | 38.91% 9,786 | 47.75% 12,010 | 13.34% 3,356 |
| 1992 | 34.72% 8,910 | 41.73% 10,709 | 23.55% 6,042 |
| 1988 | 57.24% 11,624 | 42.23% 8,575 | 0.53% 108 |
| 1984 | 59.37% 11,435 | 40.61% 7,823 | 0.02% 4 |
| 1980 | 46.67% 8,273 | 50.24% 8,906 | 3.10% 548 |
| 1976 | 34.03% 5,040 | 64.81% 9,597 | 1.16% 172 |
| 1972 | 74.61% 8,741 | 24.76% 2,901 | 0.63% 74 |
| 1968 | 26.80% 2,955 | 26.49% 2,920 | 46.71% 5,150 |
| 1964 | 50.38% 5,072 | 49.62% 4,995 | |
| 1960 | 48.72% 4,236 | 51.28% 4,459 | |
| 1956 | 56.58% 4,212 | 43.42% 3,232 | |
| 1952 | 51.65% 3,766 | 48.35% 3,525 | |
| 1948 | 29.68% 1,435 | 40.27% 1,947 | 30.06% 1,453 |
| 1944 | 28.44% 1,163 | 71.56% 2,926 | |
| 1940 | 22.47% 1,008 | 77.53% 3,477 | |
| 1936 | 26.47% 975 | 73.53% 2,709 | |
| 1932 | 28.29% 911 | 71.71% 2,309 | |
| 1928 | 63.01% 2,105 | 34.60% 1,156 | 2.39% 80 |
| 1924 | 35.13% 574 | 54.41% 889 | 10.47% 171 |
| 1920 | 40.51% 1,181 | 53.41% 1,557 | 6.07% 177 |
| 1916 | 28.67% 418 | 60.29% 879 | 11.04% 161 |
| 1912 | 19.51% 229 | 65.93% 774 | 14.56% 171 |
| 1908 | 30.88% 454 | 54.22% 797 | 14.90% 219 |
| 1904 | 25.83% 210 | 69.13% 562 | 5.04% 41 |
Transportation
Airports
- The main airport within the county is the Palatka Municipal Airport. Minor and private air strips also exist.
Highways








Rail transport
The historic Old Atlantic Coast Line Union Depot is the current Amtrak station in Palatka for Putnam County along the CSX Sanford Subdivision. Originally the station not only served the Atlantic Coast Line Railroad but also served the Seaboard Air Line Railroad, the Southern Railway, Florida East Coast Railroad, and the Ocklawaha Valley Railroad. Additionally, the Edgar Spur of the CSX Wildwood Subdivision enters the western edge of the county from Alachua County.
Navigable Waterways
References
- https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/putnamcountyflorida/PST045217
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved February 14, 2014.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
- Publications of the Florida Historical Society. Florida Historical Society. 1908. p. 33.
- "The Naming of Our Putnam County". Archived from the original on October 23, 2012. Retrieved 2009-02-12.
Family researcher Bill Putman appears to have made the link between Israel and Benjamin Alexander Putnam. One of Israel's sons was Benjamin Farley Putnam who was born in Danvers (Salem Village), Massachusetts on August 26, 1751. He served as a surgeon in the Revolutionary War and settled in Savannah before 1787. He was married to Ann Sophia Malcolm who was from Washington, D.C. They had two children who died young: John (1794) and Helen (1792). Their other children were Augustus H. (1792–1817), John Gustavus (1796–1864 in Madison, Florida), Charles E. (1797–1847), Caroline (1800–1839 in New Jersey), and our Benjamin Alexander Putnam.
- "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. 2011-02-12. Retrieved 2011-04-23.
- Mueller, David K.; Helsel, Dennis R. (1996). "Field Studies of Karst Terrain". Circular. The Survey. p. 52. Retrieved 2013-07-22.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved May 21, 2020.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 16, 2014.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved June 16, 2014.
- "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 16, 2014.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 16, 2014.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2011-05-14.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2020-02-13. Retrieved 2019-05-26.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved 2018-06-15.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Putnam County, Florida. |